|
Cantellation
In geometry, a cantellation is a 2nd-order truncation in any dimension that bevels a regular polytope at its edges and at its vertices, creating a new facet in place of each edge and of each vertex. Cantellation also applies to regular tilings and honeycombs. Cantellating a polyhedron is also rectifying its rectification. Cantellation (for polyhedra and tilings) is also called ''expansion'' by Alicia Boole Stott: it corresponds to moving the faces of the regular form away from the center, and filling in a new face in the gap for each opened edge and for each opened vertex. Notation A cantellated polytope is represented by an extended Schläfli symbol ''t''0,2 or ''r''\beginp\\q\\...\end or ''rr''. For polyhedra, a cantellation offers a direct sequence from a regular polyhedron to its dual. Example: cantellation sequence between cube and octahedron: Example: a cuboctahedron is a cantellated tetrahedron. For higher-dimensional polytopes, a cantellation offers a direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansion (geometry)
In geometry, expansion is a polytope operation where facets are separated and moved radially apart, and new facets are formed at separated elements ( vertices, edges, etc.). Equivalently this operation can be imagined by keeping facets in the same position but reducing their size. The expansion of a regular polytope creates a uniform polytope, but the operation can be applied to any convex polytope, as demonstrated for polyhedra in Conway polyhedron notation (which represents expansion with the letter ). For polyhedra, an expanded polyhedron has all the faces of the original polyhedron, all the faces of the dual polyhedron, and new square faces in place of the original edges. Expansion of regular polytopes According to Coxeter, this multidimensional term was defined by Alicia Boole StottCoxeter, ''Regular Polytopes'' (1973), p. 123. p.210 for creating new polytopes, specifically starting from regular polytopes to construct new uniform polytopes. The ''expansion'' operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncation (geometry)
In geometry, a truncation is an operation in any dimension that cuts polytope vertices, creating a new Facet (geometry), facet in place of each vertex. The term originates from Kepler's names for the Archimedean solids. Uniform truncation In general any polyhedron (or polytope) can also be truncated with a degree of freedom as to how deep the cut is, as shown in Conway polyhedron notation truncation operation. A special kind of truncation, usually implied, is a uniform truncation, a truncation operator applied to a regular polyhedron (or regular polytope) which creates a resulting uniform polyhedron (uniform polytope) with equal edge lengths. There are no degrees of freedom, and it represents a fixed geometric, just like the regular polyhedra. In general all single ringed uniform polytopes have a uniform truncation. For example, the icosidodecahedron, represented as Schläfli symbols r or \begin 5 \\ 3 \end, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram or has a uniform truncation, the truncate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
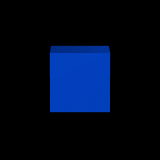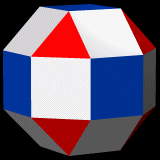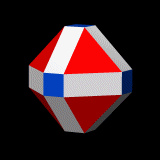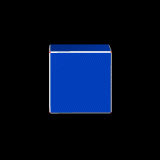
Cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it is a quasiregular polyhedron, i.e. an Archimedean solid that is not only vertex-transitive but also edge-transitive. It is radially equilateral. Its dual polyhedron is the rhombic dodecahedron. The cuboctahedron was probably known to Plato: Heron's ''Definitiones'' quotes Archimedes as saying that Plato knew of a solid made of 8 triangles and 6 squares. Synonyms *''Vector Equilibrium'' (Buckminster Fuller) because its center-to-vertex radius equals its edge length (it has radial equilateral symmetry). Fuller also called a cuboctahedron built of rigid struts and flexible vertices a ''jitterbug''; this object can be progressively transformed into an icosahedron, octahedron, and tetrahedron by folding along the diagonals of its square sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectification (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry, rectification, also known as critical truncation or complete-truncation, is the process of truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its Edge (geometry), edges, and cutting off its Vertex (geometry), vertices at those points. The resulting polytope will be bounded by vertex figure facets and the rectified facets of the original polytope. A rectification operator is sometimes denoted by the letter with a Schläfli symbol. For example, is the rectified cube, also called a cuboctahedron, and also represented as \begin 4 \\ 3 \end. And a rectified cuboctahedron is a rhombicuboctahedron, and also represented as r\begin 4 \\ 3 \end. Conway polyhedron notation uses for ambo as this operator. In graph theory this operation creates a medial graph. The rectification of any regular self-dual polyhedron or tiling will result in another regular polyhedron or tiling with a tiling order of 4, for example the tetrahedron becoming an octahedron As a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
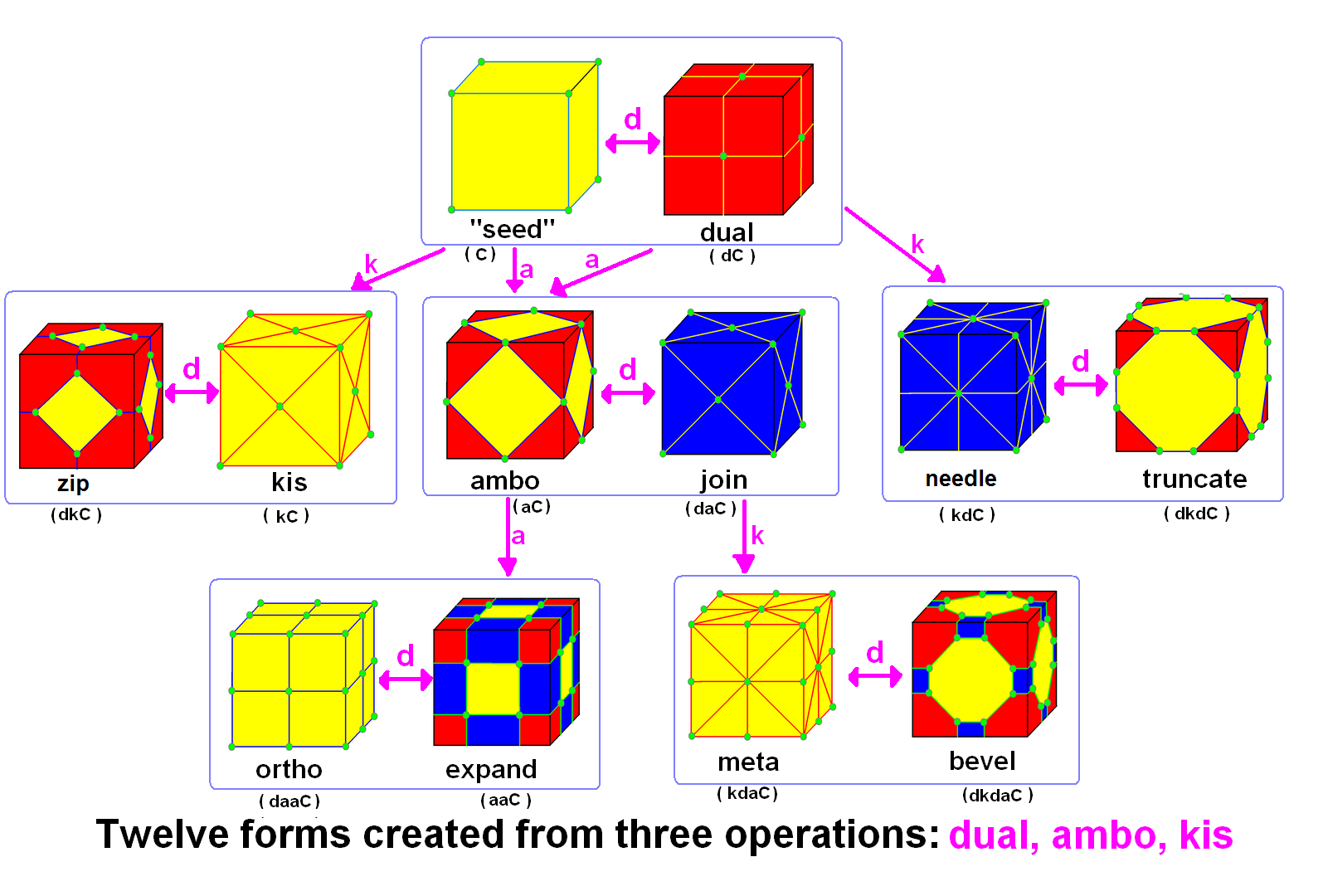
Conway Polyhedron Notation
In geometry, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations. Conway and Hart extended the idea of using operators, like truncation as defined by Kepler, to build related polyhedra of the same symmetry. For example, represents a truncated cube, and , parsed as , is ( topologically) a truncated cuboctahedron. The simplest operator dual swaps vertex and face elements; e.g., a dual cube is an octahedron: . Applied in a series, these operators allow many higher order polyhedra to be generated. Conway defined the operators (ambo), (bevel), ( dual), (expand), (gyro), (join), (kis), (meta), (ortho), (snub), and (truncate), while Hart added ( reflect) and (propellor). Later implementations named further operators, sometimes referred to as "extended" operators. Conway's basic operations are sufficient to generate the Archimedean and Catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectification (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry, rectification, also known as critical truncation or complete-truncation, is the process of truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its Edge (geometry), edges, and cutting off its Vertex (geometry), vertices at those points. The resulting polytope will be bounded by vertex figure facets and the rectified facets of the original polytope. A rectification operator is sometimes denoted by the letter with a Schläfli symbol. For example, is the rectified cube, also called a cuboctahedron, and also represented as \begin 4 \\ 3 \end. And a rectified cuboctahedron is a rhombicuboctahedron, and also represented as r\begin 4 \\ 3 \end. Conway polyhedron notation uses for ambo as this operator. In graph theory this operation creates a medial graph. The rectification of any regular self-dual polyhedron or tiling will result in another regular polyhedron or tiling with a tiling order of 4, for example the tetrahedron becoming an octahedron As a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra and the only one that has fewer than 5 faces. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Rhombicuboctahedron
In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square (geometry), square, and twelve rectangle, rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at each one. If all the rectangles are themselves square (equivalently, all the edges are the same length, ensuring the triangles are equilateral triangle, equilateral), it is an Archimedean solid. The polyhedron has octahedral symmetry, like the Cube (geometry), cube and octahedron. Its dual polyhedron, dual is called the deltoidal icositetrahedron or trapezoidal icositetrahedron, although its faces are not really true trapezoids. Names Johannes Kepler in Harmonices Mundi (1618) named this polyhedron a ''rhombicuboctahedron'', being short for ''truncated cuboctahedral rhombus'', with ''cuboctahedral rhombus'' being his name for a rhombic dodecahedron. There are different truncations of a rhombic dodecahedron int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross. The cube is the only regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. The cube is also a square parallelepiped, an equilateral cuboid and a right rhombohedron a 3-zonohedron. It is a regular square prism in three orientations, and a trigonal trapezohedron in four orientations. The cube is dual to the octahedron. It has cubical or octahedral symmetry. The cube is the only convex polyhedron whose faces are all squares. Orthogonal projections The ''cube'' has four special orthogonal projections, centered, on a vertex, edges, face and normal to its vertex figure. The first and third correspond to the A2 and B2 Coxeter planes. Spherical tiling The cube can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube Cantellation Sequence
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross. The cube is the only regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. The cube is also a square parallelepiped, an equilateral cuboid and a right rhombohedron a 3-zonohedron. It is a regular square prism in three orientations, and a trigonal trapezohedron in four orientations. The cube is dual to the octahedron. It has cubical or octahedral symmetry. The cube is the only convex polyhedron whose faces are all squares. Orthogonal projections The ''cube'' has four special orthogonal projections, centered, on a vertex, edges, face and normal to its vertex figure. The first and third correspond to the A2 and B2 Coxeter planes. Spherical tiling The cube can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes and . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the (convex, non- stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, and is represented by its Schläfli symbol , con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
