|
Carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for the treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins, carbapenems are members of the beta lactam class of antibiotics, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams. Carbapenem antibiotics were originally developed at Merck & Co. from the carbapenem thienamycin, a naturally derived product of '' Streptomyces cattleya''. Concern has arisen in recent years over increasing rates of resistance to carbapenems, as there are few therapeutic options for treating i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) or carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) are Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to the carbapenem class of antibiotics, considered the drugs of last resort for such infections. They are resistant because they produce an enzyme called a carbapenemase that disables the drug molecule. The resistance can vary from moderate to severe. Enterobacteriaceae are common commensals and infectious agents. Experts fear CRE as the new "superbug". The bacteria can kill up to half of patients who get bloodstream infections. Tom Frieden, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has referred to CRE as "nightmare bacteria". Examples of enzymes found in certain types of CRE are KPC (''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' carbapenemase) and NDM (New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase). KPC and NDM are enzymes that break down carbapenems and make them ineffective. Both of these enzymes, as well as the enzyme VIM (Verona Integron-Mediated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
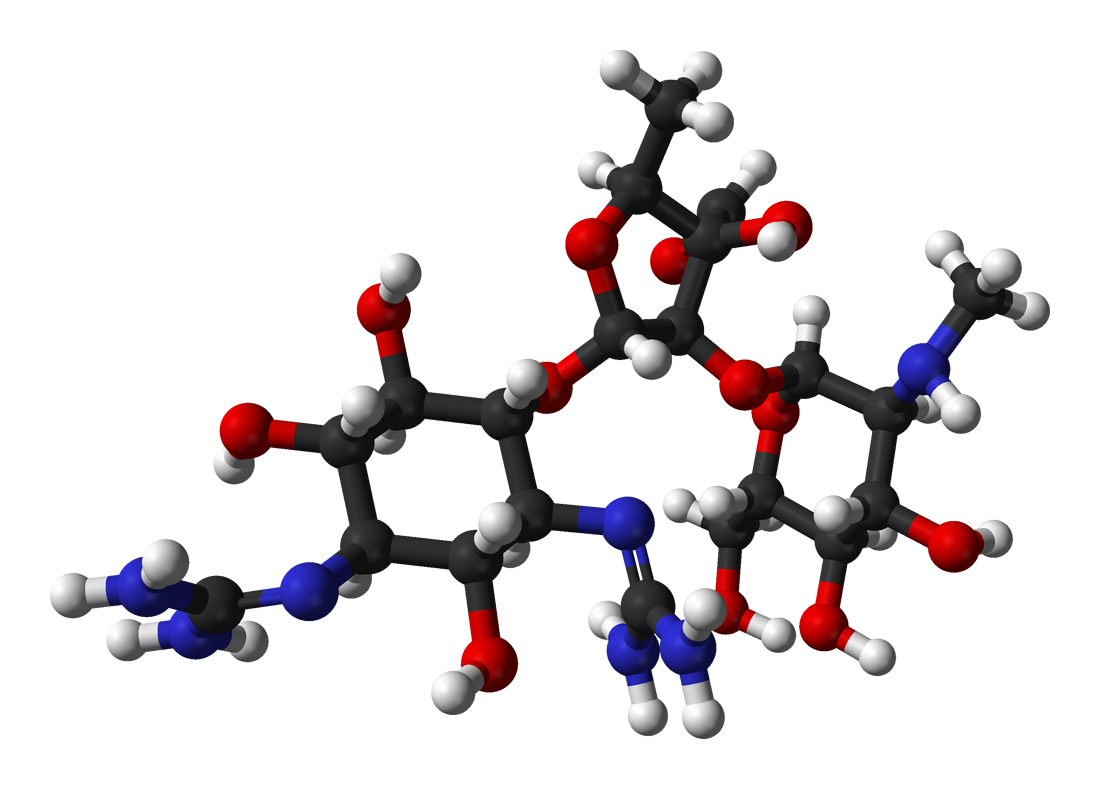
Carbapenems Structure
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for the treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multiple drug resistance, multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins, carbapenems are members of the beta lactam class of antibiotics, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antimicrobial resistance, antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams. Carbapenem antibiotics were originally developed at Merck & Co. from the carbapenem thienamycin, a naturally derived product of ''Streptomyces cattleya''. Concern has arisen in recent years over increasing rates of resistance to carbapenems, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Spectrum Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases, (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to target a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a ''Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
''Klebsiella pneumoniae'' is a Gram-negative, non-motile, encapsulated, lactose-fermenting, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It appears as a mucoid lactose fermenter on MacConkey agar. Although found in the normal flora of the mouth, skin, and intestines, it can cause destructive changes to human and animal lungs if aspirated, specifically to the alveoli resulting in bloody, brownish or yellow colored jelly like sputum. In the clinical setting, it is the most significant member of the genus ''Klebsiella'' of the Enterobacteriaceae. ''K. oxytoca'' and ''K. rhinoscleromatis'' have also been demonstrated in human clinical specimens. In recent years, ''Klebsiella'' species have become important pathogens in nosocomial infections. It naturally occurs in the soil, and about 30% of strains can fix nitrogen in anaerobic conditions. As a free-living diazotroph, its nitrogen-fixation system has been much-studied, and is of agricultural interest, as ''K. pneumoniae'' has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thienamycin
Thienamycin (also known as thienpenem) is one of the most potent naturally produced antibiotics known thus far, discovered in '' Streptomyces cattleya'' in 1976. Thienamycin has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes. Thienamycin is a zwitterion at pH 7. History In 1976, fermentation broths obtained from the soil bacterium '' Streptomyces cattleya'' were found to be active in a screen for inhibitors of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Initial attempts to isolate the active compound proved difficult due to its chemical instability. After many attempts and extensive purification, the material was finally isolated in >90% purity, allowing for the structural elucidation of thienamycin in 1979 (Figure 1). Thienamycin was the first among the naturally occurring class of carbapenem antibiotics to be discovered and isolated. Carbapenems are similar in structure to their antibiotic “cousins” the penic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imipenem
Imipenem (trade name Primaxin among others) is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic discovered by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus play a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics. Imipenem was patented in 1975 and approved for medical use in 1985. It was discovered via a lengthy trial-and-error search for a more stable version of the natural product thienamycin, which is produced by the bacterium '' Streptomyces cattleya''. Thienamycin has antibacterial activity, but is unstable in aqueous solution, so impractical to administer to patients. Imipenem has a broad spectrum of activity against aerobic and anaerobic, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is particularly important for its activity against ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and the ''Enterococc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ertapenem
Ertapenem, sold under the brand name Invanz, is a carbapenem antibiotic medication used for the treatment of infections of the abdomen, the lungs, the upper part of the female reproductive system, and the diabetic foot. The most common side effects include diarrhoea, nausea (feeling sick), headache, and problems around the area where the medicine is infused. It can significantly reduce the concentrations of valproic acid, an anti-seizure medication, in the blood to the point where it loses its effectiveness. Ertapenem was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2001, and in the European Union in April 2002. It is marketed by Merck. Medical uses Ertapenem is indicated for the treatment of intra-abdominal infections, community-acquired pneumonia, pelvic infections, and diabetic foot infections, with bacteria that are susceptible to this drug, or expected to be so. It can also be used to prevent infections after colorectal surgery. In the United States it is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meropenem
Meropenem, sold under the brand name Merrem among others, is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Some of these include meningitis, intra-abdominal infection, pneumonia, sepsis, and anthrax. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, headache, rash, and pain at the site of injection. Serious side effects include ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection, seizures, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Those who are allergic to other β-lactam antibiotics are more likely to be allergic to meropenem as well. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. It is in the carbapenem family of medications. Meropenem usually results in bacterial death through blocking their ability to make a cell wall. It is more resistant to breakdown by β-lactamase producing bacteria. Meropenem was patented in 1983. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillins
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doripenem
Doripenem (Doribax, Finibax) is an antibiotic drug in the carbapenem class. It is a beta-lactam antibiotic drug able to kill ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. Doripenem can be used for bacterial infections such as: complex abdominal infections, pneumonia within the setting of a hospital, and complicated infections of the urinary tract including kidney infections with sepsis. The greater stability of doripenem in aqueous solution compared to earlier members of the carbapenem class allows it to be administered as an infusion over 4 hours or more, which may be advantageous in the treatment of certain difficult-to-treat infections. It may present a lower risk of inducing seizures than other carbapenems. Chemistry and pharmacology Doripenem is a beta-lactam antibiotic agent belonging to the carbapenem group, with a broad spectrum of bacterial sensitivity including both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In vivo, doripenem inhibits the synthesis of cell walls by attaching itself to pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major subset o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin-binding Proteins
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are a group of proteins that are characterized by their affinity for and binding of penicillin. They are a normal constituent of many bacteria; the name just reflects the way by which the protein was discovered. All β-lactam antibiotics (except for tabtoxinine-β-lactam, which inhibits glutamine synthetase) bind to PBPs, which are essential for bacterial cell wall synthesis. PBPs are members of a subgroup of enzymes called transpeptidases. Specifically, PBPs are DD-transpeptidases. Diversity There are a large number of PBPs, usually several in each organism, and they are found as both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic proteins. For example, Spratt (1977) reports that six different PBPs are routinely detected in all strains of ''E. coli'' ranging in molecular weight from 40,000 to 91,000. The different PBPs occur in different numbers per cell and have varied affinities for penicillin. The PBPs are usually broadly classified into high-molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |