|
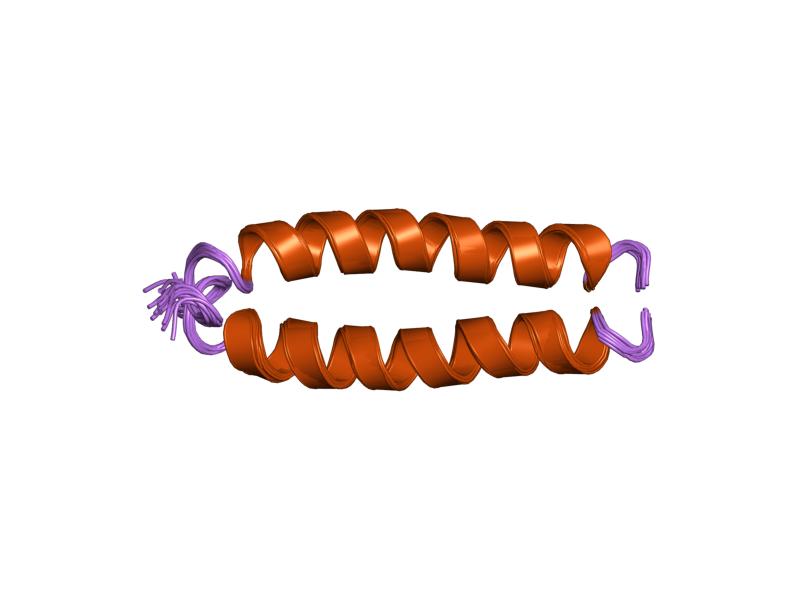
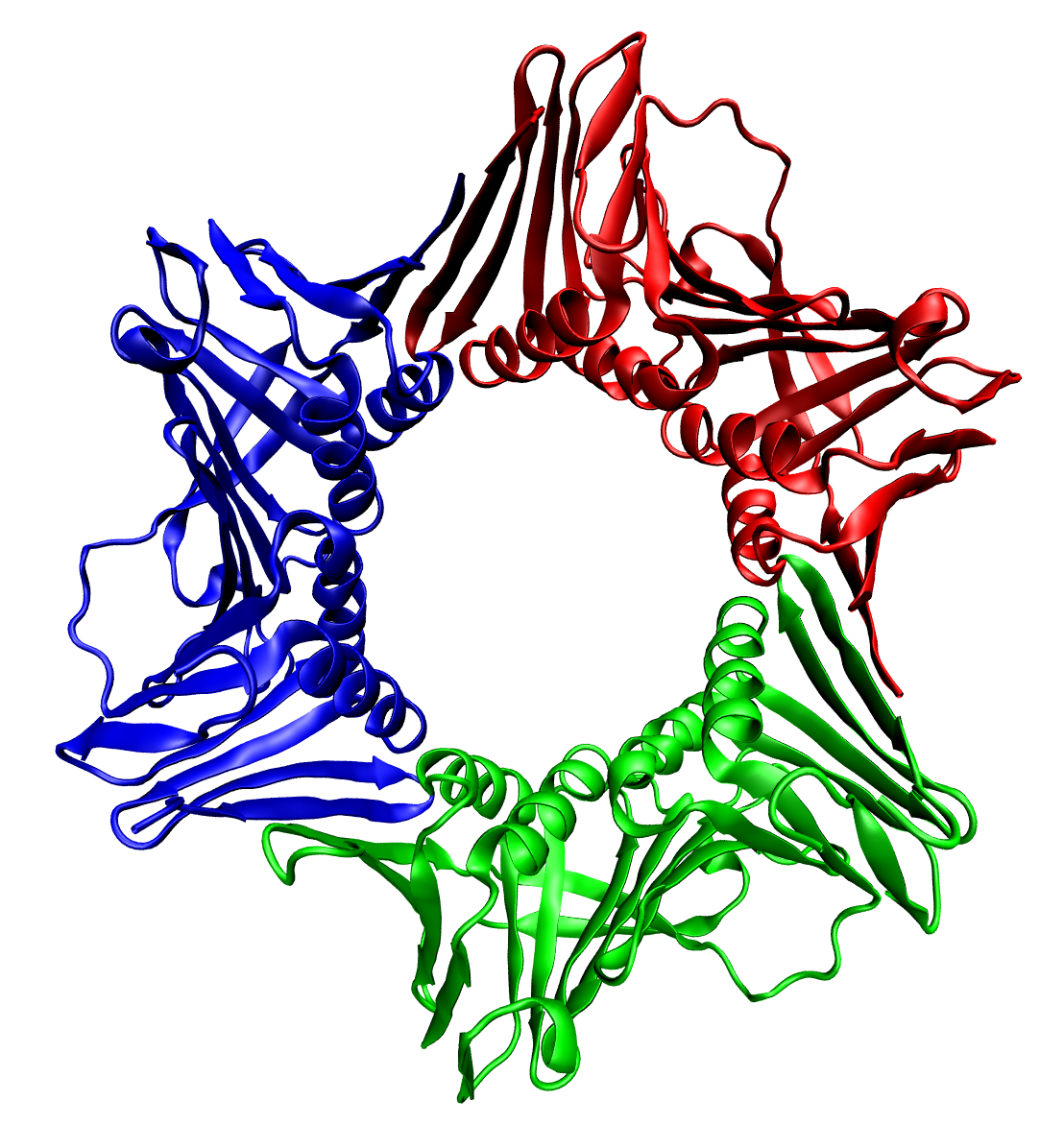
Cell–cell Fusogens
Cell–cell fusogens are glycoproteins that facilitate the fusion of cell to cell membranes. Cell–cell fusion is critical for the merging of gamete genomes and the development of organs in multicellular organisms. Cell-cell fusion occurs when both actin cytoskeleton and fusogenic proteins properly rearrange across the cell membrane. This process is led by actin-propelled membrane protrusions. Identifiers EFF-AFF are the identifiers for type 1 glycoproteins that makeup cell–cell fusogens. They were first identified when EFF-1 mutants were found to "block cell fusion in all epidermal and vulval epithelia" in the roundworm, ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. EFF-AFF is a family of type I membrane glycoproteins that act as cell–cell fusogens, named from ''Anchor cell fusion failure''. Because it was known that EFF-1 mutants successfully fused the anchor cell and (uterine seam) utse syncytium to produce a continuous uterine-vulval tube, where these connections failed, AFF-1 mutan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16-30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus (or occasionally nonclassically at the C-terminus or internally) of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles (the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi or endosomes), secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, the majority of type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide. Function (translocation) Signal peptides function to prompt a cell to translo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid Bilayer Fusion
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interbilayer Forces In Membrane Fusion
Membrane fusion is a key biophysical process that is essential for the functioning of life itself. It is defined as the event where two lipid bilayers approach each other and then merge to form a single continuous structure. In living beings, cells are made of an outer coat made of lipid bilayers; which then cause fusion to take place in events such as fertilization, embryogenesis and even infections by various types of bacteria and viruses. It is therefore an extremely important event to study. From an evolutionary angle, fusion is an extremely controlled phenomenon. Random fusion can result in severe problems to the normal functioning of the human body. Fusion of biological membranes is mediated by proteins. Regardless of the complexity of the system, fusion essentially occurs due to the interplay of various interfacial forces, namely hydration repulsion, hydrophobic attraction and van der Waals forces. Inter-bilayer forces Lipid bilayers are structures of lipid molecules consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric (kī-ˈmir-ik) proteins (literally, made of parts from different sources) are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes that originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this ''fusion gene'' results in a single or multiple polypeptides with functional properties derived from each of the original proteins. ''Recombinant fusion proteins'' are created artificially by recombinant DNA technology for use in biological research or therapeutics. '' Chimeric'' or ''chimera'' usually designate hybrid proteins made of polypeptides having different functions or physico-chemical patterns. ''Chimeric mutant proteins'' occur naturally when a complex mutation, such as a chromosomal translocation, tandem duplication, or retrotransposition creates a novel coding sequence containing parts of the coding sequences from two different genes. Naturally occurring fusion proteins are commonly found in cancer cells, where they may function as oncoproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Mechanism
A fusion mechanism is any mechanism by which cell fusion or virus–cell fusion takes place, as well as the machinery that facilitates these processes. Cell fusion is the formation of a hybrid cell from two separate cells. There are three major actions taken in both virus–cell fusion and cell–cell fusion: the dehydration of polar head groups, the promotion of a hemifusion stalk, and the opening and expansion of pores between fusing cells. Virus–cell fusions occur during infections of several viruses that are health concerns relevant today. Some of these include HIV, Ebola, and influenza. For example, HIV infects by fusing with the membranes of immune system cells. In order for HIV to fuse with a cell, it must be able to bind to the receptors CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4. Cell fusion also occurs in a multitude of mammalian cells including gametes and myoblasts. Viral mechanisms Fusogens Proteins that allow viral or cell membranes to overcome barriers to fusion are called fusogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramaticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryogenesis, embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cellular differentiation, cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Structure, Quaternary
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains (also referred to as subunits). Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple dimers to large homooligomers and complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other cofactors. Description and examples Many proteins are actually assemblies of multiple polypeptide chains. The quaternary structure refers to the number and arrangement of the protein subunits wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |