|
Commitment Ordering
Commitment ordering (CO) is a class of interoperable ''serializability'' techniques in concurrency control of databases, transaction processing, and related applications. It allows optimistic (non-blocking) implementations. With the proliferation of multi-core processors, CO has also been increasingly utilized in concurrent programming, transactional memory, and software transactional memory (STM) to achieve serializability optimistically. CO is also the name of the resulting transaction schedule (history) property, defined in 1988 with the name ''dynamic atomicity''.Alan Fekete, Nancy Lynch, Michael Merritt, William Weihl (1988)''Commutativity-based locking for nested transactions'' (PDF)MIT, LCS lab, Technical report MIT/LCS/TM-370, August 1988. In a CO compliant schedule, the chronological order of commitment events of transactions is compatible with the precedence order of the respective transactions. CO is a broad special case of '' conflict serializability'' and effective m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
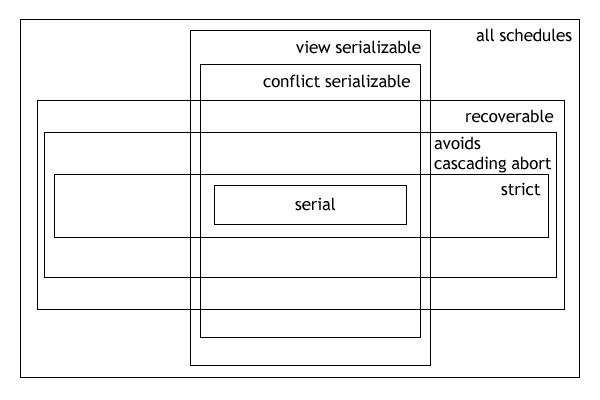
Serializability
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe the order of executions in a set of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Often, only a subset of the transaction operation types are included in a schedule. Schedules are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. In practice, most general purpose database systems employ conflict-serializable and strict recoverable schedules. Notation Grid notation: * Columns: The different transactions in the schedule. * Rows: The time order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transactional Object
Transaction or transactional may refer to: Commerce *Financial transaction, an agreement, communication, or movement carried out between a buyer and a seller to exchange an asset for payment *Debits and credits in a Double-entry bookkeeping system *Electronic funds transfer, the electronic exchange or transfer of money from one account to another *Real estate transaction, the process whereby rights in a unit of property is transferred between two or more parties *Transaction cost, a cost incurred in making an economic exchange *Transactional law, the practice of law concerning business and commerce Computing *Transaction processing, information processing that is divided into individual, indivisible operations *Database transaction, a unit of work performed within a database management system *Atomic transaction, a series of database operations such that either all occur, or nothing occurs Other uses *Transactions, the published proceedings of a learned society: ** *Transaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raz2009
Raz or RAZ may refer to: People * Raz Gal-Or (born 1994), Israeli businessman in China * Raz Hershko (born 1998), Israeli European champion and Olympic judoka * Raz (surname) * Razputin, protagonist of the video game ''Psychonauts'' Places France *Pointe du Raz, the western point of the ''commune'' of Plogoff, Finistère, France *Alderney Race (''Raz Blanchard''), a strong tidal current between La Hague and Alderney * Ile de Raz, an island offshore of Alderney *Raz de Sein, a stretch of water located between the Ile de Sein and the Pointe du Raz in Finistère in the Brittany region of France Iran * Raz, Iran, a city in North Khorasan Province, Iran * Raz, Ardabil, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran * Raz, Razavi Khorasan, a village in Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran * Raz, Zanjan, a village in Zanjan Province, Iran * Raz Galleh, a village in Kerman Province, Iran * Raz Rural District, an administrative subdivision of North Khorasan Province, Iran * Shiraz Shiraz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throughput
Network throughput (or just throughput, when in context) refers to the rate of message delivery over a communication channel in a communication network, such as Ethernet or packet radio. The data that these messages contain may be delivered over physical or logical links, or through network nodes. Throughput is usually measured in bits per second (, sometimes abbreviated bps), and sometimes in packets per second ( or pps) or data packets per time slot. The system throughput or aggregate throughput is the sum of the data rates that are delivered over all channels in a network. Throughput represents digital bandwidth consumption. The throughput of a communication system may be affected by various factors, including the limitations of the underlying physical medium, available processing power of the system components, end-user behavior, etc. When taking various protocol overheads into account, the useful rate of the data transfer can be significantly lower than the maximum a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Facto Standard
A ''de facto'' standard is a custom or convention that is commonly used even though its use is not required. is a Latin phrase (literally " of fact"), here meaning "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established". A ''de facto'' standard contrasts an international standard which is defined by an organization such as International Standards Organization, or a standard required by law (also known as ''de jure'' standards). Joint technical committee on information technology (ISO/IEC JTC1) developed a procedure in order for de facto standards to be processed through the formal standardization system to be transformed into international standards from ISO and IEC. In social sciences a voluntary standard that is also a ''de facto'' standard is a typical solution to a coordination problem. The choice of a ''de facto'' standard tends to be stable in situations in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-phase Commit Protocol
In transaction processing, databases, and computer networking, the two-phase commit protocol (2PC, ''tupac'') is a type of Atomic commit, atomic commitment protocol (ACP). It is a distributed algorithm that coordinates all the processes that participate in a Distributed transaction, distributed atomic transaction on whether to Commit (data management), commit or abort (roll back) the transaction. This protocol (a specialised type of Consensus (computer science), consensus protocol) achieves its goal even in many cases of temporary system failure (involving either process, network node, communication, etc. failures), and is thus widely used.Phil Bernstein, Philip A. Bernstein, Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman (1987) ''Concurrency Control and Recovery in Database Systems'' Chapter 7, Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen (2001) ''Transactional Information Systems'' Chapter 19, Elsevier, Philip A. Bernstein, Eric Newcomer (2009)''Principles of Transact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-phase Locking
In databases and transaction processing, two-phase locking (2PL) is a pessimistic concurrency control method that guarantees conflict-serializability. Philip A. Bernstein, Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman (1987) ''Concurrency Control and Recovery in Database Systems'' Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen (2001) ''Transactional Information Systems'' Elsevier, It is also the name of the resulting set of database transaction schedules (histories). The protocol uses locks, applied by a transaction to data, which may block (interpreted as signals to stop) other transactions from accessing the same data during the transaction's life. By the 2PL protocol, locks are applied and removed in two phases: # Expanding phase: locks are acquired and no locks are released. # Shrinking phase: locks are released and no locks are acquired. Two types of locks are used by the basic protocol: ''Shared'' and ''Exclusive'' locks. Refinements of the basic protocol may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necessary Condition
In logic and mathematics, necessity and sufficiency are terms used to describe a conditional or implicational relationship between two statements. For example, in the conditional statement: "If then ", is necessary for , because the truth of is guaranteed by the truth of . (Equivalently, it is impossible to have without , or the falsity of ensures the falsity of .) Similarly, is sufficient for , because being true always implies that is true, but not being true does not always imply that is not true. In general, a necessary condition is one (possibly one of several conditions) that must be present in order for another condition to occur, while a sufficient condition is one that produces the said condition. The assertion that a statement is a "necessary ''and'' sufficient" condition of another means that the former statement is true if and only if the latter is true. That is, the two statements must be either simultaneously true, or simultaneously false. In ordinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Commitment Protocol
Atomic may refer to: * Of or relating to the atom, the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains its chemical properties * Atomic physics, the study of the atom * Atomic Age, also known as the "Atomic Era" * Atomic scale, distances comparable to the dimensions of an atom * Atom (order theory), in mathematics * Atomic (coffee machine), a 1950s stovetop coffee machine * Atomic (cocktail), a champagne cocktail * ''Atomic'' (magazine), an Australian computing and technology magazine * Atomic Skis, an Austrian ski producer Music * Atomic (band), a Norwegian jazz quintet * ''Atomic'' (Lit album), 2001 * ''Atomic'' (Mogwai album), 2016 * ''Atomic'', an album by Rockets, 1982 * ''Atomic'' (EP), by , 2013 * "Atomic" (song), by Blondie, 1979 * "Atomic", a song by Tiger Army from '' Tiger Army III: Ghost Tigers Rise'' See also * * * Atom (other) * Atomicity (database systems) * Atomism, philosophy about the basic building blocks of reality * Atomic City ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |