|
Cuthill Court
A comhdhail or couthal was a popular court in medieval Scotland. The word derives from Old Gaelic ''comdal'', "tryst" or "assembly".McNeill and MacQueen, ''Atlas of Scottish History'', p. 191 Distinct from courts of the king, mormaers and senior barons, such courts were organized at a lower level of society, by peasant communities for themselves. It was probably similar to the English hundred or tithing court. Although most of the details of how it functioned are lost, enough evidence of it exists to be sure of its importance. In 1329, Geoffrey, abbot of Arbroath, made an agreement with one of its senior tenants, Fergus mac Donnchaidh (Fergus son of Duncan).Barrow, ''Scotland and its Neighbours'', p. 220 Abbot Geoffrey leased the land of Tulloes and Craichie (near Dunnichen) to Fergus, allowing him to introduce his own men. The agreement specified the abbot's legal rights, but allowed that "the aforesaid Fergus and his heir ... have the court which is called ''couthal'' for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Court
Popularity or social status is the quality of being well liked, admired or well known to a particular group. Popular may also refer to: In sociology * Popular culture * Popular fiction * Popular music * Popular science * Populace, the total population of a certain place ** Populism, a political philosophy, based on the idea that the common people are being exploited. * Informal usage or custom, as in Common name, popular names, as opposed to formal or scientific nomenclature Companies * Popular, Inc., also known as ''Banco Popular'', a financial services company * Popular Holdings, a Singapore-based educational book company * The Popular (department store), a chain of department stores in El Paso, Texas, from 1902 to 1995 * ''The Popular Magazine'', an American literary magazine that ran for 612 issues from November 1903 to October 1931 Media Music *Popular (Darren Hayes song), "Popular" (Darren Hayes song) (2004), on the album ''The Tension and the Spark'' *Popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Barrow
Geoffrey Wallis Steuart Barrow (28 November 1924 – 14 December 2013) was a Scottish historian and academic. The son of Charles Embleton Barrow and Marjorie née Stuart, Geoffrey Barrow was born on 28 November 1924, at Headingley near Leeds. He attended St Edward's School, Oxford, and Inverness Royal Academy, moving on to the University of St Andrews and Pembroke College, Oxford. While still a student at the University of St Andrews he joined the Royal Navy. After basic training he was sent to the Royal Navy Signals School near Petersfield in Hampshire, but he was then offered the chance to go on a Japanese course. He passed an interview in the Admiralty and, as a sub-lieutenant in the Royal Naval Volunteer Reserve, joined the seventh course at the secret Bedford Japanese School run by Captain Oswald Tuck in March 1944 for a six-month course. After completing the course he was sent to the Naval Section at the Government Code and Cypher School, Bletchley Park. He was later se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutherland
Sutherland ( gd, Cataibh) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in the Highlands of Scotland. Its county town is Dornoch. Sutherland borders Caithness and Moray Firth to the east, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire (later combined into Ross and Cromarty) to the south and the Atlantic to the north and west. Like its southern neighbour Ross-shire, Sutherland has some of the most dramatic scenery in Europe, especially on its western fringe where the mountains meet the sea. These include high sea cliffs, and very old mountains composed of Precambrian and Cambrian rocks. The name ''Sutherland'' dates from the era of Norwegian Viking rule and settlement over much of the Highlands and Islands, under the rule of the jarl of Orkney. Although it contains some of the northernmost land in the island of Great Britain, it was called ' ("southern land") from the standpoint of Orkney and Caithness. In Gaelic, the area is referred to according to its traditional areas: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peeblesshire
Peeblesshire ( gd, Siorrachd nam Pùballan), the County of Peebles or Tweeddale is a historic county of Scotland. Its county town is Peebles, and it borders Midlothian to the north, Selkirkshire to the east, Dumfriesshire to the south, and Lanarkshire to the west. History The origins of Peeblesshire are obscure, but it became a shire sometime around the twelfth century, covering part of the historic district or province of Tweeddale. The southern part of Tweeddale became the sheriffdom of Selkirkshire, also known as Ettrick Forest, whilst the northern part of Tweeddale was initially divided into two sheriffdoms, based at Peebles and Traquair, before those two were united as the single shire of Peebles, or Peeblesshire, around 1304. From then on the shires gradually became the more important areas for administration; the old provinces were not abolished as such, but their importance diminished. Peeblesshire County Council was created in 1890 under the Local Government (Scotlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey
, nativename_a = , nativename_r = , logo = Ordnance Survey 2015 Logo.svg , logo_width = 240px , logo_caption = , seal = , seal_width = , seal_caption = , picture = , picture_width = , picture_caption = , formed = , preceding1 = , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = Great BritainThe Ordnance Survey deals only with maps of Great Britain, and, to an extent, the Isle of Man, but not Northern Ireland, which has its own, separate government agency, the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland. , headquarters = Southampton, England, UK , region_code = GB , coordinates = , employees = 1,244 , budget = , minister1_name = , minister1_pfo = , chief1_name = Steve Blair , chief1_position = CEO , agency_type = , parent_agency = , child1_agency = , keydocument1 = , website = , footnotes = , map = , map_width = , map_caption = Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavin Douglas
Gavin Douglas (c. 1474 – September 1522) was a Scottish bishop, makar and translator. Although he had an important political career, he is chiefly remembered for his poetry. His main pioneering achievement was the ''Eneados'', a full and faithful vernacular translation of the ''Aeneid'' of Virgil into Scots, and the first successful example of its kind in any Anglic language. Other extant poetry of his includes ''Palice of Honour'', and possibly ''King Hart''. Life and career Early life Gavin (or Gawin, Gawane, Gawain) Douglas was born c. 1474–76, at Tantallon Castle, East Lothian, the third son of Archibald, 5th Earl of Angus by his second wife Elizabeth Boyd. A Vatican register records that Gavin Douglas was 13 in 1489, suggesting he was born in 1476. An application had been lodged to award Gavin the right to hold a Church canonry or prebend and enjoy its income. Another appeal to Rome concerning church appointments made in February 1495 states his age as 20. He was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Of Wyntoun
Andrew Wyntoun, known as Andrew of Wyntoun (), was a Scottish poet, a canon and prior of Loch Leven on St Serf's Inch and, later, a canon of St. Andrews. Andrew Wyntoun is most famous for his completion of an eight-syllabled metre entitled, ''Orygynale Cronykil of Scotland'', which contains an early mention of ''Robin Hood''; it is also cited by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' as the earliest work in English to use the word "Catholic": pelling modernised"He was a constant Catholic;/All Lollard he hated and heretic." Wyntoun wrote the 'Chronicle' at the request of his patron, Sir John of Wemyss, whose representative, Mr. Erskine Wemyss of Wemyss Castle, Fife, possessed the oldest extant manuscript of the work. The subject of the 'Chronicle' is the history of Scotland from the mythical period to the death of Robert Stewart, Duke of Albany in 1420. The nine original manuscripts of the ''Orygynale Cronykil of Scotland'' still subsist today and are preserved within various fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and has a population estimate of for the city of Aberdeen, and for the local council area making it the United Kingdom's 39th most populous built-up area. The city is northeast of Edinburgh and north of London, and is the northernmost major city in the United Kingdom. Aberdeen has a long, sandy coastline and features an oceanic climate, with cool summers and mild, rainy winters. During the mid-18th to mid-20th centuries, Aberdeen's buildings incorporated locally quarried grey granite, which may sparkle like silver because of its high mica content. Since the discovery of North Sea oil in 1969, Aberdeen has been known as the offshore oil capital of Europe. Based upon the discovery of prehistoric villages around the mouths of the rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess (title)
Burgess was a British title used in the medieval and early modern period to designate someone of the Burgher class. It originally meant a freeman of a borough or burgh but later coming to mean an official of a municipality or a representative in the House of Commons. Usage in England In England, burgess meant an elected or unelected official of a municipality, or the representative of a borough in the English House of Commons. This usage of "burgess" has since disappeared. Burgesses as freemen had the sole right to vote in municipal or parliamentary elections. However, these political privileges in Britain were removed by the Reform Act in 1832. Usage in Scotland Burgesses were originally freeman inhabitants of a city where they owned land and who contributed to the running of the town and its taxation. The title of ''burgess'' was later restricted to merchants and craftsmen, so that only burgesses could enjoy the privileges of trading or practising a craft in the city throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kincardine, Aberdeenshire
Kincardine was a burgh in Scotland, near the present-day village of Fettercairn. It served as the first county town of Kincardineshire. The settlement gradually developed around Kincardine Castle. The origin of the castle is not known, although it has been popularly identified as the place of death of Kenneth II. The Carnegies were made stewards of the castle during the reign of William the Lion. In 1296, it was the location where John Balliol confessed to rebellion against Edward I of England. It was kept in good repair over the following centuries, and was visited by Mary, Queen of Scots. By 1532, the castle was a secondary residence of William Keith, 4th Earl Marischal, and appears to have been at the centre of the small town, occupying about two hundred yards between gates on the main road. The Earl petitioned for Kincardine to be declared as a free burgh and county town for the Mearns. The petition claimed that the sheriff courts for the Mearns were already being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunnichen
Dunnichen ( gd, Dùn Neachdain, meaning the "Fort of Neachdan/Nechtan") is a small village in Angus, Scotland, situated between Letham, Angus, Letham and Forfar. It is close to Dunnichen Hill, at which the Battle of Dun Nechtain is popularly believed to have been fought. The church is part of the parish of Letham, Dunnichen and Kirkden. History During the 18th and early 19th centuries it was the home of George Dempster (lawyer), George Dempster, the agricultural reformer, author and founder of the neighbouring village of Letham. Many archaeological remains are associated with the village and its environs, including the hillforts on Dunnichen hill and Dunbarrow hill. In the early 19th century, the Dunnichen Stone, a class I Pictish stones, Pictish standing stone was unearthed at East Mains of Dunnichen. This is now located at the Meffan Institute at Forfar. An early local tradition, related by Headrick in the Second Statistical Account, claimed that the site was the location of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
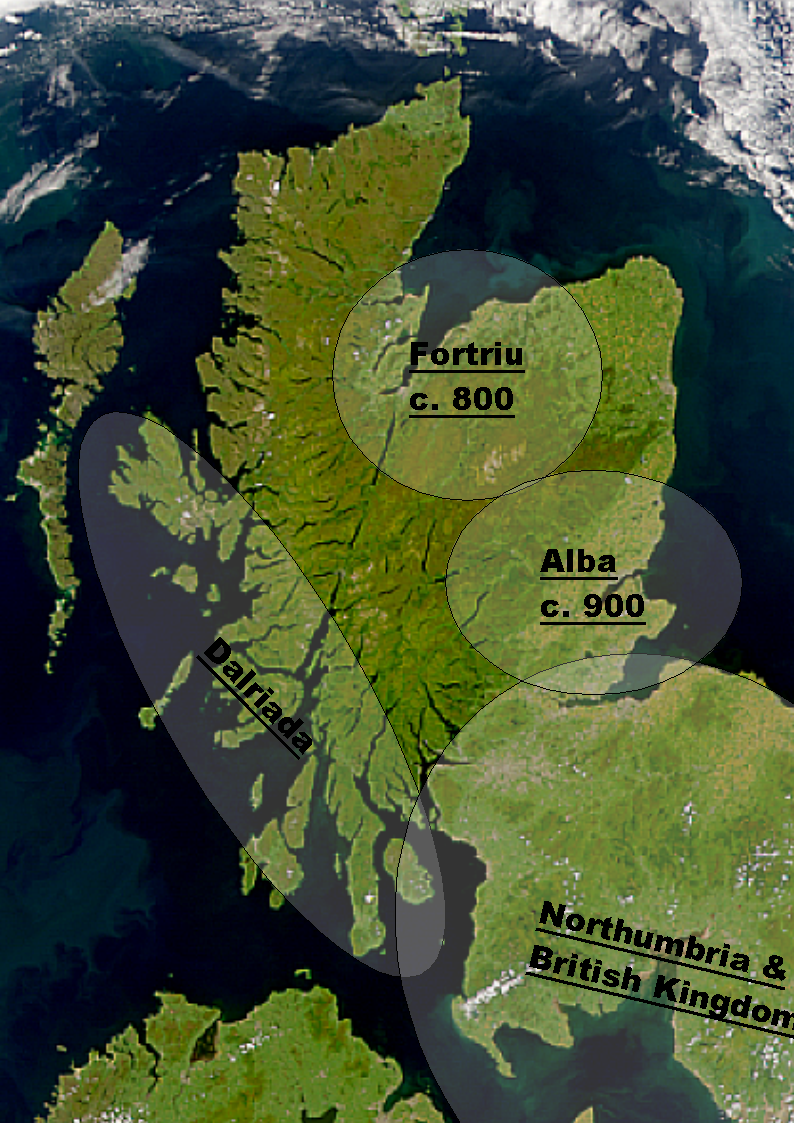
Medieval Scotland
Scotland in the Middle Ages concerns the history of Scotland from the departure of the Romans to the adoption of major aspects of the Renaissance in the early sixteenth century. From the fifth century northern Britain was divided into a series of kingdoms. Of these the four most important to emerge were the Picts, the Gaels of Dál Riata, the Britons of Strathclyde and the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Bernicia, later taken over by Northumbria. After the arrival of the Vikings in the late eighth century, Scandinavian rulers and colonies were established along parts of the coasts and in the islands. In the ninth century the Scots and Picts combined under the House of Alpin to form a single Kingdom of Alba, with a Pictish base and dominated by Gaelic culture. After the reign of King David I in the twelfth century, the Scottish monarchs are best described as Scoto-Norman, preferring French culture to native Scottish culture. Alexander II and his son Alexander III, were able to regain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)