|
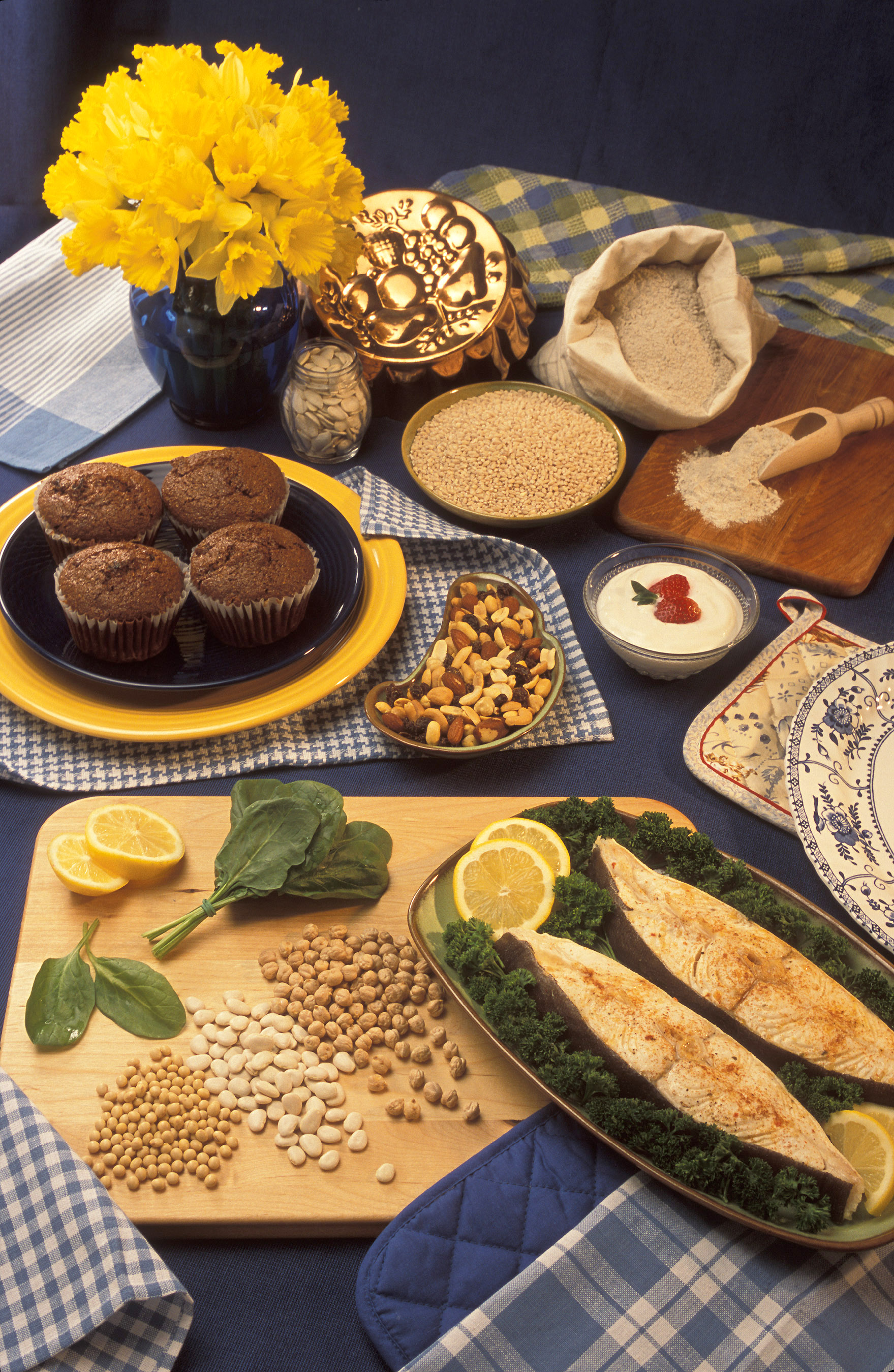
Country Food
Indigenous cuisine of the Americas includes all cuisines and food practices of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Contemporary Native peoples retain a varied culture of traditional foods, along with the addition of some post-contact foods that have become customary and even iconic of present-day Indigenous American social gatherings (for example, frybread). Foods like cornbread, turkey, cranberry, blueberry, hominy and mush have been adopted into the cuisine of the broader United States population from Native American cultures. In other cases, documents from the early periods of Indigenous American contact with European, African, and Asian peoples have allowed the recovery and revitalization of Indigenous food practices that had formerly passed out of popularity. The most important Indigenous American crops have generally included Indian corn (or maize, from the Taíno name for the plant), beans, squash, pumpkins, sunflowers, wild rice, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, peppers, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manoomin (wild Rice)
Wild rice, also called manoomin, Canada rice, Indian rice, or water oats, is any of four species of grasses that form the genus ''Zizania'', and the grain that can be harvested from them. The grain was historically gathered and eaten in both North America and China, but eaten less in China, where the plant's stem is used as a vegetable. Wild rice is not directly related to domesticated rice (''Oryza sativa'' and ''Oryza glaberrima''), although they are close cousins, all belonging to the tribe Oryzeae. Wild-rice grains have a chewy outer sheath with a tender inner grain that has a slightly vegetal taste. The plants grow in shallow water in small lakes and slow-flowing streams; often, only the flowering head of wild rice rises above the water. The grain is eaten by dabbling ducks and other aquatic wildlife. Species Three species of wild rice are native to North America: * Northern wild rice (''Zizania palustris'') is an annual plant native to the Great Lakes region of Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican Cuisine
Mexican cuisine consists of the cooking cuisines and traditions of the modern country of Mexico. Its earliest roots lie in Mesoamerican cuisine. Its ingredients and methods begin with the first agricultural communities such as the Olmec and Maya who domesticated maize, created the standard process of maize nixtamalization, and established their foodways. Successive waves of other Mesoamerican groups brought with them their own cooking methods. These included: the Teotihuacanos, Toltec, Huastec, Zapotec, Mixtec, Otomi, Purépecha, Totonac, Mazatec, Mazahua, and Nahua. With the Mexica formation of the multi-ethnic Triple Alliance (Aztec Empire), culinary foodways became infused (Aztec cuisine). Today's food staples native to the land include corn (maize), turkey, beans, squash, amaranth, chia, avocados, tomatoes, tomatillos, cacao, vanilla, agave, spirulina, sweet potato, cactus, and chili pepper. Its history over the centuries has resulted in regional cuisines based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordicity
Nordicity () is the degree of northernness. The concept was developed by Canadian geographer Louis-Edmond Hamelin in the 1960s based on previous work done in the Soviet Union. Hamelin's system defined northern territories – like northern Canada – not by literal latitude, but as a continuum based on a number of natural and human factors. Hamelin developed an index he called ''Valeurs polaires'' (French for "polar values") or VAPO, where the North Pole had a VAPO of 1000. The nordicity index had 10 natural and human components: #latitude # summer heat # annual cold # types of ice #total precipitation #natural vegetation cover #accessibility by means other than air # air service #population # degree of economic activity Each component was graded on the scale of 0–100 where 100 represented extreme nordicity, with the VAPO representing the sum of these ten components. Hamelin proposed that areas with a VAPO of more than 200 should be considered "the North". He subdivided Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, and Alaska. Inuit languages are part of the Eskimo–Aleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskaleut. Inuit Sign Language is a critically endangered language isolate used in Nunavut. Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, Nunatsiavut and NunatuKavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories, particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. With the exception of NunatuKavut, these areas are known, primarily by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Aboriginal Canadians wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis People (Canada)
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Nations In Canada
First Nations (french: Premières Nations) is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. Under Charter jurisprudence, First Nations are a "designated group," along with women, visible minorities, and people with physical or mental disabilities. First Nations are not defined as a visible minority by the criteria of Statistics Canada. North American indigenous peoples have cultures spanning thousands of years. Some of their oral traditions accurately describe historical events, such as the Cascadia earthquake of 1700 and the 18th-century Tseax Cone eruption. Written records began with the arrival of European explorers and colonists during the Age of Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples In Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and ''Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. ''Aboriginal peoples'' as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the ''Constitution Act, 1982'', though in most Indigenous circles ''Aboriginal'' has also fallen into disfavour. Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are some of the earliest known sites of human habitation in Canada. The Paleo-Indians, Paleo-Indian Clovis culture, Clovis, Plano cultures, Plano and Pre-Dorset cultures pre-date the current Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Projectile point tools, spears, pottery, bangles, chisels and Scraper (archaeology), scrapers mark archaeological sites, thus distinguishing cultural periods, traditions, and lithic reduction styles. The characteristics of Indigenous culture in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Diet
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. The word diet often implies the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management reasons (with the two often being related). Although humans are omnivores, each culture and each person holds some food preferences or some food taboos. This may be due to personal tastes or ethical reasons. Individual dietary choices may be more or less healthy. Complete nutrition requires ingestion and absorption of vitamins, minerals, essential amino acids from protein and essential fatty acids from fat-containing food, also food energy in the form of carbohydrate, protein, and fat. Dietary habits and choices play a significant role in the quality of life, health and longevity. Health A healthy diet can improve and maintain health, which can include aspects of mental and physical health. Specific diets, such as the DASH diet, can be used in treatment and management of chronic conditions. Dietary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuni People
The Zuni ( zun, A:shiwi; formerly spelled ''Zuñi'') are Native American Pueblo peoples native to the Zuni River valley. The Zuni are a Federally recognized tribe and most live in the Pueblo of Zuni on the Zuni River, a tributary of the Little Colorado River, in western New Mexico, United States. The Pueblo of Zuni is south of Gallup, New Mexico. The Zuni tribe lived in multi level adobe houses. In addition to the reservation, the tribe owns trust lands in Catron County, New Mexico, and Apache County, Arizona. The Zuni call their homeland ''Halona Idiwan’a ''or Middle Place. The word ''Zuni'' is believed to derive from the Western Keres language (Acoma) word ''sɨ̂‧ni'', or a cognate thereof. History Archaeology suggests that the Zuni have been farmers in their present location for 3,000 to 4,000 years. It is now thought that the Ancestral Zuni people have inhabited the Zuni River valley since the last millennium B.C., when they began using irrigation to farm maize o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopi
The Hopi are a Native American ethnic group who primarily live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona, United States. As of the 2010 census, there are 19,338 Hopi in the country. The Hopi Tribe is a sovereign nation within the United States and has government-to-government relations with the United States federal government. Particular villages retain autonomy under the Hopi Constitution and Bylaws. The Hopi language is one of 30 in the Uto-Aztecan language family. The majority of Hopi people are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona but some are enrolled in the Colorado River Indian Tribes. The Hopi Reservation covers a land area of . The Hopi encountered Spaniards in the 16th century, and are historically referred to as Pueblo people, because they lived in villages (''pueblos'' in the Spanish language). The Hopi are thought to be descended from the Ancestral Puebloans ( Hopi: ''Hisatsinom''), who constructed large apartment-house complexes and had an advanced cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puebloans
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zuni, and Hopi are the best-known. Pueblo people speak languages from four different language families, and each Pueblo is further divided culturally by kinship systems and agricultural practices, although all cultivate varieties of maize. Pueblo peoples have lived in the American Southwest for millennia and descend from Ancestral Pueblo peoples. The term ''Anasazi'' is sometimes used to refer to ancestral Pueblo people but it is now largely minimized. ''Anasazi'' is a Navajo word that means ''Ancient Ones'' or ''Ancient Enemy'', hence Pueblo peoples' rejection of it (see exonym). ''Pueblo'' is a Spanish term for "village." When Spaniards entered the area, beginning in the 16th-century with the founding of Nuevo México, they came across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
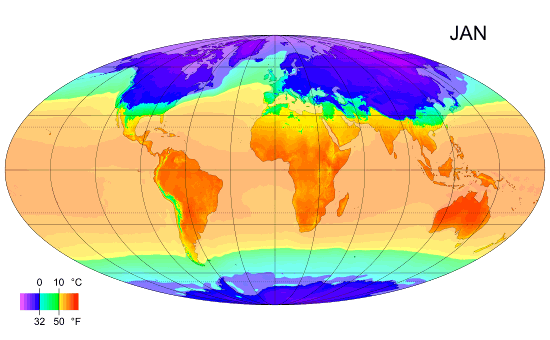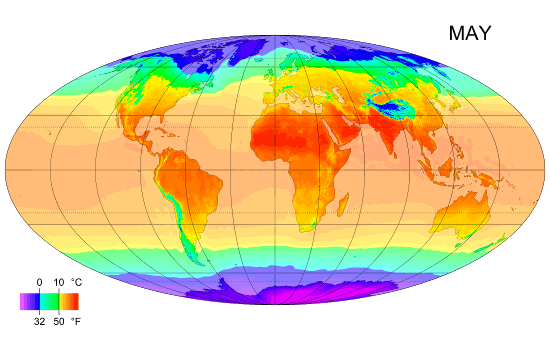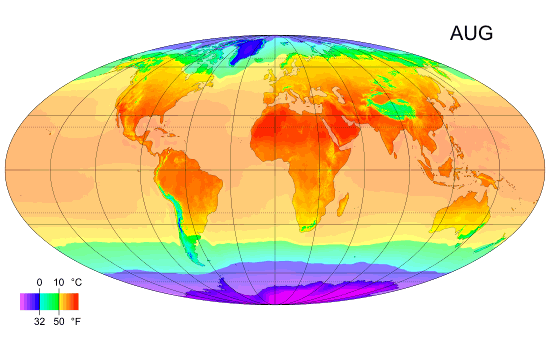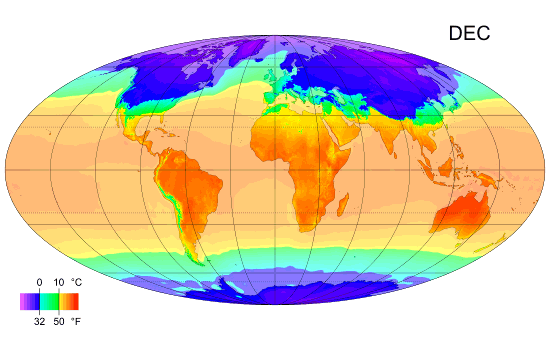
Climate Zones
Climate classifications are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. One of the most used is the Köppen climate classification scheme first developed in 1899. There are several ways to classify climates into similar regimes. Originally, climes were defined in Ancient Greece to describe the weather depending upon a location's latitude. Modern climate classification methods can be broadly divided into ''genetic'' methods, which focus on the causes of climate, and ''empiric'' methods, which focus on the effects of climate. Examples of genetic classification include methods based on the relative frequency of different air mass types or locations within synoptic weather disturbances. Examples of empiric classifications include climate zones defined by plant hardiness, evapotranspiration, or more generally the Köppen climate classification which was o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)