|
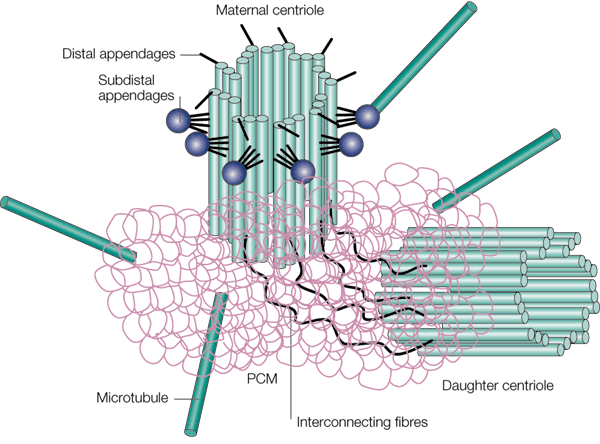
Centrioles
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and ''Ginkgo''. A bound pair of centrioles, surrounded by a highly ordered mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material (PCM), makes up a structure called a centrosome. Centrioles are typically made up of nine sets of short microtubule triplets, arranged in a cylinder. Deviations from this structure include crabs and ''Drosophila melanogaster'' embryos, with nine doublets, and ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' sperm cells and early embryos, with nine singlets. Additional proteins include centrin, cenexin and tektin. The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle during cell division. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosomes
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants lack centrosomes and therefore use other structures to organize their microtubules. Although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis in animal cells, it is not essential in certain fly and flatworm species. Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles arranged at right angles to each other, and surrounded by a dense, highly structured mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring — including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants lack centrosomes and therefore use other structures to organize their microtubules. Although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis in animal cells, it is not essential in certain fly and flatworm species. Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles arranged at right angles to each other, and surrounded by a dense, highly structured mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring — including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrin
Centrins, also known as caltractins, are a family of calcium-binding phosphoproteins found in the centrosome of eukaryotes. Centrins are present in the centrioles and pericentriolar lattice. Human centrin genes are CETN1, CETN2 and CETN3. History Centrin was first isolated and characterized from the flagellar roots of the green alga ''Tetraselmis striata'' in 1984. Function Centrins are required for duplication of centrioles. They may also play a role in severing of microtubules by causing calcium-mediated contraction. The majority of centrin in the cell is non-centrosomal whose function is not yet clear. Structure Centrin belongs to the EF-hand superfamily of calcium-binding proteins and has four calcium-binding EF-hands. It has a molecular weight of 20 kDa. See also * Centriole * Centrosome In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilium
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericentriolar Material
Pericentriolar material (PCM, sometimes also called pericent matrix) is a highly structured, dense mass of protein which makes up the part of the animal centrosome that surrounds the two centrioles. The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. Although the PCM appears amorphous by electron microscopy, super-resolution microscopy finds that it is highly organized. The PCM have 9-fold symmetry that mimics the symmetry of the centriole. Some PCM proteins are organized such that one end of the protein is found near the centriole and the other end is farther away from the centriole. The PCM size is dynamic during the cell cycle. After cell division, the PCM size is reduced in a process named centrosome reduction.Atypical centrioles during sexual reproduction Tomer Avidor-Reiss*, Atul Khire, Emily L. Fishman and Kyoung H. Jo Curr Biol. 2015 Nov 16;25(22):2956-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.09.045. Epub 2015 Oct 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenexin
Outer dense fiber protein 2, also known as cenexin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ODF2'' gene. The outer dense fibers are cytoskeletal structures that surround the axoneme in the middle piece and principal piece of the sperm tail. The fibers function in maintaining the elastic structure and recoil of the sperm tail as well as in protecting the tail from shear forces during epididymal transport and ejaculation. Defects in the outer dense fibers lead to abnormal sperm morphology and infertility. This gene encodes one of the major outer dense fiber proteins. Multiple protein isoforms A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ... are encoded by transcript variants of this gene; however, not all isoforms and variants have been fully described. References Furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tektin
Tektins are cytoskeletal proteins found in cilia and flagella as structural components of outer doublet microtubules. They are also present in centrioles and basal bodies. They are polymeric in nature, and form filaments.MA Pirner and RW LinckTektins are heterodimeric polymers in flagellar microtubules with axial periodicities matching the tubulin lattice J. Biol. Chem., Vol. 269, Issue 50, 31800-31806, Dec, 1994 They include TEKT1, TEKT2, TEKT3, TEKT4, TEKT5. Structure Tektin filaments are 2 to 3 nm diameter with two alpha helical segments. They have the consensus amino acid sequence of RPNVELCRD. Different types of tektins, designated as A (53 kDa), B (51 kDa), C (47 kDa) form dimers, trimers and oligomers in various combinations and are also associated with tubulin in the microtubule. Tektins A and B form heteropolymeric protofilaments whereas tektin C forms homodimers. Tektin filaments are present in a supercoiled state. This structure of tektins suggests that they a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aster (cell Biology)
An aster is a cellular structure shaped like a star, consisting of a centrosome and its associated microtubules during the early stages of mitosis in an animal cell. Asters do not form during mitosis in plants. Astral rays, composed of microtubules, radiate from the centrosphere and look like a cloud. Astral rays are one variant of microtubule which comes out of the centrosome; others include kinetochore microtubules and polar microtubules. During mitosis, there are five stages of cell division: Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase. During prophase, two aster-covered centrosomes migrate to opposite sides of the nucleus in preparation of mitotic spindle formation. During prometaphase there is fragmentation of the nuclear envelope and formation of the mitotic spindles. During metaphase, the kinetochore microtubules extending from each centrosome connect to the centromeres of the chromosomes. Next, during anaphase, the kinetochore microtubules pull the sister ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |