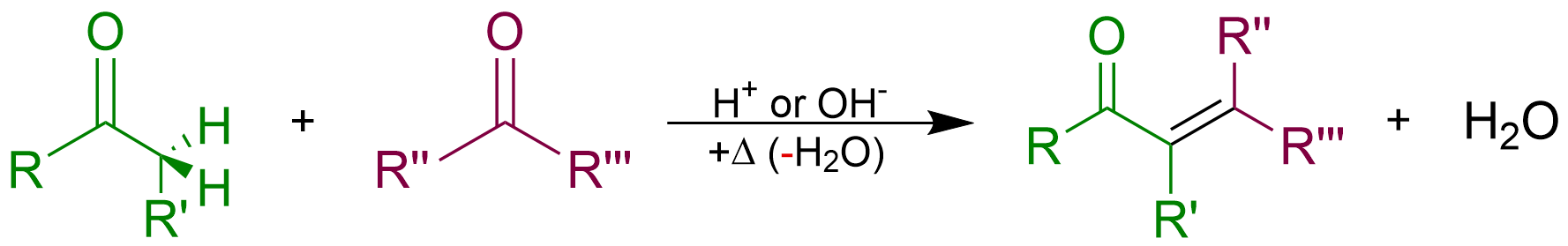|
Ciramadol
Ciramadol (WY-15,705) is an opioid analgesic that was developed in the late 1970s and is related to phencyclidine, tramadol, tapentadol and venlafaxine. It is a mixed agonist-antagonist for the μ-opioid receptor with relatively low abuse potential and a ceiling on respiratory depression which makes it a relatively safe drug. It has a slightly higher potency and effectiveness as an analgesic than codeine, but is weaker than morphine. Other side effects include sedation and nausea but these are generally less severe than with other similar drugs. Synthesis The Claisen-Schmidt reaction between 3-(methoxymethoxy)benzaldehyde 3709-05-2(1) and cyclohexanone (2) affordeCID:54364197(3). Michael addition of dimethylamine Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to aroun ... leads the am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Opioids
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used non-medically for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. Opioids can cause death and have been used for executions in the United States. Side effects of opioids may include itchiness, sedation, nausea, respiratory depression, constipation, and euphoria. Long-term use can cause tolerance, meaning that increased doses are required to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, meaning that abruptly discontinuing the drug leads to unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. The euphoria attracts recreational use, and frequent, escalating recreational use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profadol
Profadol (CI-572) is an opioid analgesic which was developed in the 1960s by Parke-Davis. It acts as a mixed agonist-antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor. The analgetic potency is about the same as of pethidine (meperidine), the antagonistic effect is 1/50 of nalorphine. Synthesis The Knoevenagel condensation between 3'-Methoxybutyrophenone 1550-06-1and Ethyl cyanoacetate gives (1). Conjugate addition of cyanide gives (2). Hydrolysis of both nitrile groups, saponification of the ester and decarboxylation gives the diacidCID:164137621(3). Imide formation occurs upon treatment with methylamine giving 3-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-1-methyl-3-propylpyrrolidine-2,5-dioneCID:163444474(4). Reduction of the imide by lithium aluminium hydride gave 505-32-429369-01-5] (5). Demethylation completed the synthesis of Profadol (6). See also * BDPC, Bromadol * C-8813 * Ciramadol * Faxeladol * Prodilidine * Tapentadol * Tramadol Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-8813
C-8813 (thiobromadol) is a potent μ-opioid receptor agonist with a distinctive chemical structure which is not closely related to other established families of opioid drugs. The ''trans''-isomer was found to be around 591 times more potent than morphine in animal studies. The same study assigned a potency of 504 times that of morphine to the related compound BDPC. C-8813 is claimed to be similarly potent at the δ-opioid receptor, which antagonizes the mu depression of breathing, presumably making the drug safer. C-8813 has never been used in humans. See also * BDPC * Ciramadol * Faxeladol * Profadol * Tapentadol * Tramadol Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an h ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Synthetic opioids Thiophenes Tertiary alcohols Organobrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromadol
BDPC (systematic name 4-(4-bromophenyl)-4-(dimethylamino)-1-(2-phenylethyl)cyclohexanol; also known as bromadol) is a potent narcotic analgesic with a distinctive arylcyclohexylamine chemical structure. It was developed by Daniel Lednicer at Upjohn in the 1970s. Initial studies estimated that it was around 10,000 times the strength of morphine in animal models. However, later studies using more modern techniques assigned a value of 504 times the potency of morphine for the more active ''trans''-isomer. This drug was first seized along with three kilograms of acetylfentanyl in an April 25, 2013 police action in Montreal, Canada, and has reportedly continued to be available on the designer drug black market internationally. Analogues where the ''para''-bromine is replaced by chlorine or a methyl group retain similar activity, as does the ''meta''-hydroxyl derivative. ] ] See also * 3-OH-PCP * 4-Keto-PCP * C-8813 * Cebranopadol * Ciramadol * Dimetamine * Faxeladol * Profadol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claisen-Schmidt Reaction
An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties (of aldehydes or ketones) react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. The overall reaction is as follows (where the Rs can be H): Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis and biochemistry as ways to form carbon–carbon bonds. In its usual form, it involves the nucleophilic addition of a ketone enolate to an aldehyde to form a β-hydroxy ketone, or "aldol" (aldehyde + alcohol), a structural unit found in many naturally occurring molecules and pharmaceuticals. The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in biochemistry, to refer to just the first (addition) stage of the process—the aldol reaction itself—as catalyzed by aldolases. However, this is formally an addition reaction rather than a condensation reaction because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an hour. It is also available by injection. It is available in combination with paracetamol (acetaminophen). As is typical of opioids, common side effects include constipation, itchiness, and nausea. Serious side effects may include hallucinations, seizures, increased risk of serotonin syndrome, decreased alertness, and drug addiction. A change in dosage may be recommended in those with kidney or liver problems. It is not recommended in those who are at risk of suicide or in those who are pregnant. While not recommended in women who are breastfeeding, those who take a single dose should not generally stop breastfeeding. Tramadol is converted in the liver to ''O''-desmethyltramadol (desmetramadol), an opioid with a stronger affinity to the μ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapentadol
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs within 32 minutes of oral administration, and lasts for 4–6 hours. It is similar to tramadol in its dual mechanism of action; namely, its ability to activate the mu opioid receptor and inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine. Unlike tramadol, it has only weak effects on the reuptake of serotonin and is a significantly more potent opioid with no known active metabolites. Tapentadol is not a pro-drug and therefore does not rely on metabolism to produce its therapeutic effects; this makes it a useful moderate-potency analgesic option for patients who do not respond adequately to more commonly used opioids due to genetic disposition (poor metabolizers of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6), as well as providing a more consistent dosage-response range among the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faxeladol
Faxeladol (INN, USAN) (code names GRTA-9906, GRTA-0009906, EM-906, GCR-9905, GRT-TA300) is an opioid analgesic which was developed by Grünenthal GmbH but was never marketed for medical use anywhere in the world. It is related to tramadol and ciramadol, and was developed shortly after tramadol in the late 1970s. Similarly to tramadol, it was believed faxeladol would have analgesic, as well as antidepressant effects, due to its action on serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. In various studies in the 1970s alongside tramadol, faxeladol was seen to be slightly more potent than tramadol, but with a higher rate of sudden seizures than tramadol, which is known to cause seizures without warning in some users. See also * Bromadol * Profadol * Tapentadol Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005. Structure and synthesis The molecule consists of a nitrogen atom with two methyl substituents and one proton. Dimethylamine is a weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3--CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79). Dimethylamine reacts with acids to form salts, such as dimethylamine hydrochloride, an odorless white solid with a melting point of 171.5 °C. Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia at elevated temperatures and high pressure: :2 CH3OH + NH3 → (CH3)2NH + 2 H2O Natural occurrence Dimethylamine is found quite widely distributed in animals and plants, and is present in many foods at the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |