|
Coumaroyl-CoA
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids. Biosynthesis and significance It is generated in nature from phenylalanine, which is converted by PAL to trans-cinnamate. Trans-cinnamate is hydroxylated by trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase to give 4-hydroxycinnamate (i.e, coumarate). Coumarate is condensed with coenzyme-A in the presence of 4-coumarate-CoA ligase: :ATP + 4-coumarate + CoA \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes using Coumaroyl-Coenzyme A * Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase * Anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase * Chalcone synthase * 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase * 6'-Deoxychalcone synthase * Agmatine N4-coum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylpropanoid
The phenylpropanoids are a diverse family of organic compounds that are synthesized by plants from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Their name is derived from the six-carbon, aromatic phenyl group and the three-carbon propene tail of coumaric acid, which is the central intermediate in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. From 4-coumaroyl-CoA emanates the biosynthesis of myriad natural products including lignols (precursors to lignin and lignocellulose), flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and phenylpropanoids. The coumaroyl component is produced from cinnamic acid. Phenylpropanoids are found throughout the plant kingdom, where they serve as essential components of a number of structural polymers, provide protection from ultraviolet light, defend against herbivores and pathogens, and also mediate plant-pollinator interactions as floral pigments and scent compounds. Hydroxycinnamic acids Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenic acid, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In acetyl-CoA, its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the Anabolism, anabolic and Catabolism, catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of Pyruvic acid, pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme-A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the anabolic and catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the early 1950s at the Lister Institute, London, together by Lipmann and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechin
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids. The name of the catechin chemical family derives from ''catechu'', which is the tannic juice or boiled extract of ''Mimosa catechu'' (''Acacia catechu'' L.f). Chemistry Catechin possesses two benzene ring Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atom ...s (called the A- and B-rings) and a dihydropyran heterocycle (the C-ring) with a hydroxyl group on carbon 3. The A-ring is similar to a resorcinol moiety while the B-ring is similar to a catechol moiety. There are two chirality (chemistry), chiral centers on the molecule on carbons 2 and 3. Therefore, it has four diastereoisomers. Two of the isomers are in trans configura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6''-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase
Anthocyanin 3-O-glucoside 6″-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase is an enzyme forming delphinidin 3-(6-''p''-coumaroyl)glucoside from delphinidin 3-''O''-glucoside (myrtillin) and ''p''-coumaroyl-CoA. It is an enzyme in the anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway. It can be isolated from ''Perilla frutescens ''Perilla frutescens'', commonly called deulkkae, perilla or Korean perilla, is a species of ''Perilla'' in the mint family Lamiaceae. It is an annual plant native to Southeast Asia and Indian highlands, and is traditionally grown in the Korean ...''. References External links Sequence at uniprot.org Transferases Anthocyanins metabolism {{transferase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanin 5-aromatic Acyltransferase
In enzymology, an anthocyanin 5-aromatic acyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA + anthocyanidin-3,5-diglucoside \rightleftharpoons CoA + anthocyanidin 3-glucoside-5-hydroxycinnamoylglucoside Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA and anthocyanidin-3,5-diglucoside, whereas its two products are CoA and anthocyanidin 3-glucoside-5-hydroxycinnamoylglucoside. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:anthocyanidin 3,5-diglucoside 5-O-glucoside-6"'-O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase. References * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
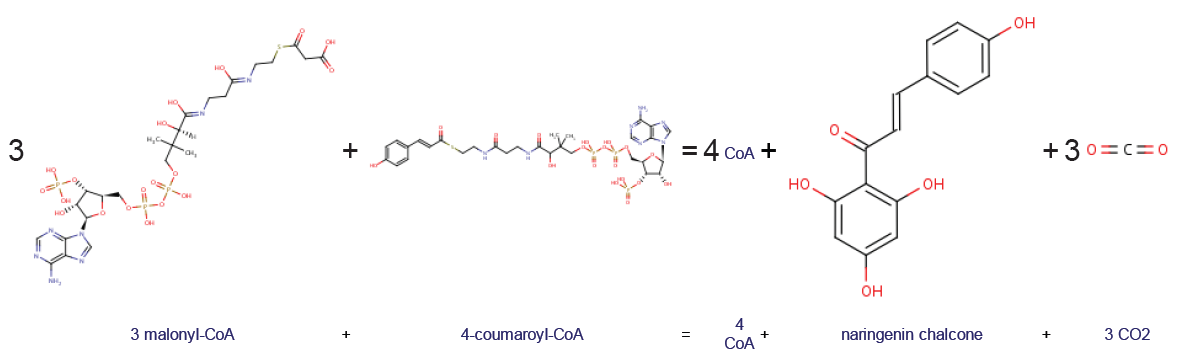
Chalcone Synthase
Chalcone synthase or naringenin-chalcone synthase (CHS) is an enzyme ubiquitous to higher plants and belongs to a family of polyketide synthase enzymes (PKS) known as type III PKS. Type III PKSs are associated with the production of chalcones, a class of organic compounds found mainly in plants as natural defense mechanisms and as synthetic intermediates. CHS was the first type III PKS to be discovered. It is the first committed enzyme in flavonoid biosynthesis. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 4-coumaroyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to naringenin chalcone. Function CHS catalysis serves as the initial step for flavonoid biosynthesis. Flavonoids are important plant secondary metabolites that serve various functions in higher plants. These include pigmentation, UV protection, fertility, antifungal defense and the recruitment of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. CHS is believed to act as a central hub for the enzymes involved in the flavonoid pathway. Studies have shown that these enzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6'-Deoxychalcone Synthase
In enzymology, a 6'-deoxychalcone synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :3 malonyl-CoA + 4-coumaroyl-CoA + NADPH + H+ \rightleftharpoons 4 CoA + isoliquiritigenin + 3 CO2 + NADP+ + H2O The 4 substrates of this enzyme are malonyl-CoA, 4-coumaroyl-CoA, NADPH, and H+, whereas its 5 products are CoA, isoliquiritigenin, CO2, NADP+, and H2O. Deoxychalcone synthase catalyzed activity is involved in the biosynthesis of retrochalcone and certain phytoalexins in the cells of ''Glycyrrhiza echinata'' (Russian licorice) and other leguminous plants. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :4-coumaroyl-CoA + a flavonol 3-O- 2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside.html" ;"title="eta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside">eta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside\rightleftharpoons CoA + a flavonol 3-O- 2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-_beta-D-glucoside.html" ;"title="-(4-coumaroyl)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)- beta-D-glucoside">-(4-coumaroyl)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)- beta-D-glucoside The 3 substrates of this enzyme are 4-coumaroyl-CoA, flavonol, and 2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside.html" ;"title="3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside">3-O-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside, whereas its 4 products are CoA, flavonol Flavonols are a class of flavonoids that have the 3-hydroxyflavone backbone (IUPAC name : 3-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |