|
Carbon Nanotube Field-effect Transistor
A carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNTFET) is a field-effect transistor that utilizes a single carbon nanotube or an array of carbon nanotubes as the channel material instead of bulk silicon in the traditional MOSFET structure. First demonstrated in 1998, there have been major developments in CNTFETs since. Introduction and background According to Moore's law, the dimensions of individual devices in an integrated circuit have been decreased by a factor of approximately two every two years. This scaling down of devices has been the driving force in technological advances since the late 20th century. However, as noted by ITRS 2009 edition, further scaling down has faced serious limits related to fabrication technology and device performances as the critical dimension shrunk down to sub-22 nm range. The limits involve electron tunneling through short channels and thin insulator films, the associated leakage currents, passive power dissipation, short channel effects, and v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
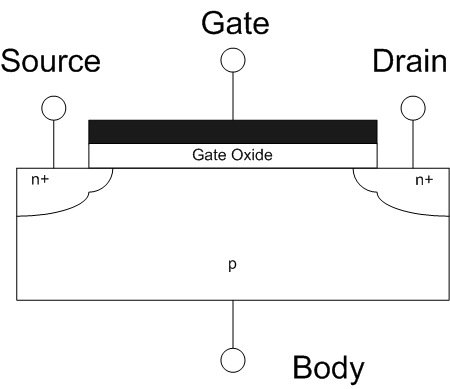
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cntfet
A carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNTFET) is a field-effect transistor that utilizes a single carbon nanotube or an array of carbon nanotubes as the channel material instead of bulk silicon in the traditional MOSFET structure. First demonstrated in 1998, there have been major developments in CNTFETs since. Introduction and background According to Moore's law, the dimensions of individual devices in an integrated circuit have been decreased by a factor of approximately two every two years. This scaling down of devices has been the driving force in technological advances since the late 20th century. However, as noted by ITRS 2009 edition, further scaling down has faced serious limits related to fabrication technology and device performances as the critical dimension shrunk down to sub-22 nm range. The limits involve electron tunneling through short channels and thin insulator films, the associated leakage currents, passive power dissipation, short channel effects, and v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Density
In electromagnetism, current density is the amount of charge per unit time that flows through a unit area of a chosen cross section. The current density vector is defined as a vector whose magnitude is the electric current per cross-sectional area at a given point in space, its direction being that of the motion of the positive charges at this point. In SI base units, the electric current density is measured in amperes per square metre. Definition Assume that ''A'' (SI unit: m2) is a small surface centred at a given point ''M'' and orthogonal to the motion of the charges at ''M''. If ''I'' (SI unit: A) is the electric current flowing through ''A'', then electric current density ''j'' at ''M'' is given by the limit: :j = \lim_ \frac = \left.\frac \_, with surface ''A'' remaining centered at ''M'' and orthogonal to the motion of the charges during the limit process. The current density vector j is the vector whose magnitude is the electric current density, and whose dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Mobility
In solid-state physics, the electron mobility characterises how quickly an electron can move through a metal or semiconductor when pulled by an electric field. There is an analogous quantity for holes, called hole mobility. The term carrier mobility refers in general to both electron and hole mobility. Electron and hole mobility are special cases of electrical mobility of charged particles in a fluid under an applied electric field. When an electric field ''E'' is applied across a piece of material, the electrons respond by moving with an average velocity called the drift velocity, v_d. Then the electron mobility ''μ'' is defined as v_d = \mu E. Electron mobility is almost always specified in units of cm2/( V⋅ s). This is different from the SI unit of mobility, m2/( V⋅ s). They are related by 1 m2/(V⋅s) = 104 cm2/(V⋅s). Conductivity is proportional to the product of mobility and carrier concentration. For example, the same conductivity could come from a small numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subthreshold Slope
The subthreshold slope is a feature of a MOSFET's current–voltage characteristic. In the subthreshold region, the drain current behaviour – though being controlled by the gate terminal – is similar to the exponentially decreasing current of a forward biased diode. Therefore a plot of drain current versus gate voltage with drain, source, and bulk voltages fixed will exhibit approximately log linear behaviour in this MOSFET operating regime. Its slope is the subthreshold slope. The subthreshold slope is also the reciprocal value of the subthreshold swing ''Ss-th'' which is usually given as:''Physics of Semiconductor Devices'', S. M. Sze. New York: Wiley, 3rd ed., with Kwok K. Ng, 2007, chapter 6.2.4, p. 315, . S_ = \ln(10) \left(1+\right) C_d = depletion layer In semiconductor physics, the depletion region, also called depletion layer, depletion zone, junction region, space charge region or space charge layer, is an insulating region within a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Voltage
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth or VGS(th), of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage (VGS) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important scaling factor to maintain power efficiency. When referring to a junction field-effect transistor (JFET), the threshold voltage is often called pinch-off voltage instead. This is somewhat confusing since ''pinch off'' applied to insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET) refers to the channel pinching that leads to current saturation behaviour under high source–drain bias, even though the current is never off. Unlike ''pinch off'', the term ''threshold voltage'' is unambiguous and refers to the same concept in any field-effect transistor. Basic principles In n-channel ''enhancement-mode'' devices, a conductive channel does not exist naturally within the transistor, and a positive gate-to-source voltage is necessary to create one su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion Layer (semiconductors)
In semiconductor physics, the depletion region, also called depletion layer, depletion zone, junction region, space charge region or space charge layer, is an insulating region within a conductive, doped semiconductor material where the mobile charge carriers have been diffused away, or have been forced away by an electric field. The only elements left in the depletion region are ionized donor or acceptor impurities. This region of uncovered positive and negative ions is called the depletion region due to the depletion of carriers in this region. The depletion region is so named because it is formed from a conducting region by removal of all free charge carriers, leaving none to carry a current. Understanding the depletion region is key to explaining modern semiconductor electronics: diodes, bipolar junction transistors, field-effect transistors, and variable capacitance diodes all rely on depletion region phenomena. Formation in a p–n junction A depletion region for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Planck Constant
The Planck constant, or Planck's constant, is a fundamental physical constant of foundational importance in quantum mechanics. The constant gives the relationship between the energy of a photon and its frequency, and by the mass-energy equivalence, the relationship between mass and frequency. Specifically, a photon's energy is equal to its frequency multiplied by the Planck constant. The constant is generally denoted by h. The reduced Planck constant, or Dirac constant, equal to the constant divided by 2 \pi, is denoted by \hbar. In metrology it is used, together with other constants, to define the kilogram, the SI unit of mass. The SI units are defined in such a way that, when the Planck constant is expressed in SI units, it has the exact value The constant was first postulated by Max Planck in 1900 as part of a solution to the ultraviolet catastrophe. At the end of the 19th century, accurate measurements of the spectrum of black body radiation existed, but the distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, and in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven " defining constants" that have been given exact definitions. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly . Roles of the Boltzmann constant Macroscopically, the ideal gas law states that, for an ideal gas, the product of pressure and volume is proportional to the product of amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Dirac Statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics (F–D statistics) is a type of quantum statistics that applies to the physics of a system consisting of many non-interacting, identical particles that obey the Pauli exclusion principle. A result is the Fermi–Dirac distribution of particles over energy states. It is named after Enrico Fermi and Paul Dirac, each of whom derived the distribution independently in 1926 (although Fermi derived it before Dirac). Fermi–Dirac statistics is a part of the field of statistical mechanics and uses the principles of quantum mechanics. F–D statistics applies to identical and indistinguishable particles with half-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, etc.), called fermions, in thermodynamic equilibrium. For the case of negligible interaction between particles, the system can be described in terms of single-particle energy states. A result is the F–D distribution of particles over these states where no two particles can occupy the same state, which has a considerable effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi–Dirac
Fermi–Dirac may refer to: * Fermi–Dirac statistics or Fermi–Dirac distribution * Fermi–Dirac integral (other) ** Complete Fermi–Dirac integral ** Incomplete Fermi–Dirac integral See also * Fermi (other) Enrico Fermi (1901–1954) was an Italian physicist who created the world's first nuclear reactor. Fermi or Enrico Fermi may also refer to: * Fermi (crater), a large lunar impact crater * Fermi (microarchitecture), a microarchitecture developed by ... * Dirac (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity towards ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |