|
Chub Mackerel
The chub mackerel, Pacific mackerel, or Pacific chub mackerel (''Scomber japonicus'') is a species of fish in the tuna and mackerel family, Scombridae. This species of mackerel closely resembles the Atlantic chub mackerel. Characteristics The chub mackerel has a well-developed swim bladder attached with the esophagus, which the "true mackerels" in the genus ''Scomber'' lack, and a characteristic color difference is seen between the chub and the Atlantic chub, the latter being silvery-sided below the midline, whereas the lower part of the sides of the chub (otherwise colored somewhat like the Atlantic) are mottled with small dusky blotches, and the chub has a larger eye than the Atlantic. Less obvious differences are that the dorsal fins are closer together in the chub and only 9 or 10 spines are in its first dorsal fin instead of 11 or more, which is the usual count in the Atlantic mackerel. In most species, the mackerel is known to travel in large schools. It is a smaller fish tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean. The region has an exceptionally high species richness, with the world's highest species richness being found in at its heart in the Coral Triangle, and a remarkable gradient of decreasing species richness radiating outward in al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purse Seine
Seine fishing (or seine-haul fishing; ) is a method of fishing that employs a surrounding net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be deployed from the shore as a beach seine, or from a boat. Boats deploying seine nets are known as seiners. Two main types of seine net are deployed from seiners: ''purse seines'' and ''Danish seines''. A seine differs from a gillnet, in that a seine encloses fish, where a gillnet directly snares fish. Etymology The word ''seine'' has its origins in the Old English ''segne'', which entered the language via Latin ''sagena'', from the original Greek σαγήνη ''sagēnē'' (a drag-net). History Seines have been used widely in the past, including by Stone Age societies. For example, the Māori used large canoes to deploy seine nets which could be over a kilometer long. The nets were woven from green flax, with stone weights and light wood o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisheries Capture Of Scomber Japonicus
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies (about 10% of all catch) and the oceans (about 90%). About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem — causing declines in some populations. Because of their economic and social importance, fisheries are governed by complex fisheries management practices and legal regimes that vary widely across countries. Historically, fisheries were treated with a " first-come, first-served " approach, but recent threats by human overfishing and environmental issues have required increased regulation of fisheries to prevent conflict and increase profitable economic activity on the fishery. Modern jurisdictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
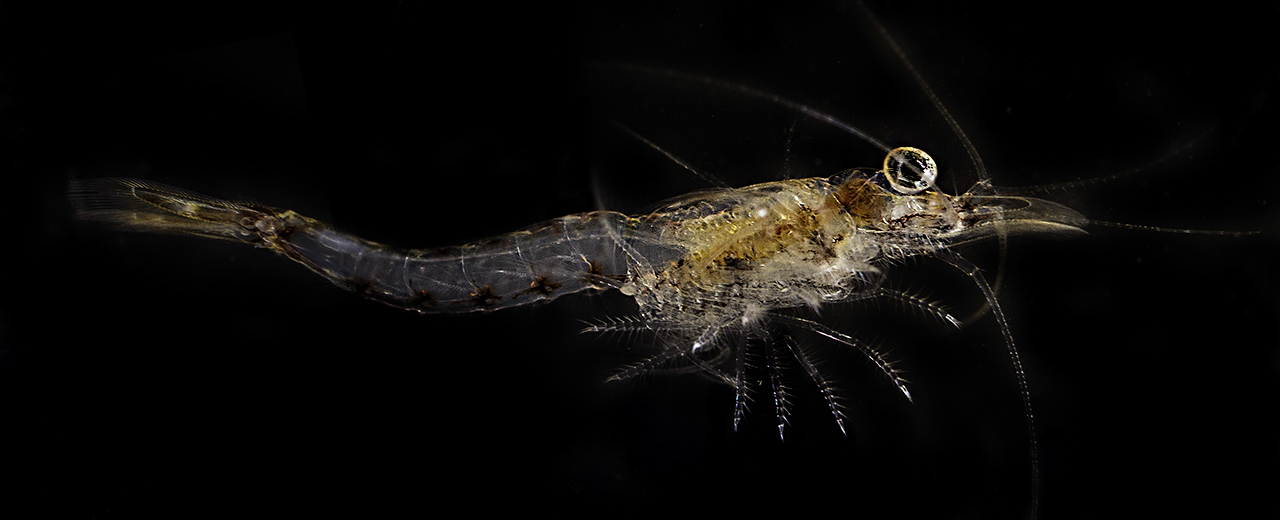
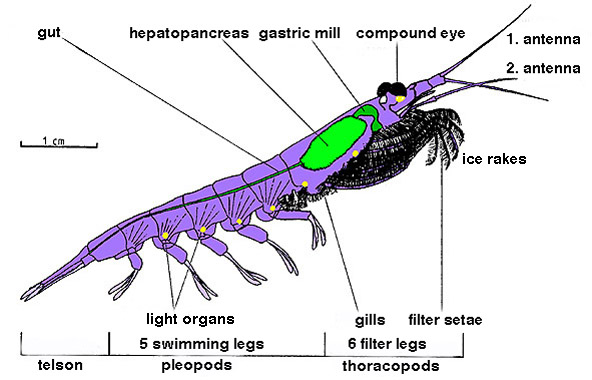
Euphausid
Krill are small crustaceans of the order (biology), order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian language, Norwegian word ', meaning "small Fry (biology), fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection – near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and (to a lesser extent) zooplankton, yet also are the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, ''Euphausia superba'', makes up an estimated biomass (ecology), biomass of around 379,000,000 tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, Pinniped, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large diel vertical migration, daily vertical migrations, thus providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysid
Mysida is an order of small, shrimp-like crustaceans in the malacostracan superorder Peracarida. Their common name opossum shrimps stems from the presence of a brood pouch or "marsupium" in females. The fact that the larvae are reared in this pouch and are not free-swimming characterises the order. The mysid's head bears a pair of stalked eyes and two pairs of antennae. The thorax consists of eight segments each bearing branching limbs, the whole concealed beneath a protective carapace and the abdomen has six segments and usually further small limbs. Mysids are found throughout the world in both shallow and deep marine waters where they can be benthic or pelagic, but they are also important in some fresh water and brackish ecosystems. Many benthic species make daily vertical migrations into higher parts of the water column. Mysids are filter feeders, omnivores that feed on algae, detritus and zooplankton. Some mysids are cultured in laboratories for experimental purposes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile Fish
Fish go through various life stages between fertilization and adulthood. The life of a fish start as spawned eggs which hatch into immotile larvae. These larval hatchlings are not yet capable of feeding themselves and carry a yolk sac which provides stored nutrition. Before the yolk sac completely disappears, the young fish must mature enough to be able to forage independently. When they have developed to the point where they are capable of feeding by themselves, the fish are called fry. When, in addition, they have developed scales and working fins, the transition to a juvenile fish is complete and it is called a fingerling, so called as they are typically about the size of human fingers. The juvenile stage lasts until the fish is fully grown, sexually mature and interacting with other adult fish. Growth stages Ichthyoplankton ''(planktonic or drifting fish)'' are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are usually found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotifer
The rotifers (, from the Latin , "wheel", and , "bearing"), commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703. Most rotifers are around long (although their size can range from to over ), and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species. Some rotifers are free swimming and truly planktonic, others move by inchworming along a substrate, and some are sessile, living inside tubes or gelatinous holdfasts that are attached to a substrate. About 25 species are colonial (e.g., '' Sinantherina semibullata''), either sessile or planktonic. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton, being a major foodsource and with many species also contributing to the decomposition of soil organic matter. Most species of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Larva
Ichthyoplankton (from Greek: ἰχθύς, , "fish"; and πλαγκτός, , "drifter") are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are mostly found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 metres deep, which is sometimes called the epipelagic or photic zone. Ichthyoplankton are planktonic, meaning they cannot swim effectively under their own power, but must drift with the ocean currents. Fish eggs cannot swim at all, and are unambiguously planktonic. Early stage larvae swim poorly, but later stage larvae swim better and cease to be planktonic as they grow into juveniles. Fish larvae are part of the zooplankton that eat smaller plankton, while fish eggs carry their own food supply. Both eggs and larvae are themselves eaten by larger animals. Fish can produce high numbers of eggs which are often released into the open water column. Fish eggs typically have a diameter of about . The newly hatched young of oviparous fish are called larvae. They are usually poorly formed, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 2020. About two-thirds of these inhabitants live in the metropolitan area of Cape Town, which is also the provincial capital. The Western Cape was created in 1994 from part of the former Cape Province. The two largest cities are Cape Town and George. Geography The Western Cape Province is roughly L-shaped, extending north and east from the Cape of Good Hope, in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It stretches about northwards along the Atlantic coast and about eastwards along the South African south coast (Southern Indian Ocean). It is bordered on the north by the Northern Cape and on the east by the Eastern Cape. The total land area of the province is , about 10.6% of the country's total. It is roughly the size of England or the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpeg)





.jpg)
