|
Condensin
Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome assembly and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xenopus'' egg extracts. Subunit composition Eukaryotic types Many eukaryotic cells possess two different types of condensin complexes, known as condensin I and condensin II, each of which is composed of five subunits (Figure 2). Condensins I and II share the same pair of core subunits, SMC2 and SMC4, both belonging to a large family of chromosomal ATPases, known as SMC proteins (SMC stands for Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes). Each of the complexes contains a distinct set of non-SMC regulatory subunits (a kleisin subunit and a pair of HEAT repeat subunits). Both complexes are large, having a total molecular mass of 650-700 kDa. The core subunits condensins (SMC2 and SMC4) are conserved among all eukaryotic species that have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMC Proteins
SMC complexes represent a large family of ATPases that participate in many aspects of higher-order chromosome organization and dynamics. SMC stands for Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes. Classification Eukaryotic SMCs Eukaryotes have at least six SMC proteins in individual organisms, and they form three distinct heterodimers with specialized functions: * A pair of SMC1 and SMC3 constitutes the core subunits of the cohesin complexes involved in sister chromatid cohesion. * Likewise, a pair of SMC2 and SMC4 acts as the core of the condensin complexes implicated in DNA condensation, chromosome condensation. * A dimer composed of SMC5 and SMC6 functions as part of a yet-to-be-named complex implicated in DNA repair and checkpoint responses. Each complex contains a distinct set of non-SMC regulatory subunits. Some organisms have variants of SMC proteins. For instance, mammals have a meiosis-specific variant of SMC1, known as SMC1β. The nematode ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCAPD2
Condensin complex subunit 1 also known as chromosome-associated protein D2 (CAP-D2) or non-SMC condensin I complex subunit D2 (NCAPD2) or XCAP-D2 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCAPD2'' gene. CAP-D2 is a subunit of condensin Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome assembly and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xenop ... I, a large protein complex involved in chromosome condensation. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * Human proteins {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCAPH2
Condensin-2 complex subunit H2, also known as chromosome-associated protein H2 (CAP-H2) or non-SMC condensin II complex subunit H2 (NCAPH2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCAPH2'' gene. CAP-H2 is a subunit of condensin Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome assembly and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xenop ... II, a large protein complex involved in chromosome condensation. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-22-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCAPG
Condensin complex subunit 3 also known as condensin subunit CAP-G (CAP-G) or non-SMC condensin I complex subunit G (NCAPG) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCAPG'' gene. CAP-G is a subunit of condensin I, a large protein complex involved in chromosome condensation. Interactions NCAPG has been shown to interact with DNMT3B DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3 beta, is an enzyme that in humans in encoded by the DNMT3B gene. Mutation in this gene are associated with immunodeficiency, centromere instability and facial anomalies syndrome. Function CpG methylation i .... References Further reading * * * * * Human proteins {{gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCAPH
Condensin complex subunit 2 also known as chromosome-associated protein H (CAP-H) or non-SMC condensin I complex subunit H (NCAPH) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCAPH'' gene. CAP-H is a subunit of condensin I, a large protein complex involved in chromosome condensation Function CAP-H is a member of the barr protein family and a regulatory subunit of the condensin complex. This complex is required for the conversion of interphase chromatin into condensed chromosomes. CAP-H is associated with mitotic chromosomes, except during the early phase of chromosome condensation. During interphase, the protein has a distinct punctate nucleolar localization. Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of NCAPH function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called ''Ncaphtm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi'' was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program — a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCAPD3
Condensin-2 complex subunit D3 (CAP-D3) also known as non-SMC condensin II complex subunit D3 (NCAPD3) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''NCAPD3'' gene. CAP-D3 is a subunit of condensin Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome assembly and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xeno ... II, a large protein complex involved in chromosome condensation. References Further reading * * * * * * * Human proteins {{gene-11-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCAPG2
Condensin-2 complex subunit G2 (CAP-G2) also known as chromosome-associated protein G2 (CAP-G2) or leucine zipper protein 5 (LUZP5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCAPG2'' gene. CAP-G2 is a subunit of condensin II, a large protein complex involved in chromosome condensation. It interacts with PLK1 through its C-terminal region during mitosis Clinical importance Mutations in this gene in humans have been associated with severe neurodevelopmental defects, failure to thrive Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ..., ocular abnormalities, and defects in urogenital and limb morphogenesis. References Further reading * * Human proteins {{gene-7-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HEAT Repeat
A HEAT repeat is a protein tandem repeat structural motif composed of two alpha helices linked by a short loop. HEAT repeats can form alpha solenoids, a type of solenoid protein domain found in a number of cytoplasmic proteins. The name "HEAT" is an acronym for four proteins in which this repeat structure is found: Huntingtin, elongation factor 3 (EF3), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and the yeast kinase TOR1. HEAT repeats form extended superhelical structures which are often involved in intracellular transport; they are structurally related to armadillo repeats. The nuclear transport protein importin beta contains 19 HEAT repeats. Various HEAT repeat proteins and their structures Representative examples of HEAT repeat proteins include importin β (also known as karyopherin β) family, regulatory subunits of condensin and cohesin, separase, PIKKs (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinases) such as ATM (Ataxia telangiectasia mutated) and ATR (Ataxia telangiectasia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMC2
Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 2 (SMC-2) also known as chromosome-associated protein E (CAP-E) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMC2'' gene. SMC-2 is a subunit of condensin I and II, large protein complexes involved in chromosome condensation. Interactions SMC2 has been shown to interact with DNMT3B DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3 beta, is an enzyme that in humans in encoded by the DNMT3B gene. Mutation in this gene are associated with immunodeficiency, centromere instability and facial anomalies syndrome. Function CpG methylation i .... References Further reading * * * * * * * External links PDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 2 PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Mouse Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 2 {{Nucleus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dosage Compensation
Dosage compensation is the process by which organisms equalize the expression of genes between members of different biological sexes. Across species, different sexes are often characterized by different types and numbers of sex chromosomes. In order to neutralize the large difference in gene dosage produced by differing numbers of sex chromosomes among the sexes, various evolutionary branches have acquired various methods to equalize gene expression among the sexes. Because sex chromosomes contain different numbers of genes, different species of organisms have developed different mechanisms to cope with this inequality. Replicating the actual ''gene'' is impossible; thus organisms instead equalize the ''expression'' from each gene. For example, in humans, females (XX) silence the transcription of one X chromosome of each pair, and transcribe all information from the other, expressed X chromosome. Thus, human females have the same number of expressed X-linked genes as do human males ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
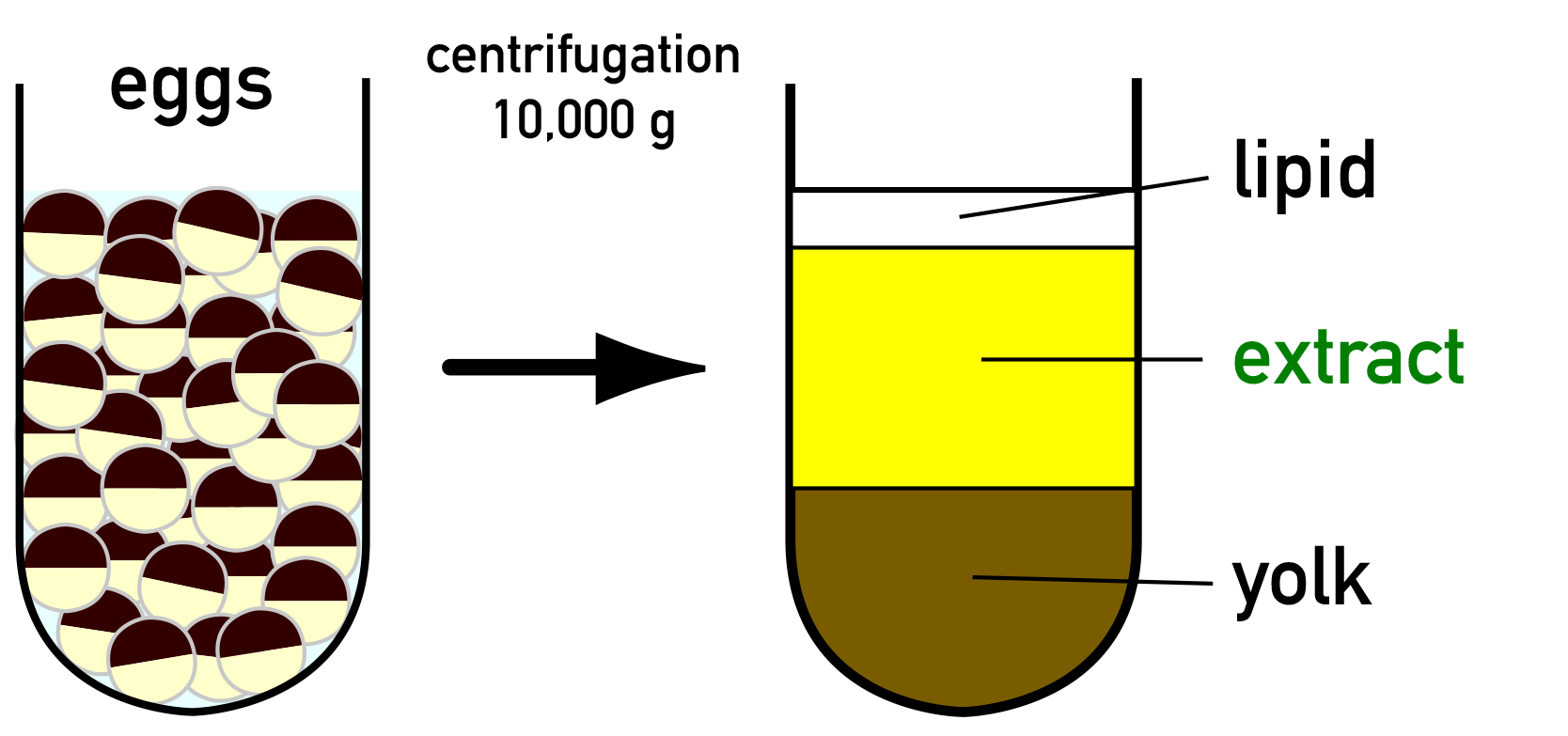
Xenopus Egg Extract
''Xenopus'' egg extract is a lysate that is prepared by crushing the eggs of the African clawed frog ''Xenopus laevis''. It offers a powerful cell-free (or ''in vitro'') system for studying various cell biological processes, including cell cycle progression, nuclear transport, DNA replication and chromosome segregation. It is also called ''Xenopus'' egg cell-free system or ''Xenopus'' egg cell-free extract. History The first frog egg extract was reported in 1983 by Lohka and Masui. This pioneering work used eggs of the Northern leopard frog ''Rana pipiens'' to prepare an extract. Later, the same procedure was applied to eggs of ''Xenopus laevis'', becoming popular for studying cell cycle progression and cell cycle-dependent cellular events. Extracts derived from eggs of the Japanese common toad ''Bufo japonicus'' or of the Western clawed frog ''Xenopus tropicalis'' have also been reported. Basics of extract preparation The cell cycle of unfertilized eggs of ''X. laevis'' is arrested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |