|
Chronobiotic
A chronobiotic is an agent that can cause phase adjustment of the circadian rhythm (biological body clock). That is, it is a substance capable of therapeutically entraining or re-entraining long-term desynchronized or short-term dissociated circadian rhythms in mammals, or prophylactically preventing their disruption following an environmental insult such as is caused by rapid travel across several time zones. The most widely recognized chronobiotic is the hormone melatonin, secreted at night in both diurnal and nocturnal species. History The concept of chronobiotics arose from the characterization of the pineal gland. In 1917, Carey Pratt McCord and Floyd Pierpont Allen at Johns Hopkins University demonstrated that tadpoles hatched in water that contained crushed pineal gland were much lighter in color than tadpoles hatched in normal water. No one could explain this phenomenon, and pineal gland research halted until the 1950s. Mark Altschule and Julian Kitay, both physicians a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melatonin
Melatonin is a natural product found in plants and animals. It is primarily known in animals as a hormone released by the pineal gland in the brain at night, and has long been associated with control of the sleep–wake cycle. In vertebrates, melatonin is involved in synchronizing circadian rhythms, including sleep–wake timing and blood pressure regulation, and in control of seasonal rhythmicity including reproduction, fattening, moulting and hibernation. Many of its effects are through activation of the melatonin receptors, while others are due to its role as an antioxidant. In plants, it functions to defend against oxidative stress. It is also present in various foods. Melatonin was discovered in 1958. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, melatonin is used as a dietary supplement and medication in the treatment of sleep disorders such as insomnia and circadian rhythm sleep disorders; for information on melatonin as a supplement and medication, see the melatoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland, conarium, or epiphysis cerebri, is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. The pineal gland produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone which modulates sleep, sleep patterns in both circadian rhythm, circadian and Season, seasonal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two cerebral hemisphere, hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. The pineal gland is one of the neuroendocrinology, neuroendocrine Circumventricular organs, secretory circumventricular organs in which capillaries are mostly Vascular permeability, permeable to solutes in the blood. Nearly all vertebrate species possess a pineal gland. The most important exception is a primitive vertebrate, the hagfish. Even in the hagfish, however, there may be a "pineal equivalent" structure in the dorsal diencephalon. The lanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the environment (Entrainment (chronobiology), entrained by the environment). These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ''wikt:circa#Latin, circa'', meaning "approximately", and ''dies'', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers (German for "time givers"), which include light, temperature and redox cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and maternal attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Structure T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronobiology
Chronobiology is a field of biology that examines timing processes, including periodic (cyclic) phenomena in living organisms, such as their adaptation to solar- and lunar-related rhythms. These cycles are known as biological rhythms. Chronobiology comes from the ancient Greek χρόνος (''chrónos'', meaning "time"), and biology, which pertains to the study, or science, of life. The related terms ''chronomics'' and ''chronome'' have been used in some cases to describe either the molecular mechanisms involved in chronobiological phenomena or the more quantitative aspects of chronobiology, particularly where comparison of cycles between organisms is required. Chronobiological studies include but are not limited to comparative anatomy, physiology, genetics, molecular biology and behavior of organisms related to their biological rhythms. Other aspects include epigenetics, development, reproduction, ecology and evolution. The subject Chronobiology studies variations of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
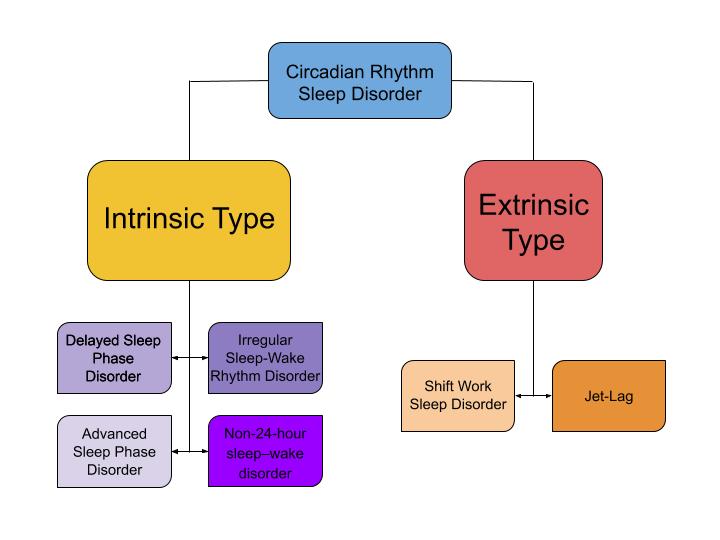
Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSD), also known as circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders (CRSWD), are a family of sleep disorders which affect the timing of sleep. CRSDs arise from a persistent pattern of sleep/wake disturbances that can be caused either by dysfunction in one's biological clock system, or by misalignment between one's endogenous oscillator and externally imposed cues. As a result of this mismatch, those affected by circadian rhythm sleep disorders have a tendency to fall asleep at unconventional time points in the day. These occurrences often lead to recurring instances of disturbed rest, where individuals affected by the disorder are unable to go to sleep and awaken at "normal" times for work, school, and other social obligations. Delayed sleep phase disorder, advanced sleep phase disorder, non-24-hour sleep–wake disorder and irregular sleep–wake rhythm disorder represents the four main types of CRSD. Overview Humans, like most living organisms, have v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic beta carbon substituent. It is essential in humans, meaning that the body cannot synthesize it and it must be obtained from the diet. Tryptophan is also a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, the hormone melatonin, and vitamin B3. It is encoded by the codon UGG. Like other amino acids, tryptophan is a zwitterion at physiological pH where the amino group is protonated (–; pKa = 9.39) and the carboxylic acid is deprotonated ( –COO−; pKa = 2.38). Humans and many animals cannot synthesize tryptophan: they need to obtain it through their diet, making it an essential amino acid. Function Amino acids, including tryptophan, are used as building blocks in protein biosynthesis, and proteins are required to sustain life. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
The suprachiasmatic nucleus or nuclei (SCN) is a tiny region of the brain in the hypothalamus, situated directly above the optic chiasm. It is responsible for controlling circadian rhythms. The neuronal and hormonal activities it generates regulate many different body functions in a 24-hour cycle. The mouse SCN contains approximately 20,000 neurons. The SCN interacts with many other regions of the brain. It contains several cell types and several different peptides (including vasopressin and vasoactive intestinal peptide) and neurotransmitters. Neuroanatomy The SCN is situated in the anterior part of the hypothalamus immediately dorsal, or ''superior'' (hence supra) to the optic chiasm (CHO) bilateral to (on either side of) the third ventricle. The nucleus can be divided into ventrolateral and dorsolateral portions, also known as the core and shell, respectively. These regions differ in their expression of the clock genes, the core expresses them in response to stimuli whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranquilizer
A tranquilizer is a drug that is designed for the treatment of anxiety, fear, tension, agitation, and disturbances of the mind, specifically to reduce states of anxiety and tension. Etymology Tranquilizer, as a term, was first used by F.F. Yonkman (1953), from the conclusions of investigative studies using the drug reserpine, which showed the drug had a calming effect on all animals to which it was administered. Reserpine is a centrally acting Rauwolfia alkaloid. The word directly refers to the state of tranquillity in a person and other animals. The term is considered ''popular'' or ''common'', meaning it is not generally in use in the field of medicine. Specifically, it is used in reference to antipsychotic or neuroleptic medications. The term is generally used as a synonym for sedative. When used by health care professionals, it is usually qualified or replaced with more precise terms: * minor tranquilizer usually refers to anxiolytics. * major tranquilizer might refer to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperazine
Piperazine () is an organic compound that consists of a six-membered ring containing two nitrogen atoms at opposite positions in the ring. Piperazine exists as small alkaline deliquescent crystals with a saline taste. The piperazines are a broad class of chemical compounds, many with important pharmacological properties, which contain a core piperazine functional group. Origin and naming Piperazines were originally named because of their chemical similarity with piperidine, part of the structure of piperine in the black pepper plant (''Piper nigrum''). The -az- infix added to "piperazine" refers to the extra nitrogen atom, compared to piperidine. It is important to note, however, that piperazines are ''not'' derived from plants in the '' Piper'' genus. Chemistry Piperazine is freely soluble in water and ethylene glycol, but insoluble in diethyl ether. It is a weak base with two pKb of 5.35 and 9.73 at 25 °C.; the pH of a 10% aqueous solution of piperazine is 10.8–11.8. Pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Since lesions can occur anywhere in the body and the definition of a lesion is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, their sizes, their locations, or their causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries. Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, a "skin lesion" or a " bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |