Xenopus Egg Extract on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Xenopus'' egg extract is a lysate that is prepared by crushing the eggs of the
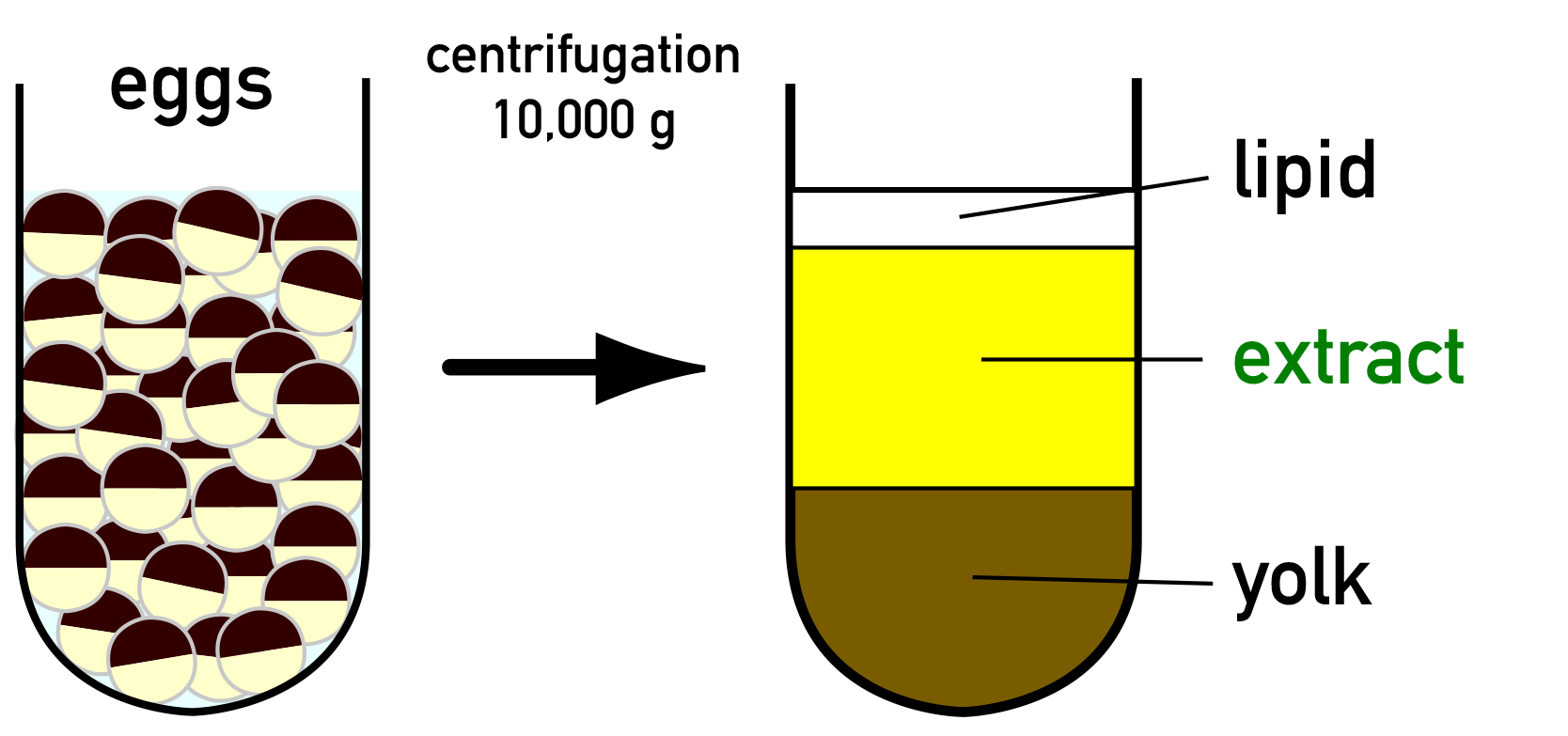 Unfertilized eggs in a buffer containing the Ca2+
Unfertilized eggs in a buffer containing the Ca2+

African clawed frog
The African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'', also known as the xenopus, African clawed toad, African claw-toed frog or the ''platanna'') is a species of African aquatic frog of the family Pipidae. Its name is derived from the three short claws o ...
''Xenopus laevis
The African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'', also known as the xenopus, African clawed toad, African claw-toed frog or the ''platanna'') is a species of African aquatic frog of the family Pipidae. Its name is derived from the three short claws ...
''. It offers a powerful cell-free (or ''in vitro'') system for studying various cell biological processes, including cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
progression, nuclear transport Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecul ...
, DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
and chromosome segregation
Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregati ...
. It is also called ''Xenopus'' egg cell-free system A cell-free system is an ''in vitro'' tool widely used to study biological reactions that happen within cells apart from a full cell system, thus reducing the complex interactions typically found when working in a whole cell. Subcellular fractions c ...
or ''Xenopus'' egg cell-free extract.
History
The first frog egg extract was reported in 1983 by Lohka and Masui. This pioneering work used eggs of theNorthern leopard frog
''Lithobates pipiens''Integrated Taxonomic Information System nternet2012''Lithobates pipiens'' pdated 2012 Sept; cited 2012 Dec 26Available from: www.itis.gov/ or ''Rana pipiens'', commonly known as the northern leopard frog, is a species of le ...
''Rana pipiens'' to prepare an extract. Later, the same procedure was applied to eggs of ''Xenopus laevis
The African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'', also known as the xenopus, African clawed toad, African claw-toed frog or the ''platanna'') is a species of African aquatic frog of the family Pipidae. Its name is derived from the three short claws ...
'', becoming popular for studying cell cycle progression and cell cycle-dependent cellular events. Extracts derived from eggs of the Japanese common toad
The Japanese common toad, Japanese warty toad or Japanese toad (''Bufo japonicus'') is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Japan. Its natural habitats are subarctic forests, temperate forests, temperate shrubland, swamps ...
''Bufo japonicus
The Japanese common toad, Japanese warty toad or Japanese toad (''Bufo japonicus'') is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Japan. Its natural habitats are subarctic forests, temperate forests, temperate shrubland, swamps, f ...
'' or of the Western clawed frog
The western clawed frog (''Xenopus tropicalis'') is a species of frog in the family Pipidae, also known as tropical clawed frog. It is the only species in the genus ''Xenopus'' to have a diploid genome. Its genome has been sequenced, making it ...
''Xenopus tropicalis
The western clawed frog (''Xenopus tropicalis'') is a species of frog in the family Pipidae, also known as tropical clawed frog. It is the only species in the genus ''Xenopus'' to have a diploid genome. Its genome has been sequenced, making it a ...
'' have also been reported.
Basics of extract preparation
Thecell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
of unfertilized eggs of ''X. laevis'' is arrested highly synchronously at metaphase of meiosis II. Upon fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Proce ...
, the metaphase arrest is released by the action of Ca2+ ions released from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby initiating early embryonic cell cycles that alternates S phase (DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
) and M phase ( mitosis).
M phase extract
 Unfertilized eggs in a buffer containing the Ca2+
Unfertilized eggs in a buffer containing the Ca2+ chelator
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
EGTA EGTA may refer to:
* EGTA (chemical)
EGTA (ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-''N'',''N'',''N''′,''N''′-tetraacetic acid), also known as egtazic acid ( INN, USAN), is an aminopolycarboxylic acid, a chelating agent. It is a white soli ...
(ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid) are packed into a centrifuge tube. After removing excess buffer, the eggs are crushed by centrifugation (~10,000 g). A soluble fraction that appears between the lipid cap and the yolk is called an M phase extract. This extract contains a high level of cyclin B
Cyclin B is a member of the cyclin family. Cyclin B is a mitotic cyclin. The amount of cyclin B (which binds to Cdk1) and the activity of the cyclin B-Cdk complex rise through the cell cycle until mitosis, where they fall abruptly due to degra ...
-Cdk1
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 also known as CDK1 or cell division cycle protein 2 homolog is a highly conserved protein that functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase, and is a key player in cell cycle regulation. It has been highly studied in t ...
. When demembranated sperm nuclei are incubated with this extract, it undergoes a series of structural changes and is eventually converted into a set of M phase chromosomes with bipolar spindles.
Interphase (S phase) extract
Different types of egg extracts
Cycling extract

High-speed supernatant (HSS)
Nucleoplasmic extract (NPE)
Discoveries made using egg extracts
*Purification of M-phase promoting factor (MPF) *Elucidation of the role of synthesis and degradation of cyclin B in cell cycle progression *Discovery that degradation of a protein(s) other than cyclin B is necessary for initiating chromosome segregation *Discovery of a mechanism ofspindle
Spindle may refer to:
Textiles and manufacturing
* Spindle (textiles), a straight spike to spin fibers into yarn
* Spindle (tool), a rotating axis of a machine tool
Biology
* Common spindle and other species of shrubs and trees in genus ''Euony ...
assembly that depends on chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in r ...
, but not centrosomes
*Proposal of a DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
licensing system and identification of its responsible factor
Factor, a Latin word meaning "who/which acts", may refer to:
Commerce
* Factor (agent), a person who acts for, notably a mercantile and colonial agent
* Factor (Scotland), a person or firm managing a Scottish estate
* Factors of production, suc ...
*Identification of importin
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the cell's cytoplasm to the nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS).
Importin has two subunits, impo ...
α/β responsible for nuclear transport Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecul ...
*Discovery of the condensin
Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome assembly and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xenop ...
complex essential for mitotic chromosome assembly
*Identification of the cohesin
Cohesin is a protein complex that mediates sister chromatid cohesion, homologous recombination, and DNA looping. Cohesin is formed of SMC3, SMC1, SCC1 and SCC3 ( SA1 or SA2 in humans). Cohesin holds sister chromatids together after DNA rep ...
complex essential for sister chromatid cohesion
More recently, the egg extracts have been used to study reprogramming of differentiated nuclei, physical properties of spindles and nuclei, and theoretical understanding of cell cycle control.
See also
* Yoshio Masui *cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
* Cdk1
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 also known as CDK1 or cell division cycle protein 2 homolog is a highly conserved protein that functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase, and is a key player in cell cycle regulation. It has been highly studied in t ...
* cyclin
* DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
* nuclear transport Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecul ...
* spindle apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a p ...
* condensin
Condensins are large protein complexes that play a central role in chromosome assembly and segregation during mitosis and meiosis (Figure 1). Their subunits were originally identified as major components of mitotic chromosomes assembled in ''Xenop ...
* cohesin
Cohesin is a protein complex that mediates sister chromatid cohesion, homologous recombination, and DNA looping. Cohesin is formed of SMC3, SMC1, SCC1 and SCC3 ( SA1 or SA2 in humans). Cohesin holds sister chromatids together after DNA rep ...
References
{{reflist, 2 Cell cycle Mitosis DNA replication