|
Carbenium
A carbenium ion is a positive ion with the structure RR′R″C+, that is, a chemical species with a trivalent carbon that bears a +1 formal charge. In older literature the name carbonium ion was used for this class, but now it refers exclusively to another family of carbocations, the carbonium ions, where the charged carbon is pentavalent. The current definitions were proposed by the chemist George Andrew Olah in 1972, and are now widely accepted. Carbenium ions are generally highly reactive due to having an incomplete octet of electrons; however, certain carbenium ions, such as the tropylium ion, are relatively stable due to the positive charge being delocalised between the carbon atoms. Nomenclature Carbenium ions are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on whether the number of carbon atoms bonded to the ionized carbon is 1, 2, or 3. (Ions with zero carbons attached to the ionized carbon, such as methenium, , are usually included in the primary class) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbocation
A carbocation is an ion with a positively charged carbon atom. Among the simplest examples are the methenium , methanium and vinyl cations. Occasionally, carbocations that bear more than one positively charged carbon atom are also encountered (e.g., ethylene dication ). Until the early 1970s, all carbocations were called ''carbonium ions''. In the present-day definition given by the IUPAC, a carbocation is any even-electron cation with significant partial positive charge on a carbon atom. They are further classified in two main categories according to the coordination number of the charged carbon: three in the carbenium ions and five in the carbonium ions. This nomenclature was proposed by G. A. Olah. Carbonium ions, as originally defined by Olah, are characterized by a three-center two-electron delocalized bonding scheme and are essentially synonymous with so-called 'non-classical carbocations', which are carbocations that contain bridging C–C or C–H σ-bonds. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonium Ion
In chemistry, a carbonium ion is any cation that has a pentavalent carbon atom. The name carbonium may also be used for the simplest member of the class, properly called methanium (), where the five valences are filled with hydrogen atoms. The next simplest carbonium ions after methanium have two carbon atoms. Ethynium, or protonated acetylene , and ethenium are usually classified in other families. The ethanium ion has been studied as an extremely rarefied gas by infrared spectroscopy. The isomers of octonium (protonated octane, ) have been studied. The carbonium ion has a planar geometry. In older literature, the name "carbonium ion" was used for what is today called carbenium. The current definitions were proposed by the chemist George Andrew Olah in 1972 and are now widely accepted. A stable carbonium ion is the complex pentakis(triphenylphosphinegold(I))methanium , produced by Schmidbauer and others. Preparation Carbonium ions can be obtained by treating alkanes with v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Cation
In organic chemistry, methenium (also called methylium, carbenium, methyl cation, or protonated methylene) is a cation with the formula . It can be viewed as a methylene radical (:) with an added proton (), or as a methyl radical (•) with one electron removed. It is a carbocation and an enium ion, making it the simplest of the carbenium ions. Structure Experiments and calculations generally agree that the methenium ion is planar, with threefold symmetry. The carbon atom is a prototypical (and exact) example of sp2 hybridization. Preparation and reactions For mass spectrometry studies at low pressure, methenium can be obtained by ultraviolet photoionization of methyl radical, or by collisions of monatomic cations such as and with neutral methane. In such conditions, it will react with acetonitrile to form the ion . Upon capture of a low-energy electron (less than ), it will spontaneously dissociate. It is seldom encountered as an intermediate in the condensed phase. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methenium
In organic chemistry, methenium (also called methylium, carbenium, methyl cation, or protonated methylene) is a cation with the formula . It can be viewed as a methylene radical (:) with an added proton (), or as a methyl radical (•) with one electron removed. It is a carbocation and an enium ion, making it the simplest of the carbenium ions. Structure Experiments and calculations generally agree that the methenium ion is planar, with threefold symmetry. The carbon atom is a prototypical (and exact) example of sp2 hybridization. Preparation and reactions For mass spectrometry studies at low pressure, methenium can be obtained by ultraviolet photoionization of methyl radical, or by collisions of monatomic cations such as and with neutral methane. In such conditions, it will react with acetonitrile to form the ion . Upon capture of a low-energy electron (less than ), it will spontaneously dissociate. It is seldom encountered as an intermediate in the condensed phase. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzyl
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group. Nomenclature In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substituent, for example benzyl chloride or benzyl benzoate. Benzyl is not to be confused with phenyl with the formula . The term benzylic is used to describe the position of the first carbon bonded to a benzene or other aromatic ring. For example, is referred to as a "benzylic" carbocation. The benzyl free radical has the formula . The benzyl cation or phenylcarbenium ion is the carbocation with formula ; the benzyl anion or phenylmethanide ion is the carbanion with the formula . None of these species can be formed in significant amounts in the solution phase under normal conditions, but they are useful referents for discussion of reaction mechanisms and may exist as reactive intermediates. Abbreviations The abbreviation "Bn" denotes benzyl. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
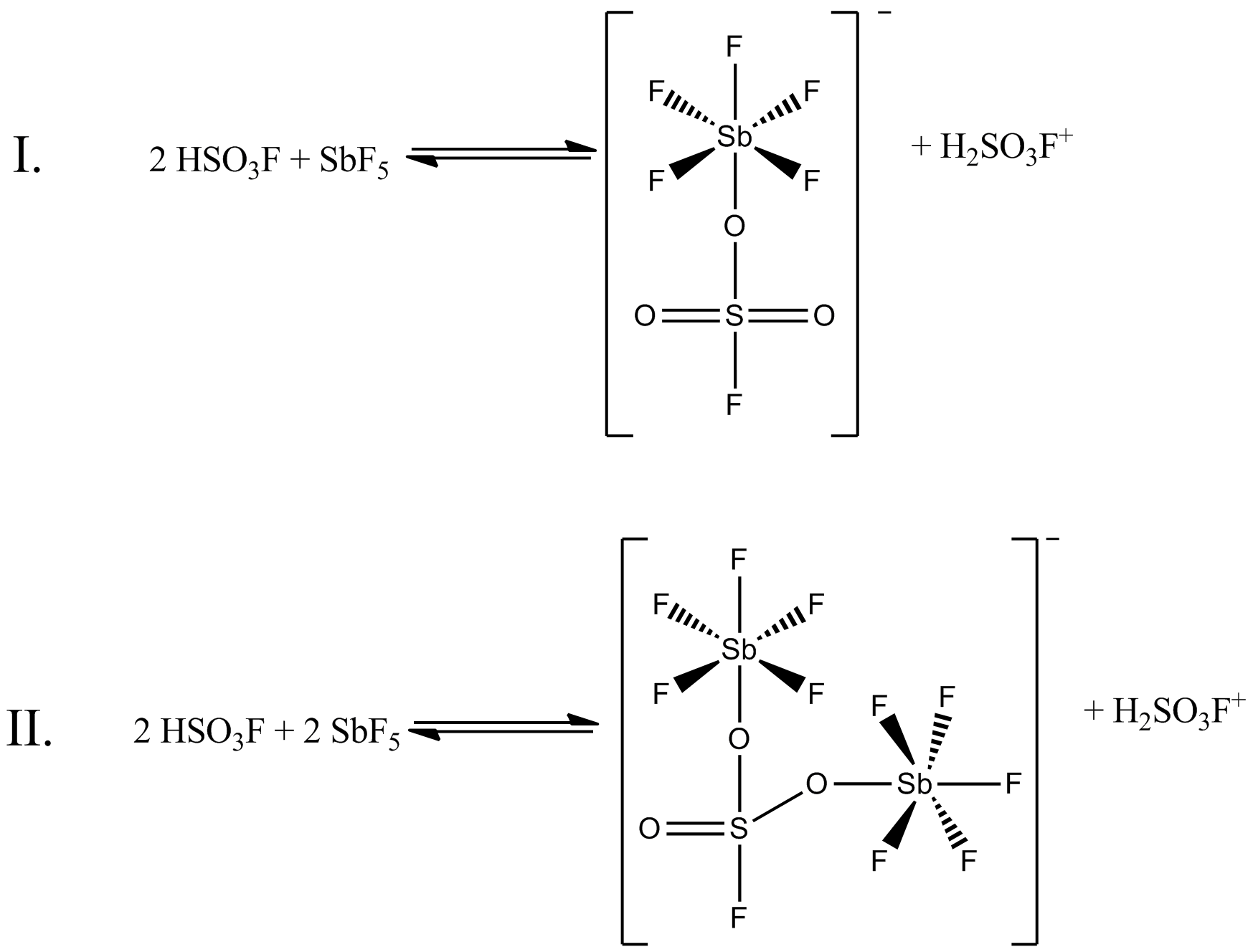
Magic Acid
Magic acid (FSO3H·SbF5) is a superacid consisting of a mixture, most commonly in a 1:1 molar ratio, of fluorosulfuric acid (HSO3F) and antimony pentafluoride (SbF5). This conjugate Brønsted–Lewis superacid system was developed in the 1960s by the George Olah lab at Case Western Reserve University, and has been used to stabilize carbocations and hypercoordinated carbonium ions in liquid media. Magic acid and other superacids are also used to catalyze isomerization of saturated hydrocarbons, and have been shown to protonate even weak bases, including methane, xenon, halogens, and molecular hydrogen. History The term "superacid" was first used in 1927 when James Bryant Conant found that perchloric acid could protonate ketones and aldehydes to form salts in nonaqueous solution. The term itself was coined by R. J. Gillespie later, after Conant combined sulfuric acid with fluorosulfuric acid, and found the solution to be several million times more acidic than sulfuric acid alone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorosulfuric Acid
Fluorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurofluoridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula HSO3F. It is one of the strongest acids commercially available. It is a tetrahedral molecule and is closely related to sulfuric acid, H2SO4, substituting a fluorine atom for one of the hydroxyl groups. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples are often yellow.Erhardt Tabel, Eberhard Zirngiebl, Joachim Maas "Fluorosulfuric Acid" in "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Chemical properties Fluorosulfuric acid is a free-flowing colorless liquid. It is soluble in polar organic solvents (e.g. nitrobenzene, acetic acid, and ethyl acetate), but poorly soluble in nonpolar solvents such as alkanes. Reflecting its strong acidity, it dissolves almost all organic compounds that are even weak proton acceptors. HSO3F hydrolyzes slowly to hydrogen fluoride (HF) and sulfuric acid. The related triflic acid Triflic acid, the short name for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Pentafluoride
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb F5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a valuable Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed when mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in a 2:1 ratio. It is notable for its Lewis acidity and its ability to react with almost all known compounds. Preparation Antimony pentafluoride is prepared by the reaction of antimony pentachloride with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride:Sabina C. Grund, Kunibert Hanusch, Hans J. Breunig, Hans Uwe Wolf "Antimony and Antimony Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. :SbCl5 + 5 HF → SbF5 + 5 HCl It can also be prepared from antimony trifluoride and fluorine. Structure and chemical reactions In the gas phase, SbF5 adopts a trigonal bipyramidal structure of D3h point group symmetry (see picture). The material adopts a more complicated structure in the liquid and solid states. The liquid contains polymers wherein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance structures'' or ''canonical structures'') into a resonance hybrid (or ''hybrid structure'') in valence bond theory. It has particular value for analyzing delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis structure. Overview Under the framework of valence bond theory, resonance is an extension of the idea that the bonding in a chemical species can be described by a Lewis structure. For many chemical species, a single Lewis structure, consisting of atoms obeying the octet rule, possibly bearing formal charges, and connected by bonds of positive integer order, is sufficient for describing the chemical bonding and rationalizing experimentally determined molecular properties like bond lengths, angles, and dipole moment. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. For inorganic chemists, hydrides refer to compounds and ions in which hydrogen is covalently attached to a less electronegative element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Pm, Os, Ir, Rn, Fr, and Ra. Exotic molecules such as positronium hydride have also been made. Bonds Bonds between hydrogen and the other elements range from highly to somewhat covalent. Some hydrides, e.g. boron hydrides, do not conform to classical electron-counting rules and the bonding is described in terms of multi-centered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula . The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (), where ''n'' = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane () or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl) octane, an isomer of tetradecane (). The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) defines alkanes as "acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula , and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms". However, some sources use the term to denote ''any'' saturated hydrocarbon, including those that are either monocyclic (i.e. the cycloalkanes) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Constant
In chemical kinetics a reaction rate constant or reaction rate coefficient, ''k'', quantifies the rate and direction of a chemical reaction. For a reaction between reactants A and B to form product C the reaction rate is often found to have the form: r = k(T) mathrmm mathrm Here ''k''(''T'') is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature, and and are the molar concentrations of substances A and B in moles per unit volume of solution, assuming the reaction is taking place throughout the volume of the solution. (For a reaction taking place at a boundary, one would use moles of A or B per unit area instead.) The exponents ''m'' and ''n'' are called partial orders of reaction and are ''not'' generally equal to the stoichiometric coefficients ''a'' and ''b''. Instead they depend on the reaction mechanism and can be determined experimentally. Elementary steps For an elementary step, there ''is'' a relationship between stoichiometry and rate law, as determined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |