|
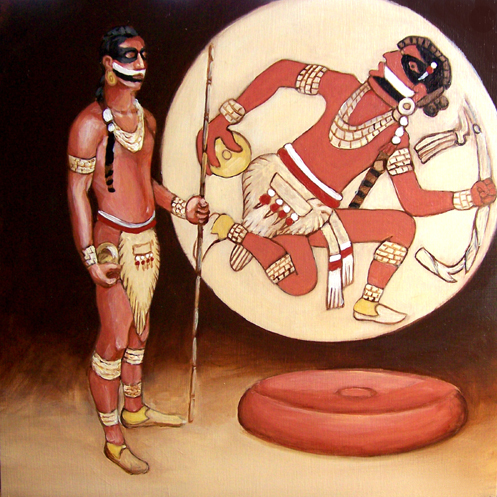
Chunkey
Chunkey (also known as chunky, chenco, tchung-kee or the hoop and stick game ) is a game of Native American origin. It was played by rolling disc-shaped stones across the ground and throwing spears at them in an attempt to land the spear as close to the stopped stone as possible. It originated around 600 CE in the Cahokia region of what is now the United States (near modern St. Louis, Missouri). Chunkey was played in huge arenas as large as 47 acres (19 ha) that housed great audiences designed to bring people of the region together (i.e. Cahokians, farmers, immigrants, and even visitors). It continued to be played after the fall of the Mississippian culture around 1500 CE. Variations were played throughout North America. Early ethnographer James Adair translated the name to mean "running hard labor". Gambling was frequently connected with the game, with some players wagering everything they owned on the outcome of the game. Losers were even known to commit suicide. Graphic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
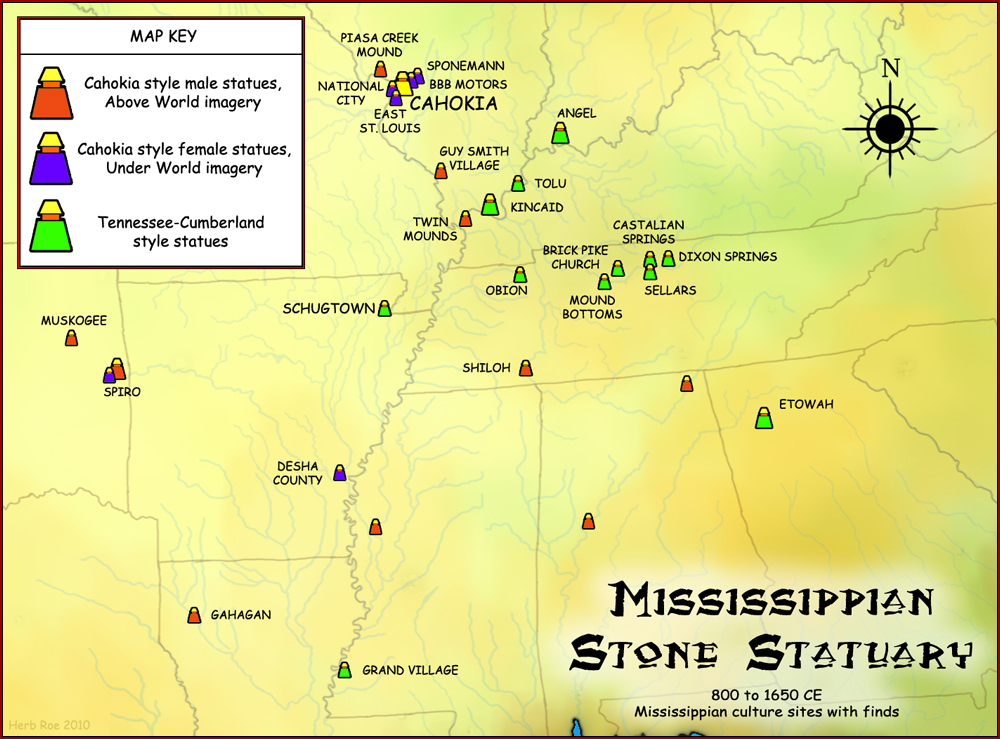
Mississippian Stone Statuary
The Mississippian stone statuary are artifacts of polished stone in the shape of human figurines made by members of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE) and found in archaeological sites in the American Midwest and Southeast. Two distinct styles exist; the first is a style of carved flint clay found over a wide geographical area but believed to be from the American Bottom area and manufactured at the Cahokia site specifically; the second is a variety of carved and polished locally available stone primarily found in the Tennessee-Cumberland region and northern Georgia (although there are lone outliers of this style in other regions). Early European explorers reported seeing stone and wooden statues in native temples, but the first documented modern discovery was made in 1790 in Kentucky, and given as a gift to Thomas Jefferson. History Archaeologists have divided what is known about Mississippian culture religious practices into three major "cult" manifestations. The '' Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahokia
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south-western Illinois between East St. Louis and Collinsville. The park covers , or about , and contains about 80 manmade mounds, but the ancient city was much larger. At its apex around 1100 CE, the city covered about and included about 120 earthworks in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and functions."Nomination – Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site, Illinois" ''US World Heritage Sites'', National Park Service, accessed 2012-05-03 Cahokia was the largest and most influential urban settlement of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
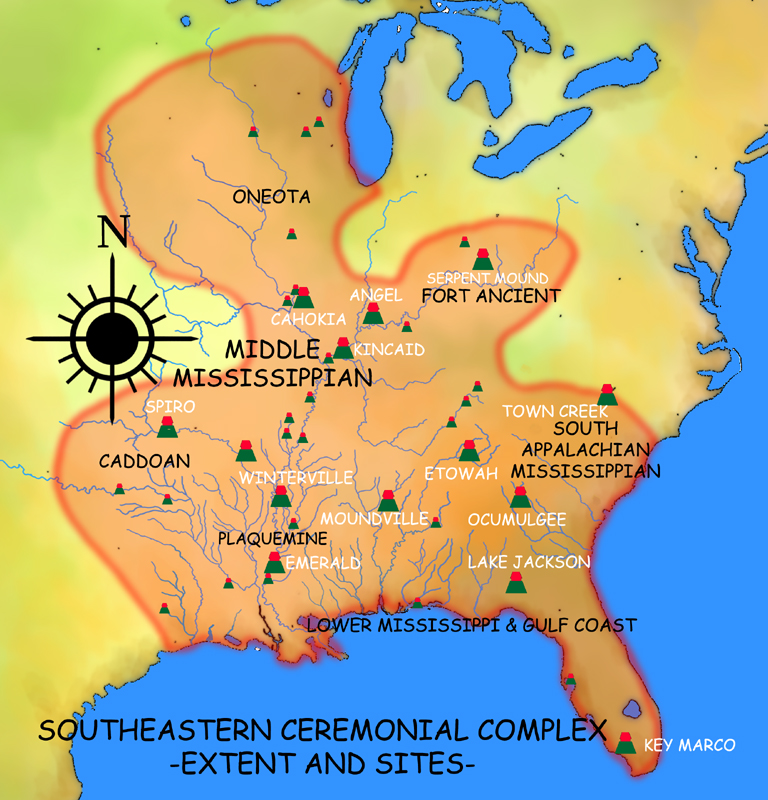
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
The Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly the Southern Cult), aka S.E.C.C., is the name given to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. But, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that their civilizations developed independently. Obsolete names for this ceremonial complex, found in some anthropological sources, include Buzzard Cult and Southern Death Cult. Theories and names The complex operated as an exchange network. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
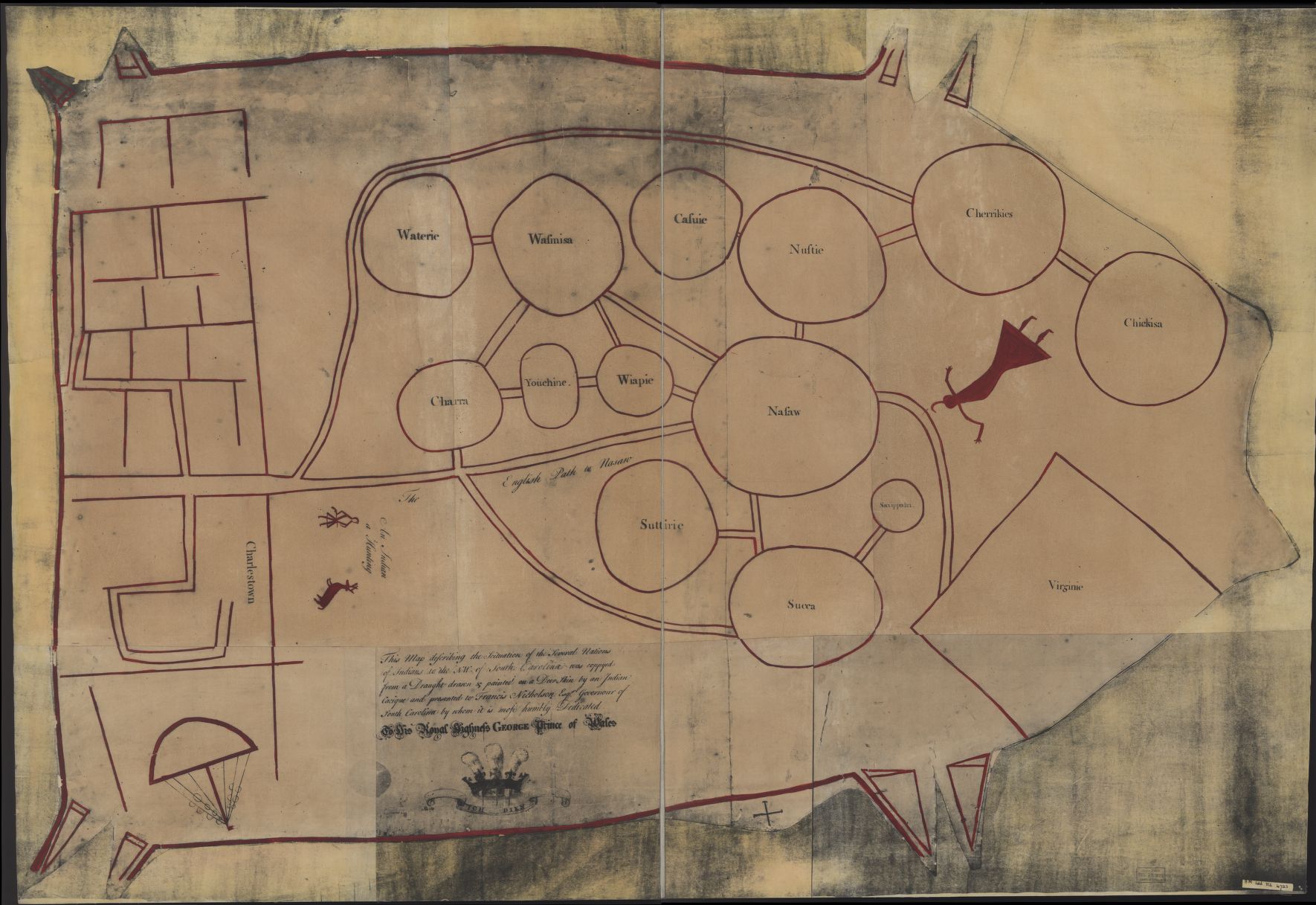
Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes: the Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians, and Jena Band of Choctaw Indians in Louisiana. The Choctaw were first noted by Europeans in French written records of 1675. Their mother mound is Nanih Waiya, a great earthwork platform mound located in central-east Mississippi. Early Spanish explorers of the mid-16th century in the Southeast encountered ancestral Mississippian culture villages and chiefs. The Choctaw coalesced as a people in the 17th century and developed at least three distinct political and geographical divisions: eastern, western, and southern. These different groups sometimes created distinct, independent alliances with nearby European powers. These i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandan
The Mandan are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still reside in the area of the reservation; the rest reside around the United States and in Canada. The Mandan historically lived along both banks of the Upper Missouri River and two of its tributaries—the Heart and Knife rivers— in present-day North and South Dakota. Speakers of Mandan, a Siouan language, they developed a settled, agrarian culture. They established permanent villages featuring large, round, earth lodges, some in diameter, surrounding a central plaza. Matrilineal families lived in the lodges. The Mandan were a great trading nation, trading especially their large corn surpluses with other tribes in exchange for bison meat and fat. Food was the primary item, but they also traded for horses, guns, and other trade goods. Popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscogee
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsTranscribed documents Sequoyah Research Center and the American Native Press Archives in the . Their original homelands are in what now comprises southern , much of , western |
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Chickasaw Nation. Chickasaw people have a migration story in which they moved from a land west of the Mississippi River, where they settled mostly in present-day northeast Mississippi, northwest Alabama, and into Lawrence County, Tennessee. They had interaction with French, English, and Spanish colonists during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial period. The United States considered the Chickasaw one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted numerous practices of European Americans. Resisting European-American settlers encroaching on their territory, they were force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that the origin of the proto-Iroquoian language was likely the Appalachian region, and the split betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Catlin
George Catlin (July 26, 1796 – December 23, 1872) was an American adventurer, lawyer, painter, author, and traveler, who specialized in portraits of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in the Old West. Traveling to the Western United States, American West five times during the 1830s, Catlin wrote about and painted portraits that depicted the life of the Plains Indians. His early work included engravings, drawn from nature, of sites along the route of the Erie Canal in New York State. Several of his renderings were published in one of the first printed books to use lithography, Cadwallader D. Colden's ''Memoir, Prepared at the Request of a Committee of the Common Council of the City of New York, and Presented to the Mayor of the City, at the Celebration of the Completion of the New York Canals'', published in 1825, with early images of the Buffalo, New York, City of Buffalo. Background and education George Catlin was born in 1796 in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Lacrosse
Lacrosse has its origins in a tribal game played by eastern Woodlands Native Americans and by some Plains Indians tribes in what is now the United States of America and Canada. The game was extensively modified by European settlers to create its current collegiate and professional form. There were hundreds of native men playing a ball game with sticks. The game began with the ball being tossed into the air and the two sides rushing to catch it. Because of the large number of players involved, these games generally tended to involve a huge mob of players swarming the ball and slowly moving across the field. Passing the ball was thought of as a trick, and it was seen as cowardly to dodge an opponent. Years later lacrosse is still a popular sport played all over the world. Indigenous North American game Modern day lacrosse descends from and resembles games played by various Native American communities. These include games called ''dehontsigwaehs'' in Oee ("they bump hips"), ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)