|
Cleaver (knife)
A cleaver is a large knife that varies in its shape but usually resembles a rectangular-bladed tomahawk. It is largely used as a kitchen or butcher knife and is mostly intended for splitting up large pieces of soft bones and slashing through thick pieces of meat. The knife's broad side can also be used for crushing in food preparation (such as garlic) and can also be used to scoop up chopped items. Tools described as cleavers have been in use since the Acheulean period. "Cleaver" was commonly spelled ''clever'' in the late 17th century. Design In contrast to other kitchen knives, the cleaver has an especially tough edge meant to withstand repeated blows directly into thick meat, dense cartilage, bone, and the cutting board below. This resilience is accomplished by using a softer, tougher steel and a thicker blade, because a harder steel or thinner blade might fracture or buckle under hard use. In use, it is swung like a meat tenderizer or hammer the knife's design re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butcher
A butcher is a person who may Animal slaughter, slaughter animals, dress their flesh, sell their meat, or participate within any combination of these three tasks. They may prepare standard cuts of meat and poultry for sale in retail or wholesale food establishments. A butcher may be employed by supermarkets, grocery stores, butcher shops and fish markets, slaughter houses, or may be Self-employment, self-employed. Butchery is an ancient trade, whose duties may date back to the domestication of livestock; its practitioners formed guilds in England as far back as 1272. Since the 20th century, many countries and local jurisdictions offer Professional certification, trade certifications for butchers in order to ensure quality, safety, and health standards but not all butchers have formal certification or training. Trade qualification in English-speaking countries is often earned through an apprenticeship although some training organisations also certify their students. In Canada, onc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Food Preparation Utensils
Chinese may refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China. **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese characters in traditional and simplified forms) *** Standard Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchen Knives
A kitchen knife is any knife that is intended to be used in food preparation. While much of this work can be accomplished with a few general-purpose knives — notably a large chef's knife and a smaller serrated blade utility knife — there are also many specialized knives that are designed for specific tasks such as a toughness, tough cleaver, a small #Paring, paring knife, and a bread knife. Kitchen knives can be made from several different materials, though the most common is a hardened steel blade with a wooden handle. Historically, knives were made in "knife cities" that are noted for being the best at their production in that country with the pre-emininent, in Europe, being: Sheffield in Yorkshire, North of England; Thiers, Puy-de-Dôme in the Auvergne of France; Solingen in the North Rhine-Westphalia, Northern Rhineland of Germany; and Eskilstuna of Södermanland County in Sweden. Each of these produced knives in a styles particular to the city, with Thiers especially bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deba Bōchō
— "fish-preparer" — are a style of Japanese kitchen knives primarily used to cut fish, though are also used occasionally in cutting meat. ''Debas'' have wide blades and are the thickest of all Japanese kitchen knives and come in different sizes — sometimes up to in length and thick — but usually considerably shorter, normally between long with a blade between thick. The larger form of knife is called an ''hon-deba'', ("true deba") whereas the smaller form is a ''ko-deba''. The ''deba bōchō'' first appeared during the Edo period in Sakai. Following the traditions of Japanese knives, they have just a single bevel to the edge — with an urasuki hollow back on premium blades — so generally come in just right-handed versions, but left-handed ones can be found in specialist shops. It is designed to behead and fillet fish. A deba's thickness, and often a more obtuse angle on the back of the heel allow it to cut off the heads of fish without damage. The rest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Cutlery
A Japanese kitchen knife is a type of kitchen knife used for food preparation. These knives come in many different varieties and are often made using traditional Japanese blacksmithing techniques. They can be made from stainless steel, or ''hagane'', which is the same kind of steel used to make Japanese swords. Most knives are referred to as or the variation ''-bōchō'' in compound words (because of rendaku) but can have other names including . There are four general categories used to distinguish the Japanese knife designs: handle (Western vs. Japanese); blade grind (single bevel, '' kataba'' v. double bevel, '' ryōba''); steel (stainless v. carbon); and construction (laminated v. mono-steel). Handles Western handles have a bolster and a full or partial tang. These handles are often heavier, but are smaller in volume and surface area than most Japanese handles. The scale materials are often synthetic or resin-cured wood and are non-porous. Chefs who prefer the feel of a W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Chef's Knife
A Chinese chef's knife — sometimes referred to as a Càidāo ( zh, 菜刀, lit. "vegetable knife"), is a Chinese, rectangular-bladed, all-purpose chef's knife used to prepare a variety of meats, fish and vegetables. The popularity of this style of knife has spread with the associated cuisines. They resemble Western cleavers in appearance, but most Chinese chef's knives are relatively thin-bladed and designed for slicing, finely chopping and mincing vegetables, fish and boneless meats. The heavier ''gǔdāo'' ( zh, 骨刀, lit. "bone knife") are produced and are used much like Western-type meat cleavers to prepare large sides of beef, pork and other boned meats. However, Chinese-style knives of this mass are not common in the West. The Chinese chef's knife is frequently incorrectly referred to as a "cleaver", due its similar rectangular shape. However, Chinese chef's knives are much thinner in cross-section and are intended more as general-purpose kitchen knives, and mostly used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
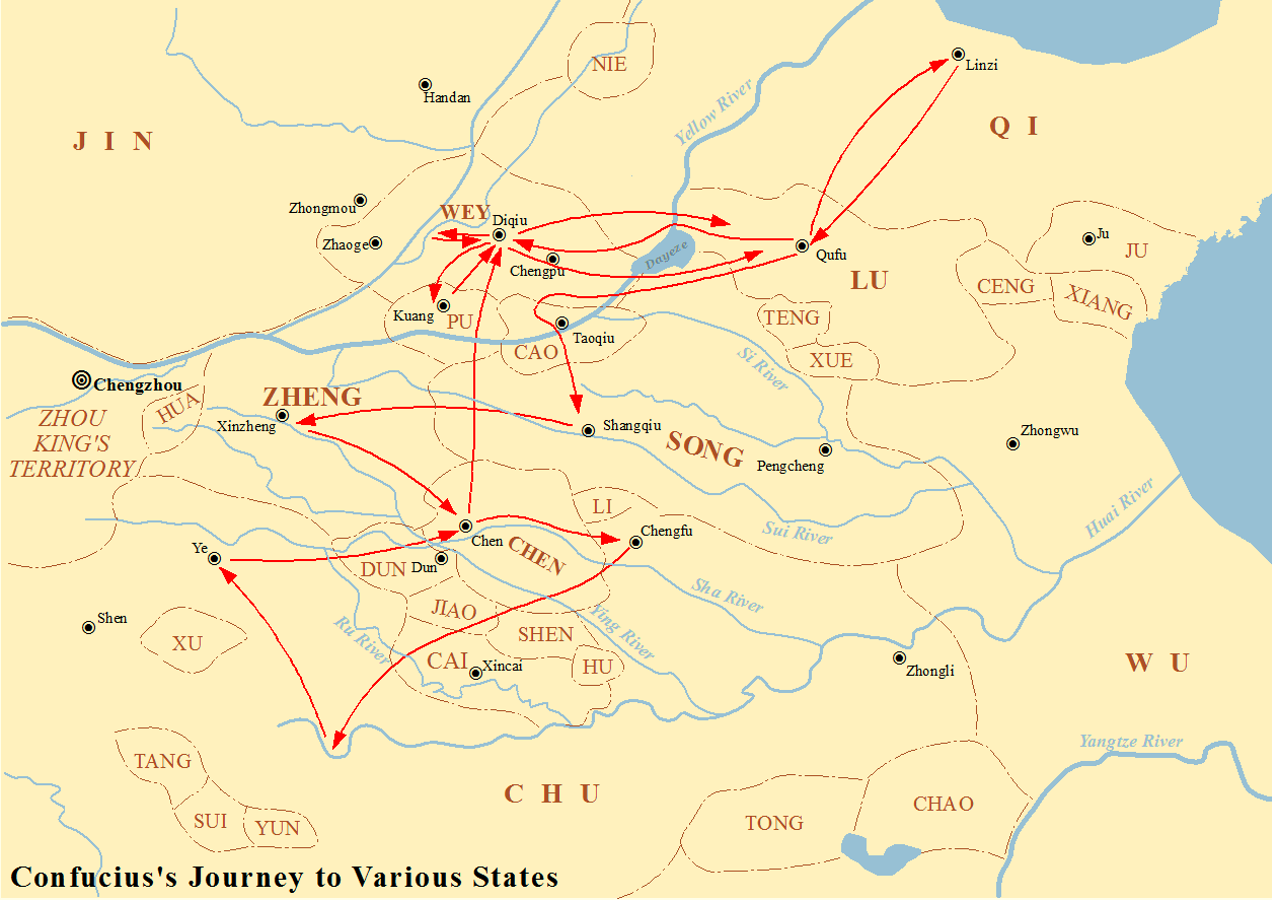
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junzi
The word junzi ( or "Son of the Vassal, or Monarch") is a Chinese philosophical term often translated as "gentleman", "superior person",Sometimes "exemplary person". Paul R. Goldin translates it "noble man" in an attempt to capture both its early political and later moral meaning. Cf.Confucian Key Terms: Junzi". or "noble man". Since the characters are overtly gendered, the term is frequently translated as "gentleman"; gentry and distinguished/moral person are common gender-neutral translations. Traditionally referring to the "aristocratic nobility of the Zhou", ''Junzi'' is employed in the Book of Changes to mean a superior man, and by Confucius in his works to describe a virtuous person with noble characters. In Confucianism In Confucianism, the ideal personality is the 聖 ''shèng'', translated as saint or sage. However, since sagehood is unattainable for most people, Confucius articulated a less demanding ideal of a cultured and moral life, using the term ''junzi''—or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuangzi (book)
The ''Zhuangzi'' (historically romanized ) is an ancient Chinese text that is one of the two foundational texts of Taoism, alongside the ''Tao Te Ching''. It was written during the late Warring States period (476–221 BC) and is named for its traditional author, Zhuang Zhou, who is customarily known as "Zhuangzi" ("Master Zhuang"). The ''Zhuangzi'' consists of stories and maxims that exemplify the nature of the ideal Taoist sage. It recounts many anecdotes, allegories, parables, and fables, often expressed with irreverence or humor. Recurring themes include embracing spontaneity and achieving freedom from the human world and its conventions. The text aims to illustrate the arbitrariness and false dichotomy, ultimate falsity of dichotomies normally embraced by human societies, such as those between good and bad, large and small, life and death, or human and nature. In contrast with the focus on good morals and personal duty expressed by many Chinese philosophers of the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Saw
A bone cutter is a surgical instrument used to cut or remove bones. In addition to surgery, they are also used in forensics and dismemberment. Types of medical bone cutters include: * unpowered saw, Unpowered – Unpowered bone cutting implements include varieties of hacksaw. In many applications, the saw is used in specialised jig (tool), jigs to provide accurate, measurable cuts, e.g. in knee surgery. Specialized saws such as the Gigli saw, a cable made of sharp strands of wire, are also used in some procedures. * reciprocating saw, Reciprocating – Usually a powered rotary oscillation is applied to a specialised cutting implement to provide smooth controllable cuts into bone, for applications, from skull cutting to rib cutting. A sternal saw is a reciprocating bone cutter. * Sonic (or sound cutting) – The sonic cutter is still experimental, but its primary focus is to use high frequency, high amplitude sound to remove material (in this case bone), providing the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |