|
Club Chair
A club chair is a type of armchair, usually covered in leather. It was created and made in France. Before it came to be known under its current name, it first appeared as the , the 'comfortable armchair'. It was given this name to distinguish it from the , which had straighter lines and was less enveloping. The craftsmen involved in the design of the chair were unknown. The origins of the term "club" are unclear, but it may be a reference to the gentlemen's club. Characteristics Shape While the club chair is undoubtedly a classic feature of interior decor in France, it remains just as relevant as ever today. As time has passed, the chair's charm, diversity and fame have grown. With great simplicity, the Art Deco era produced armchairs with clean, flexible lines, in contrast to the Art Nouveau style of the 1910s. After the Second World War, dozens of different shapes appeared. Some have stood the test of time, such as the "moustache" and the "gendarme’s hat", named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauteuil Rond2
A ''fauteuil'' () is a style of open-armchair with a primarily exposed wooden frame originating in France during the early 17th century. A ''fauteuil'' is made of wood and frequently with carved relief ornament. It is typically upholstered on the seat, the seat back and on the arms (''manchettes''). Some ''fauteuils'' have a valenced front seat rail which is padding that extends slightly over the apron. The exposed wooden elements are often gilded or otherwise painted. See also * Bergere *Couch *Louis XVI Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ... Chairs {{furniture-stub pl:Fotel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
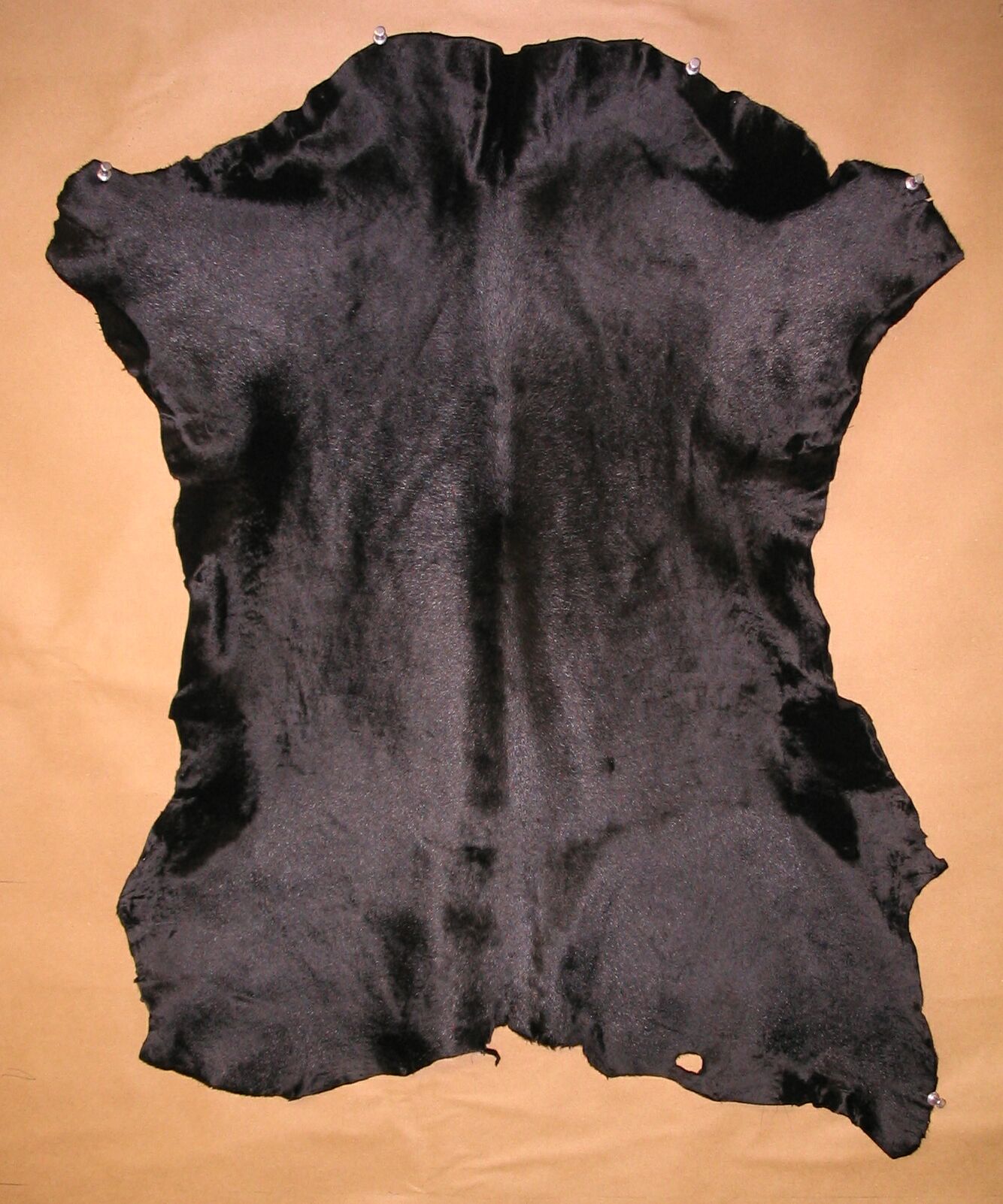
Fellmonger
A fellmonger was a dealer in hides or skins, particularly sheepskins, who might also prepare skins for tanning. The name is derived from the Old English ‘fell’ meaning skins and ‘monger’ meaning dealer. Fellmongery is one of the oldest professions in the world and since ancient times, humans have used the skins of animals to clothe themselves, and for making domestic articles. Historically, fellmongers belonged to a guild or company which had its own rules and by-laws to regulate the quality of the skins, workmanship, treatment of apprentices and trading rights. See also * Pulled wool The pulled wool is a wool plucked from the dead sheep skin. It is a product of Wool pulling industry. Mazamet was the biggest center of "wool pulling industry" in Europe for Pulled wool also referred to as "skin wool". Alternative names Pulled ... References External links * {{cite web, url=http://boar.org.uk/aaiwxw3MusprattL6Preparation.htm , title=Sheridan Muspratt's description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
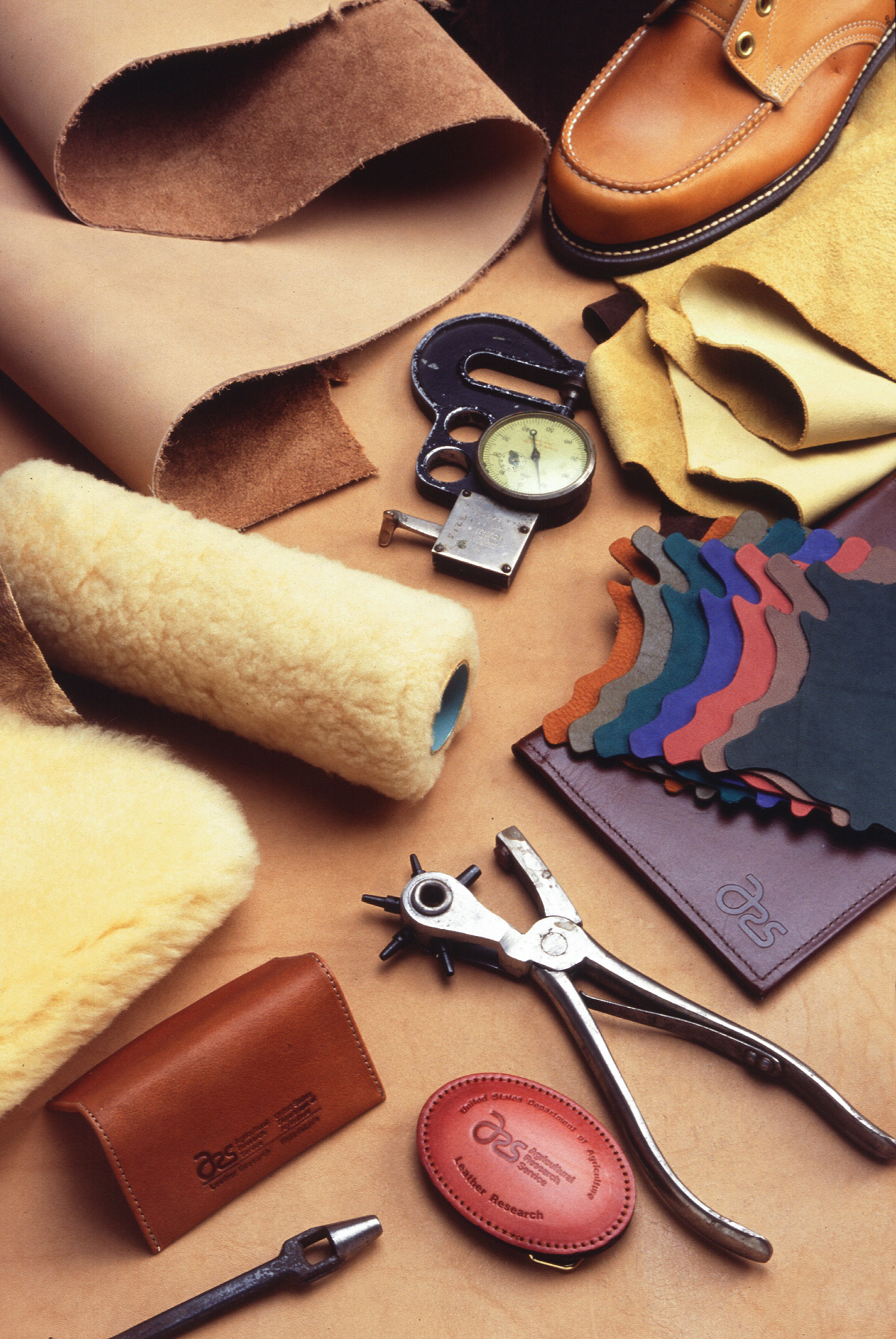
Leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Animal rights groups claim that modern commercial leather making and the consumption of its products is unethically killing animals. According to the life-cycle assessment (LCA) report for the United Nations Industrial Development Organization, 99% of the raw hides and skins used in the production of leather derive from animals raised for meat and/or dairy production. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in uns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Commonw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicast Leather
Bicast leather (also spelled as bi-cast leather or bycast leather) is a material made with a split leather backing covered with an embossed layer of polyurethane or vinyl. Bicast leather was originally made for the apparel industry for glossy shoes, and was later adopted by the furniture industry. Production and features The hide material used in the making of bicast is usually a portion of the fibrous, lower grade of leather that remains when the higher-grade grain layer is split off. Bicast leather is produced by building up a layer of plastic (typically polyurethane) on top of an embossed release paper known as ''casting paper''. The embossing is usually giving the appearance of top grain leather, although it may be smooth depending on the desired finish. The plastic layer may optionally include: pigment, foams of various consistencies, and adhesives. Split leather is then applied and pressed onto the plastic, which may have been dried. After the resultant bicast leather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calfskin
Calfskin or calf leather is a leather or membrane produced from the hide of a calf, or juvenile domestic cattle. Calfskin is particularly valuable because of its softness and fine grain, as well as durability. It is commonly used for high-quality clothing, shoes, wallets, and similar products, as well as traditional leather bookbindings. In these contexts, just "calf" is commonly used. Fine calfskin is one of the skins used for vellum and parchment manuscripts. In Spanish, the word is ''Ternera/Novillo'', referring to leather from animals less than three years old. Chickenskin, despite its name, is a form of calfskin made using the skin of unborn calves. In fashion, soft finished calfskin is sometimes described as'' veau velours'' (French for "velvet calf"). See also *Goldbeater's skin, made from the intestine of a calf *Sheepskin (material) Sheepskin is the hide of a sheep, sometimes also called lambskin. Unlike common leather, sheepskin is tanned with the fleece intact, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercerised Cotton
Mercerisation is a textile finishing treatment for cellulose fabric and yarn, mainly cotton and flax, which improves dye uptake and tear strength, reduces fabric shrinkage, and imparts a silk-like luster. Development The process was devised in 1844 by John Mercer, who treated cotton with solutions of20–30% sodium hydroxide followed by washing. Mercer observed that the treatment shrank the fabric and increased its tensile strength and affinity for dyes. In the original process of Mercer, no tension was applied. The product was termed ''fulled cotton'', a nod to the process of fulling in woven wool fabric. Mercer regarded the increased affinity for dyes as the most important technical aspect. Mercer also experimented with sulfuric acid and zinc chloride solutions and discovered the parchmentising effect of sulfuric acid. The silk-like lustre now commonly associated with mercerising is produced by tension and was discovered by Horace Lowe in 1889. Process Treatment wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coir
Coir (), also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell and the outer coat of a coconut. Other uses of brown coir (made from ripe coconut) are in upholstery padding, sacking and horticulture. White coir, harvested from unripe coconuts, is used for making finer brushes, string, rope and fishing nets. It has the advantage of not sinking, so can be used in long lengths in deep water without the added weight dragging down boats and buoys. Coir must not be confused with coir pith, which is the powdery and spongy material resulting from the processing of the coir fibre. Coir fibre is locally named 'coprah' in some countries, adding to confusion. Pith is chemically similar to coir, but contains much shorter fibers. The name coco peat may refer either to coir or the pith or a mixture, as both have go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upholstery
Upholstery is the work of providing furniture, especially seats, with padding, springs, webbing, and fabric or leather covers. The word also refers to the materials used to upholster something. ''Upholstery'' comes from the Middle English word ''upholder'', which referred to an artisan who makes fabric furnishings. The term is equally applicable to domestic, automobile, airplane and boat furniture, and can be applied to mattresses, particularly the upper layers, though these often differ significantly in design. A person who works with upholstery is called an ''upholsterer''. An apprentice upholsterer is sometimes called an ''outsider'' or ''trimmer''. Traditional upholstery uses materials like coil springs (post-1850), animal hair (horse, hog and cow), coir, straw and hay, hessians, linen scrims, wadding, etc., and is done by hand, building each layer up. In contrast, today's upholsterers employ synthetic materials like dacron and vinyl, serpentine springs, and so on. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpentry
Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenters traditionally worked with natural wood and did rougher work such as framing, but today many other materials are also used and sometimes the finer trades of cabinetmaking and furniture building are considered carpentry. In the United States, 98.5% of carpenters are male, and it was the fourth most male-dominated occupation in the country in 1999. In 2006 in the United States, there were about 1.5 million carpentry positions. Carpenters are usually the first tradesmen on a job and the last to leave. Carpenters normally framed post-and-beam buildings until the end of the 19th century; now this old-fashioned carpentry is called timber framing. Carpenters learn this trade by being employed through an apprenticeship training—normally 4 years—an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chair
A chair is a type of seat, typically designed for one person and consisting of one or more legs, a flat or slightly angled seat and a back-rest. They may be made of wood, metal, or synthetic materials, and may be padded or upholstered in various colors and fabrics. Chairs vary in design. An armchair has armrests fixed to the seat; a recliner is upholstered and features a mechanism that lowers the chair's back and raises into place a footrest; a rocking chair has legs fixed to two long curved slats; and a wheelchair has wheels fixed to an axis under the seat. Etymology ''Chair'' comes from the early 13th-century English word ''chaere'', from Old French ''chaiere'' ("chair, seat, throne"), from Latin ''cathedra'' ("seat"). History The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Club Chair
A club chair is a type of armchair, usually covered in leather. It was created and made in France. Before it came to be known under its current name, it first appeared as the , the 'comfortable armchair'. It was given this name to distinguish it from the , which had straighter lines and was less enveloping. The craftsmen involved in the design of the chair were unknown. The origins of the term "club" are unclear, but it may be a reference to the gentlemen's club. Characteristics Shape While the club chair is undoubtedly a classic feature of interior decor in France, it remains just as relevant as ever today. As time has passed, the chair's charm, diversity and fame have grown. With great simplicity, the Art Deco era produced armchairs with clean, flexible lines, in contrast to the Art Nouveau style of the 1910s. After the Second World War, dozens of different shapes appeared. Some have stood the test of time, such as the "moustache" and the "gendarme’s hat", named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |