|
Conformal Film
Conformal coating is a protective coating of thin polymeric film, applied to printed circuit boards (PCB). The coating is named conformal since it ''conforms'' to the contours of the PCB. Conformal coatings are typically applied at 25-250 μm to the electronic circuitry and provides it protection against moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremities. Coatings can be applied in a number of ways, including brushing, spraying, dispensing and dip coating. Furthermore, a number of materials can be used as a conformal coating, such as acrylics, silicones, urethanes and parylene. Each has their own characteristics, making them preferred for certain environments and manufacturing scenarios. Most circuit board assembly firms coat assemblies with a layer of transparent conformal coating, which is lighter and easier to inspect than potting. Reasons for use Conformal coatings are used to protect electronic components from the environmental factors they are exposed to. Examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymeric
A polymer (; Greek ''poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meaning " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
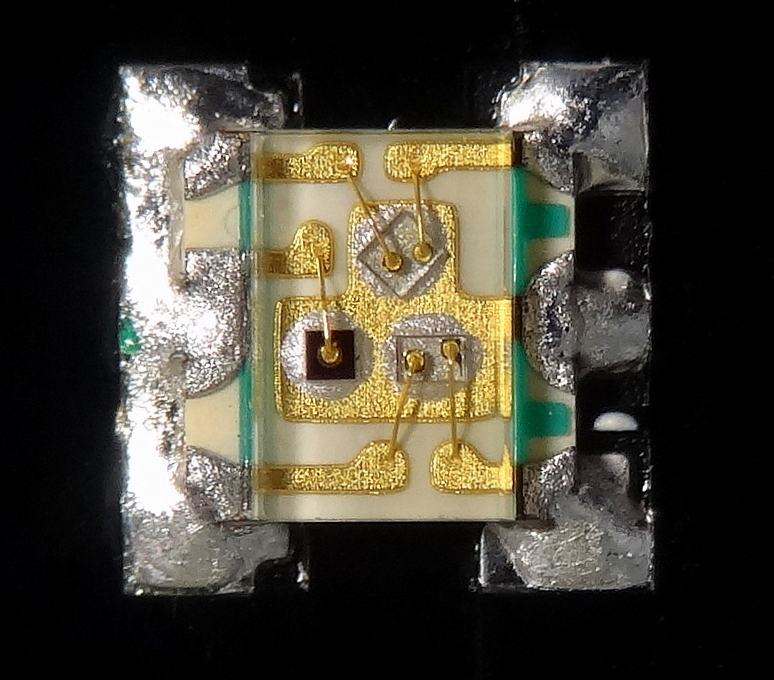
Wire Bonding
Wire bonding is the method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its integrated circuit packaging, packaging during Fabrication (semiconductor), semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one printed circuit board (PCB) to another. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages. Wire bonding can be used at frequencies above 100 GHz. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with an artwork pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers in the shape designed to accept the component's terminals, generally by means of soldering, to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it. Another manufacturing process adds vias: plated-through holes that allow interconnections between layers. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all electronic products. Alternatives to PCBs include wire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DS101 Dip Coating System For Application Of Conformal Coatings
DS1 or DS-1 may refer to: * BOSS DS-1, a guitar distortion pedal * Digital Signal 1, a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs * Deep Space 1, a mission to 9969 Braille & 19P/Borrelly * DS-1 (drug), a selective GABAA α4β3δ agonist drug * South African Class DS1, a diesel locomotive class * Datsun ''DS-1'', a car by Nissan, see Datsun DS Series * ''Dark Souls'', an action role-playing game * Dead Space (2008 video game), a survival horror game * VR Class Ds1 The VR Class Ds1 Also known as "Puumotti" (Roughly translated to Wood Cubic meter "motti" being a means to measure wood volume) was the first railbus of the Finnish State Railways. It was ordered in 1927. The Ds1 was built by the Pasila workshop, b ..., a Finnish railbus class See also * DS (other) * Canon EOS-1Ds series {{Letter-number combination disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spray Booth Designed For Application Of Conformal Coatings, Lacquers And RFI Shielding Paints
Spray or spraying commonly refer to: * Spray (liquid drop) ** Aerosol spray ** Blood spray ** Hair spray ** Nasal spray ** Pepper spray ** PAVA spray ** Road spray or tire spray, road debris kicked up from a vehicle tire ** Sea spray, refers to aerosol particles that form in the ocean * Spraying, or the creation of a spray ** Spraying (animal behavior), the action of an animal marking its territory with urine ** The use of a spray bottle ** The use of a sprayer ** Aerial application of chemicals ** Spray painting Spray or spraying may also refer to: People * Ruth Hinshaw Spray (1848-1929), American peace activist Places * Spray, North Carolina, a former mill town in Rockingham County, North Carolina, now part of Eden, North Carolina Arts, entertainment, and media * Spray (band), a British synthpop band * ''Spray'' (video game), a 2008 video game for Nintendo's Wii video game console Brands and enterprises * Spray Network, a Swedish Internet company Computing * Heap spraying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Degreasing
Vapor degreasing is a surface finishing process. It involves solvents in vapor form to cleanse the workpiece in preparation for further finishing operations. Process The acting principle behind the vapor degreaser process is that the solvents will dissolve the contaminants on the workpiece and remove them by dripping off the part. A basin of solvent is set up with a heating coil to bring the solvent to boil. As the solvent evaporates it rises to the fill-line in the chamber, above which is air with a much lower density than the solvent. This contains the vaporized solvent in a closed space where the workpiece is placed. The solvent condenses on the more frigid workpiece and the now liquid solvent dissolves the greases on the part. With the impurities contained in the liquid beads, the solvent runs off the part. Some systems are designed to capture and reclaim this solvent, making the process much more economical. Other adaptations to the simple system include: *Several tank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also function as elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Node (circuits)
In electrical engineering, a node is any region on a circuit between two circuit elements. In circuit diagrams, connections are ideal wires with zero resistance, so a node consists of the entire section of wire between elements, not just a single point. According to Ohm's law, ''V = IR'', the voltage across any two points of a node with negligible resistance is :V = IR = I\cdot 0 = 0, showing that the electric potential at every point of a node is the same. There are some notable exceptions where the voltage difference is large enough to become significant: * High-precision resistance measurements using a Kelvin connection * The difference in voltage between ground and neutral, between the neutral wire and the ground in domestic AC power plugs and sockets, can be fatal. A properly installed electrical system connects them together at only one location, leading many people to the fatally incorrect conclusion that they are at "the same" voltage, or that the safety ground is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parylene
Parylene is the common name of a polymer whose backbone consists of ''para''- benzenediyl rings –– connected by 1,2-ethanediyl bridges –––. It can be obtained by polymerization of ''para''-xylylene . The name is also used for several polymers with the same backbone, where some hydrogen atoms are replaced by other functional groups. Some of these variants are designated in commerce by letter-number codes such as "parylene C" and "parylene AF-4". Some of these names are registered trademarks in some countries. Coatings of parylene are often applied to electronic circuits and other equipment as electrical insulation, moisture barriers, or protection against corrosion and chemical attack. They are also used to reduce friction, and in medicine to prevent adverse reactions to implanted devices. These coatings are typically applied by chemical vapor deposition in an atmosphere of the monomer ''para''-xylylene. Parylene is considered a "green" polymer because its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field for a system of charged particles. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, one of the four fundamental interactions (also called forces) of nature. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics, and are exploited in electrical technology. In atomic physics and chemistry, for instance, the electric field is the attractive force holding the atomic nucleus and electrons together in atoms. It is also the force responsible for chemical bonding between atoms that result in molecules. The electric field is defined as a vector field that associates to each point in space the electrostatic (Coulomb) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named '' volt''. The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in generator, inductors, and transformers). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. A voltmeter can be used to measure the voltage between two points in a system. Often a common reference potential such as the ground of the system is used as one of the points. A voltage can represent eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |