|
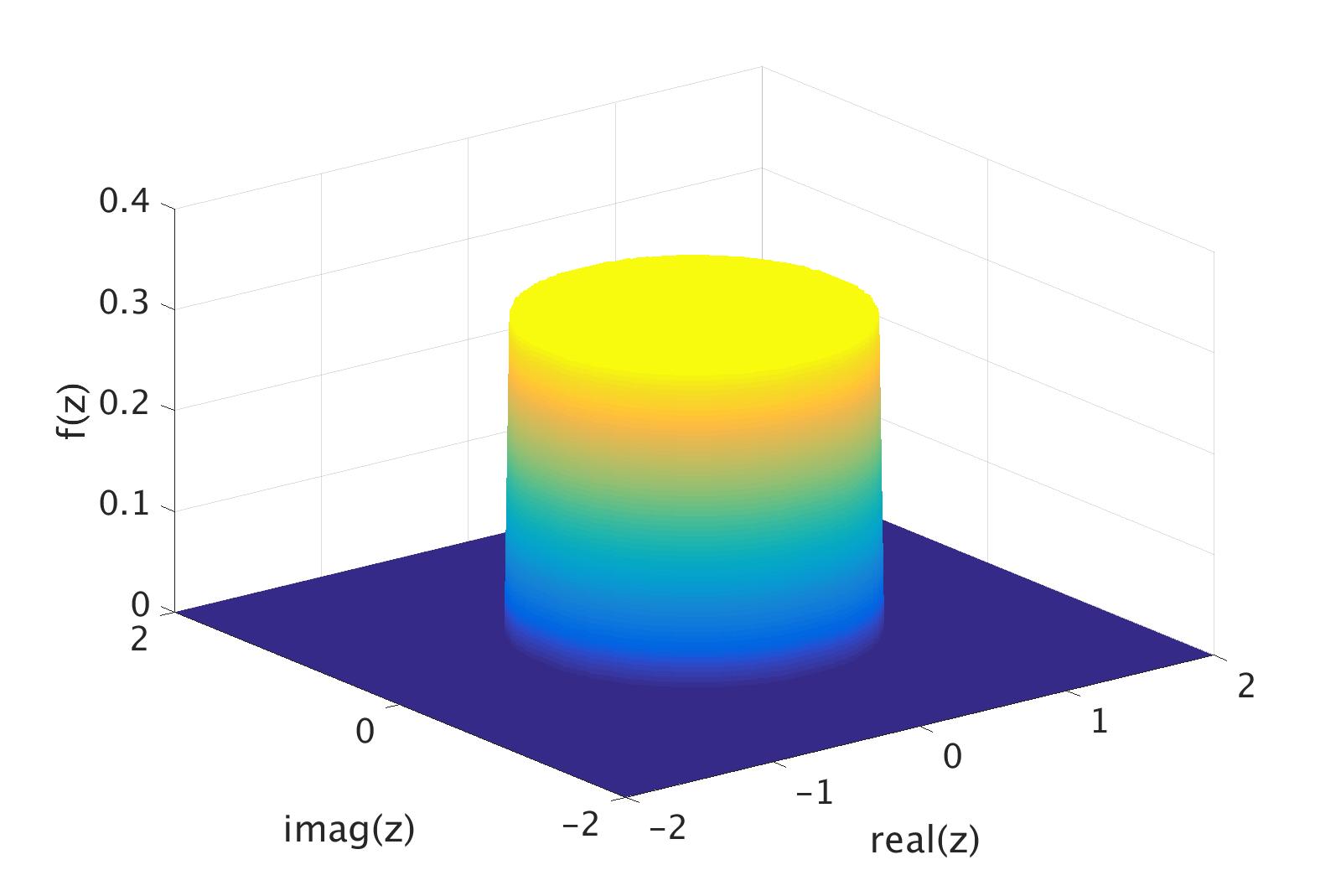
Characteristic Function (probability Theory)
In probability theory and statistics, the characteristic function of any real-valued random variable completely defines its probability distribution. If a random variable admits a probability density function, then the characteristic function is the Fourier transform (with sign reversal) of the probability density function. Thus it provides an alternative route to analytical results compared with working directly with probability density functions or cumulative distribution functions. There are particularly simple results for the characteristic functions of distributions defined by the weighted sums of random variables. In addition to univariate distributions, characteristic functions can be defined for vector- or matrix-valued random variables, and can also be extended to more generic cases. The characteristic function always exists when treated as a function of a real-valued argument, unlike the moment-generating function. There are relations between the behavior of the charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sinc Simple
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function ( ), denoted by , has two forms, normalized and unnormalized.. In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for by \operatorname(x) = \frac. Alternatively, the unnormalized sinc function is often called the sampling function, indicated as Sa(''x''). In digital signal processing and information theory, the normalized sinc function is commonly defined for by \operatorname(x) = \frac. In either case, the value at is defined to be the limiting value \operatorname(0) := \lim_\frac = 1 for all real (the limit can be proven using the Squeeze theorem#Second example, squeeze theorem). The Normalizing constant, normalization causes the integral, definite integral of the function over the real numbers to equal 1 (whereas the same integral of the unnormalized sinc function has a value of pi, ). As a further useful property, the zeros of the normalized sinc function are the nonzero integer values of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imaginary Unit
The imaginary unit or unit imaginary number () is a mathematical constant that is a solution to the quadratic equation Although there is no real number with this property, can be used to extend the real numbers to what are called complex numbers, using addition and multiplication. A simple example of the use of in a complex number is Imaginary numbers are an important mathematical concept; they extend the real number system \mathbb to the complex number system \mathbb, in which at least one Root of a function, root for every nonconstant polynomial exists (see Algebraic closure and Fundamental theorem of algebra). Here, the term ''imaginary'' is used because there is no real number having a negative square (algebra), square. There are two complex square roots of and , just as there are two complex square roots of every real number other than zero (which has one multiple root, double square root). In contexts in which use of the letter is ambiguous or problematic, the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Complex Random Vector
In probability theory and statistics, a complex random vector is typically a tuple of complex-valued random variables, and generally is a random variable taking values in a vector space over the field of complex numbers. If Z_1,\ldots,Z_n are complex-valued random variables, then the ''n''-tuple \left( Z_1,\ldots,Z_n \right) is a complex random vector. Complex random variables can always be considered as pairs of real random vectors: their real and imaginary parts. Some concepts of real random vectors have a straightforward generalization to complex random vectors. For example, the definition of the mean of a complex random vector. Other concepts are unique to complex random vectors. Applications of complex random vectors are found in digital signal processing. Definition A complex random vector \mathbf = (Z_1,\ldots,Z_n)^T on the probability space (\Omega,\mathcal,P) is a function \mathbf \colon \Omega \rightarrow \mathbb^n such that the vector (\Re,\Im,\ldots,\Re,\Im)^T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Real Part
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficients h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Complex Conjugate
In mathematics, the complex conjugate of a complex number is the number with an equal real part and an imaginary part equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. That is, if a and b are real numbers, then the complex conjugate of a + bi is a - bi. The complex conjugate of z is often denoted as \overline or z^*. In polar form, if r and \varphi are real numbers then the conjugate of r e^ is r e^. This can be shown using Euler's formula. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is a real number: a^2 + b^2 (or r^2 in polar coordinates). If a root of a univariate polynomial with real coefficients is complex, then its complex conjugate is also a root. Notation The complex conjugate of a complex number z is written as \overline z or z^*. The first notation, a vinculum, avoids confusion with the notation for the conjugate transpose of a matrix, which can be thought of as a generalization of the complex conjugate. The second is preferred in physics, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Complex Random Variable
In probability theory and statistics, complex random variables are a generalization of real-valued random variables to complex numbers, i.e. the possible values a complex random variable may take are complex numbers. Complex random variables can always be considered as pairs of real random variables: their real and imaginary parts. Therefore, the #Cumulative distribution function, distribution of one complex random variable may be interpreted as the Joint probability distribution, joint distribution of two real random variables. Some concepts of real random variables have a straightforward generalization to complex random variables—e.g., the definition of the #Expectation, mean of a complex random variable. Other concepts are unique to complex random variables. Applications of complex random variables are found in digital signal processing, quadrature amplitude modulation and information theory. Definition A complex random variable Z on the probability space (\Omega,\mathcal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trace (linear Algebra)
In linear algebra, the trace of a square matrix , denoted , is the sum of the elements on its main diagonal, a_ + a_ + \dots + a_. It is only defined for a square matrix (). The trace of a matrix is the sum of its eigenvalues (counted with multiplicities). Also, for any matrices and of the same size. Thus, similar matrices have the same trace. As a consequence, one can define the trace of a linear operator mapping a finite-dimensional vector space into itself, since all matrices describing such an operator with respect to a basis are similar. The trace is related to the derivative of the determinant (see Jacobi's formula). Definition The trace of an square matrix is defined as \operatorname(\mathbf) = \sum_^n a_ = a_ + a_ + \dots + a_ where denotes the entry on the row and column of . The entries of can be real numbers, complex numbers, or more generally elements of a field . The trace is not defined for non-square matrices. Example Let be a matrix, with \m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Random Matrix
In probability theory and mathematical physics, a random matrix is a matrix-valued random variable—that is, a matrix in which some or all of its entries are sampled randomly from a probability distribution. Random matrix theory (RMT) is the study of properties of random matrices, often as they become large. RMT provides techniques like mean-field theory, diagrammatic methods, the cavity method, or the replica method to compute quantities like traces, spectral densities, or scalar products between eigenvectors. Many physical phenomena, such as the spectrum of nuclei of heavy atoms, the thermal conductivity of a lattice, or the emergence of quantum chaos, can be modeled mathematically as problems concerning large, random matrices. Applications Physics In nuclear physics, random matrices were introduced by Eugene Wigner to model the nuclei of heavy atoms. Wigner postulated that the spacings between the lines in the spectrum of a heavy atom nucleus should resemble the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Transpose
In linear algebra, the transpose of a Matrix (mathematics), matrix is an operator which flips a matrix over its diagonal; that is, it switches the row and column indices of the matrix by producing another matrix, often denoted by (among other notations). The transpose of a matrix was introduced in 1858 by the British mathematician Arthur Cayley. Transpose of a matrix Definition The transpose of a matrix , denoted by , , , A^, , , or , may be constructed by any one of the following methods: #Reflection (mathematics), Reflect over its main diagonal (which runs from top-left to bottom-right) to obtain #Write the rows of as the columns of #Write the columns of as the rows of Formally, the -th row, -th column element of is the -th row, -th column element of : :\left[\mathbf^\operatorname\right]_ = \left[\mathbf\right]_. If is an matrix, then is an matrix. In the case of square matrices, may also denote the th power of the matrix . For avoiding a possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Random Vector
In probability, and statistics, a multivariate random variable or random vector is a list or vector of mathematical variables each of whose value is unknown, either because the value has not yet occurred or because there is imperfect knowledge of its value. The individual variables in a random vector are grouped together because they are all part of a single mathematical system — often they represent different properties of an individual statistical unit. For example, while a given person has a specific age, height and weight, the representation of these features of ''an unspecified person'' from within a group would be a random vector. Normally each element of a random vector is a real number. Random vectors are often used as the underlying implementation of various types of aggregate random variables, e.g. a random matrix, random tree, random sequence, stochastic process, etc. Formally, a multivariate random variable is a column vector \mathbf = (X_1,\dots,X_n)^\maths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |