|
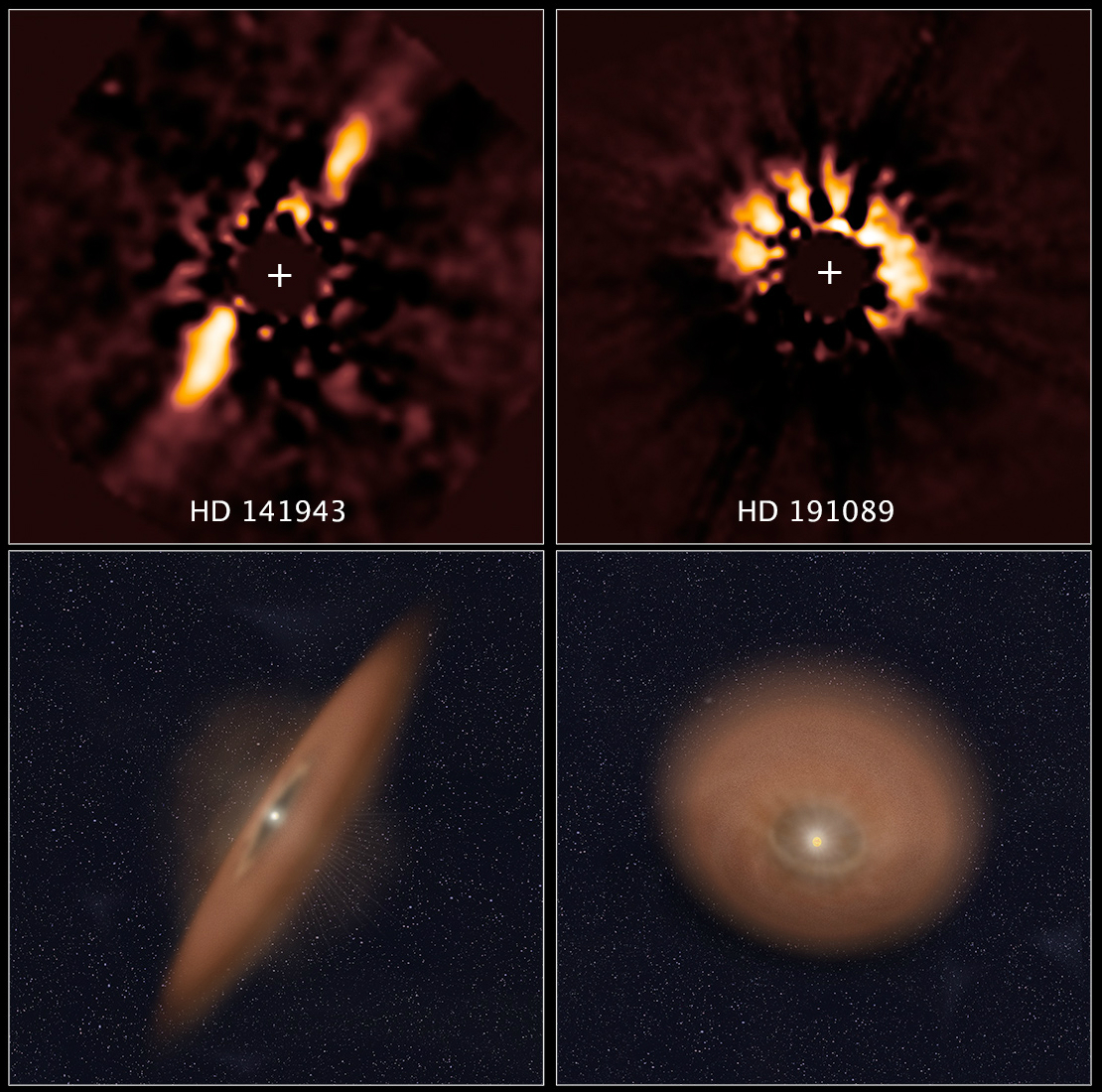
Circumstellar Dust
Circumstellar dust is cosmic dust around a star. It can be in the form of a spherical shell or a disc, e.g. an accretion disk. Circumstellar dust can be responsible for significant extinction and is usually the source of an infrared excess for stars that have it. For some evolved stars on the asymptotic giant branch, the dust is composed of silicate emissions while others contain the presence of other dust components. According to a study, it is still uncertain whether the dust is a result of crystalline silicate or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. However, recent observations revealed that Vega-type stars display broad silicate emission. It is suggested that the circumstellar dust components can depend on the evolutionary stage of a star and is related to the changes in its physical conditions. The motion of circumstellar dust is governed by forces due to stellar gravity and radiation pressure. Circumstellar dust in the Solar System causes the zodiacal light. See also * Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
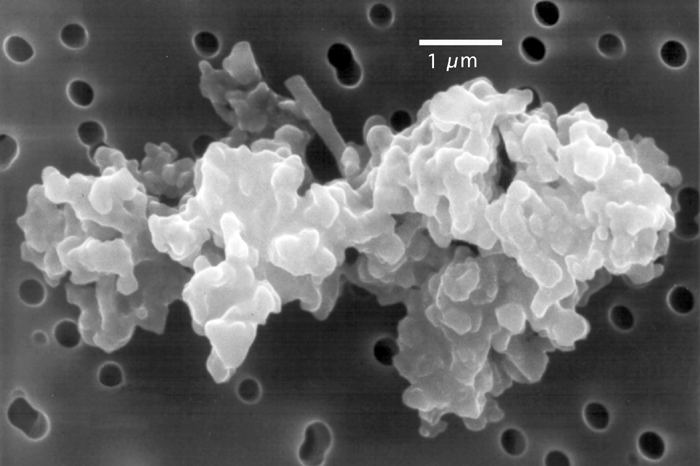
Cosmic Dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are called meteoroids. Cosmic dust can be further distinguished by its astronomical location: intergalactic dust, interstellar dust, interplanetary dust (such as in the zodiacal cloud) and circumplanetary dust (such as in a planetary ring). There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement. In the Solar System, interplanetary dust causes the zodiacal light. Solar System dust includes comet dust, asteroidal dust, dust from the Kuiper belt, and interstellar dust passing through the Solar System. Thousands of tons of cosmic dust are estimated to reach the Earth's surface every year, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, profes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System about 4.6 billion years ago, they aid study of its formation. Formation A widely accepted theory of planet formation, the so-called planetesimal hypotheses, the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis and that of Viktor Safronov, states that planets form from cosmic dust grains that collide and stick to form ever-larger bodies. Once a body reaches around a kilometer in size, its constituent grains can attract each other directly through mutual gravity, enormously aiding further growth into moon-sized protoplanets. Smaller bodies must instead rely on Brownian motion or turbulence to cause the collisions leading to sticking. The mechanics of collisions and mechanisms of sticking are intricate. Alternatively, planetesimals may for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
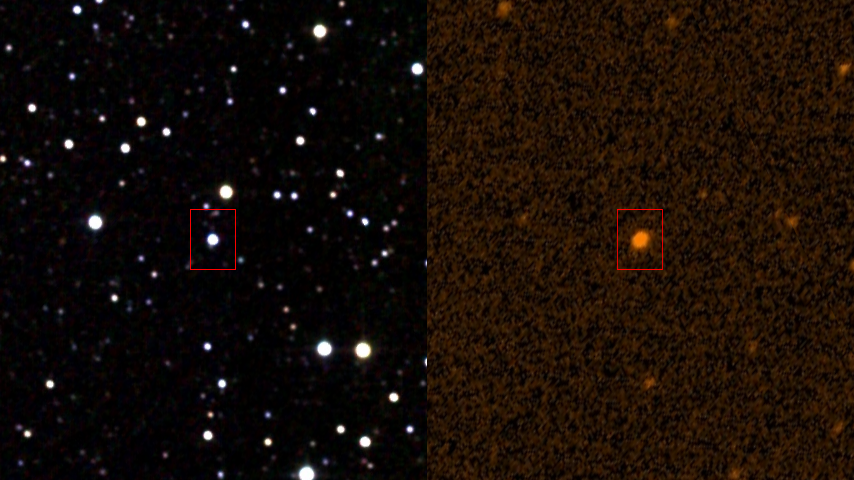
WD 1145+017
WD 1145+017 (also known as EPIC 201563164) is a white dwarf approximately from Earth in the constellation of Virgo. It is the first white dwarf to be observed with a transiting planetary-mass object orbiting it. Stellar characteristics The white dwarf has a mass of 0.6 , radius of 0.02 (1.4 ) and a temperature of 15,020 K, typical for white dwarf stars. It has been a white dwarf for 224 million years. The star included strong absorption lines due to magnesium, aluminium, silicon, calcium, iron and nickel. These elements commonly found in rocky planets are polluting the surface of the star, and would normally be expected to mix through the star and disappear from view after a million years. A circumstellar dust cloud and disk (likely due to disintegrating asteroids, located at 97 to 103 R_wd, and emitting thermal IR radiation) surrounds the star. In addition, a circumstellar gas disk (located ~ 25 to 40 R_wd, and undergoing relativistic precession with a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Stars That Have Unusual Dimming Periods
This list of stars that have unusual dimming periods is a table of stars that have been observed to darken and brighten and don't appear to be eclipsing binaries or intrinsic variables. It's based on studies searching for analogs of Tabby's Star. The listing here is ordered alphabetically. __TOC__ List See also * BD+20°307 * Disrupted planet * Ecliptic Plane Input Catalog (EPIC) * Gaia16aye * Lists of astronomical objects * List of semiregular variable stars * Lists of stars * List of variable stars * Search for extraterrestrial intelligence * WD 0145+234 (star disrupting an exoasteroid) References External links SIMBAD Astronomical Databaseby the Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentrici ... {{DEFAULT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabby's Star
Tabby's Star (also known as Boyajian's Star and WTF Star, and designated KIC 8462852 in the Kepler Input Catalog) is an F-type main-sequence star in the constellation Cygnus approximately from Earth. Unusual light fluctuations of the star, including up to a 22% dimming in brightness, were discovered by citizen scientists as part of the Planet Hunters project. In September 2015, astronomers and citizen scientists associated with the project posted a preprint of an article describing the data and possible interpretations. The discovery was made from data collected by the Kepler space telescope, which observed changes in the brightness of distant stars to detect exoplanets. Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the star's large irregular changes in brightness as measured by its light curve, but none to date fully explain all aspects of the curve. One explanation is that an " uneven ring of dust" orbits Tabby's Star. In another explanation, the star's lumino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumplanetary Disk
A circumplanetary disk (or circumplanetary disc) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accumulation of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids or collision fragments in orbit around a planet. Around the planets, they are the reservoirs of material out of which moons (or exomoons or subsatellites) may form. Such a disk can manifest itself in various ways. In August 2018 astronomers reported the probable detection of a circumplanetary disk around CS Cha B. The authors state that "The CS Cha system is the only system in which a circumplanetary disc is likely present as well as a resolved circumstellar disc." In 2020 though, the parameters of CS Cha B were revised, making it an accreting red dwarf star, and making the disk circumstellar. In June 2019 astronomers reported the detection of evidence of a circumplanetary disk around PDS 70b using spectroscopy and accretion signatures. Both types of these signatures were also detected for other planetary candidates before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion Disc
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other forces induce instabilities causing orbiting material in the disk to spiral inward towards the central body. Gravitational and frictional forces compress and raise the temperature of the material, causing the emission of electromagnetic radiation. The frequency range of that radiation depends on the central object's mass. Accretion disks of young stars and protostars radiate in the infrared; those around neutron stars and black holes in the X-ray part of the spectrum. The study of oscillation modes in accretion disks is referred to as diskoseismology. Manifestations Accretion disks are a ubiquitous phenomenon in astrophysics; active galactic nuclei, protoplanetary disks, and gamma ray bursts all involve accretion disks. These disks ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zodiacal Light
The zodiacal light (also called false dawn when seen before sunrise) is a faint glow of diffuse sunlight scattered by interplanetary dust. Brighter around the Sun, it appears in a particularly dark night sky to extend from the Sun's direction in a roughly triangular shape along the zodiac, and appears with less intensity and visibility along the whole ecliptic as the zodiacal band. Zodiacal light spans the entire sky and contributes to the natural light of a clear and moonless night sky. A related phenomenon is '' gegenschein'' (or ''counterglow''), sunlight backscattered from the interplanetary dust, appearing directly opposite to the Sun as a faint but slightly brighter oval glow. Zodiacal light is very faint, often outshined and rendered invisible by moonlight or light pollution. The interplanetary dust in the Solar System forms a thick, pancake-shaped cloud called the zodiacal cloud which straddles the ecliptic plane. The particle sizes range from 10 to 300 microm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
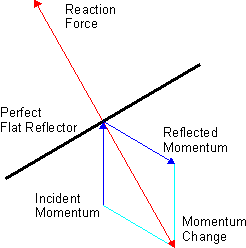
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |