|
Coenzyme-A
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the anabolic and catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of pyruvate synthesis and degradation. Discovery of structure Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946, who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the early 1950s at the Lister Institute, London, together by Lipmann and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar Attenuation Coefficient
In chemistry, the molar absorption coefficient or molar attenuation coefficient is a measurement of how strongly a chemical species absorbs, and thereby attenuates, light at a given wavelength. It is an intrinsic property of the species. The International System of Units, SI unit of molar absorption coefficient is the square metre per Mole (unit), mole (), but in practice, quantities are usually expressed in terms of Molar concentration#Units, M−1⋅cm−1 or L⋅mol−1⋅cm−1 (the latter two units are both equal to ). In older literature, the cm2/mol is sometimes used; 1 M−1⋅cm−1 equals 1000 cm2/mol. The molar absorption coefficient is also known as the molar extinction coefficient and molar absorptivity, but the use of these alternative terms has been discouraged by the International_Union_of_Pure_and_Applied_Chemistry, IUPAC. Beer–Lambert law The absorbance of a material that has only one absorbing species also depends on the pathlength and the concentration of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is usually encountered as a component, referred to as E1, of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). PDC consists of other enzymes, referred to as E2 and E3. Collectively E1-E3 transform pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A into acetyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH. The conversion is crucial because acetyl-CoA may then be used in the citric acid cycle to carry out cellular respiration. To distinguish between this enzyme and the PDC, it is systematically called pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). Mechanism The thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) converts to an ylide by deprotonation. The ylide attack the ketone group of pyruvate. The resulting adduct decarboxylates. The resulting 1,3-dipole reductively acetylates lipoamide-E2. In terms of details, bioch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
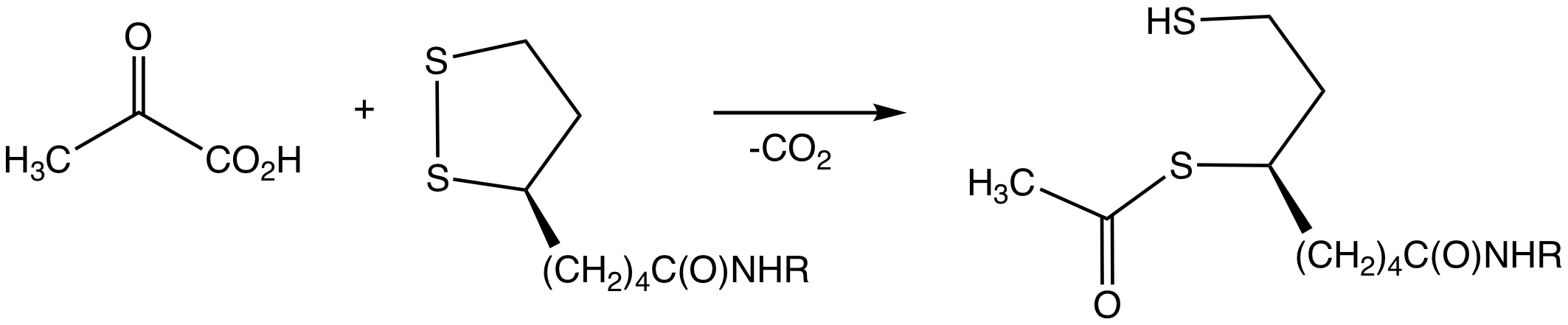
CoA Biosynthetic Pathway
Coa may refer to: Places * Coa, County Fermanagh, a rural community in County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland * Côa River, a tributary of the Douro, Portugal ** Battle of Coa, part of the Peninsular War period of the Napoleonic Wars ** Côa Valley Paleolithic Art, one of the biggest open air Paleolithic art sites * Quwê (or Coa), an Assyrian vassal state or province from the 9th century BC to around 627 BCE in the lowlands of eastern Cilicia ** Adana, the ancient capital of Quwê, also called Quwê or Coa * Côa (Mozambique), central Mozambique People * Eibar Coa (born 1971) Other uses * Coa de jima, or coa, a specialized tool for harvesting agave cactus * Continental Airlines, major US airline * c.o.a., coat of arms * Coa (argot) ( es), criminal slang used in Chile See also * COA (other) * ''Coea'', a genus of butterflies * ''Coua Couas are large, mostly terrestrial birds of the cuckoo family, endemic to the island of Madagascar. Couas are reminiscent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantothenic Acid
Pantothenic acid, also called vitamin B5 is a water-soluble B vitamin and therefore an essential nutrient. All animals require pantothenic acid in order to synthesize coenzyme A (CoA) – essential for fatty acid metabolism – as well as to, in general, synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Pantothenic acid is the combination of pantoic acid and β-alanine. Its name derives from the Greek ''pantos'', meaning "from everywhere", as minimally, at least small quantities of pantothenic acid are found in nearly every food. Human deficiency is very rare. As a dietary supplement or animal feed ingredient, the form commonly used is calcium pantothenate because of chemical stability, and hence long product shelf life, compared to sodium pantothenate or free pantothenic acid. Definition Pantothenic acid is a water-soluble vitamin, one of the B vitamins. It is synthesized from the amino acid β-alanine and pantoic acid (see biosynthesis and structure of coenzyme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathan O
Nathan or Natan may refer to: People *Nathan (given name), including a list of people and characters with this name *Nathan (surname) *Nathan (prophet), a person in the Hebrew Bible *Nathan (son of David), biblical figure, son of King David and Bathsheba *Nathan of Gaza, a charismatic figure who spread the word of Eli the Prophet *Starboy Nathan, a British singer who used the stage name "Nathan" from 2006 to 2011 * Nathan (footballer, born 1994), full name ''Nathan Athaydes Campos Ferreira'', Brazilian winger * Nathan (footballer, born 1995), full name ''Nathan Raphael Pelae Cardoso'', Brazilian centre back *Nathan (footballer, born 1996), full name ''Nathan Allan de Souza'', Brazilian midfielder *Nathan (footballer, born May 1999), full name ''Nathan Crepaldi da Cruz'', Brazilian forward *Nathan (footballer, born August 1999), full name ''Nathan Palafoz de Sousa'', Brazilian forward Other uses *Nathan, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane in Australia *Nathan (band), an alt-coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beverly Guirard
Beverly Marie Guirard was a microbiologist who worked on the biochemistry of microbial growth, especially with respect to vitamin B6. She is also known for her work defining the components of coenzyme A which was a part of the research that led to a Nobel Prize for Fritz Albert Lipmann. Education and career Guirard grew up in Louisiana and went to high school in St. Martinville, Louisiana. Guirard received a B.S. from Southwestern Louisiana Institute in 1936, and a masters degree from Louisiana State University in 1938. She went on to earn a Ph.D. from the University of Texas in 1945 where she worked on lactic acid bacteria and their conversion of acetate into lipids and steroidal material, research which built upon Esmond Emerson Snell's earliest work that identified acetate as a key factor leading to reliable growth of microorganisms. After her Ph.D. she remained at the University of Texas, where she joined Snell's lab in 1951. She moved with the lab to the University of Calif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the third oldest general hospital in the United States and has a capacity of 999 beds. With Brigham and Women's Hospital, it is one of the two founding members of Mass General Brigham (formerly known as Partners HealthCare), the largest healthcare provider in Massachusetts. Massachusetts General Hospital houses the largest hospital-based research program in the world, the Mass General Research Institute, with an annual research budget of more than $1 billion in 2019. It is currently ranked as the #8 best hospital in the United States by '' U.S. News & World Report''. In , ''The Boston Globe'' ranked MGH the fifth best place to work out of Massachusetts companies with over 1,000 employees. History Founded in 1811, the original hospital was designed by the famous American architect Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School (HMS) is the graduate medical school of Harvard University and is located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. Founded in 1782, HMS is one of the oldest medical schools in the United States and is consistently ranked first for research among medical schools by '' U.S. News & World Report''. Unlike most other leading medical schools, HMS does not operate in conjunction with a single hospital but is directly affiliated with several teaching hospitals in the Boston area. Affiliated teaching hospitals and research institutes include Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston Children's Hospital, McLean Hospital, Cambridge Health Alliance, The Baker Center for Children and Families, and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital. History Harvard Medical School was founded on September 19, 1782, after President Joseph Willard presented a report with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lister Institute
The Lister Institute of Preventive Medicine, informally known as the Lister Institute, was established as a research institute (the British Institute of Preventive Medicine) in 1891, with bacteriologist Marc Armand Ruffer as its first director, using a grant of £250,000 from Edward Cecil Guinness of the Guinness family. It had premises in Chelsea in London, Sudbury in Suffolk, and Elstree in Hertfordshire, England. It was the first medical research charity in the United Kingdom. It was renamed the Jenner Institute (after Edward Jenner, the pioneer of smallpox vaccine) in 1898 and then, in 1903, as the Lister Institute in honour of the great surgeon and medical pioneer, Dr Joseph Lister. In 1905, the institute became a school of the University of London. History Until the 1970s the institute maintained laboratories and conducted research on infectious disease and vaccines. It was funded by manufacturing and selling vaccines. In the 1970s the institute ran into financial diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Lipmann
Fritz Albert Lipmann (; June 12, 1899 – July 24, 1986) was a German-American biochemist and a co-discoverer in 1945 of coenzyme A. For this, together with other research on coenzyme A, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1953 (shared with Hans Adolf Krebs). Early life and education Lipmann was born in Königsberg, Germany, to a Jewish family. His parents were Gertrud (Lachmanski) and Leopold Lipmann, an attorney. Lipmann studied medicine at the University of Königsberg, Berlin, and Munich, graduating in Berlin in 1924. He returned to Königsberg to study chemistry under Professor Hans Meerwein. In 1926 he joined Otto Meyerhof at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Biology, Dahlem, Berlin, for his doctoral thesis. After that he followed Meyerhof to Heidelberg to the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Medical Research. Career From 1939 on, Lipmann lived and worked in the United States. He was a Research Associate in the Department of Biochemistry, Cornell Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |