|
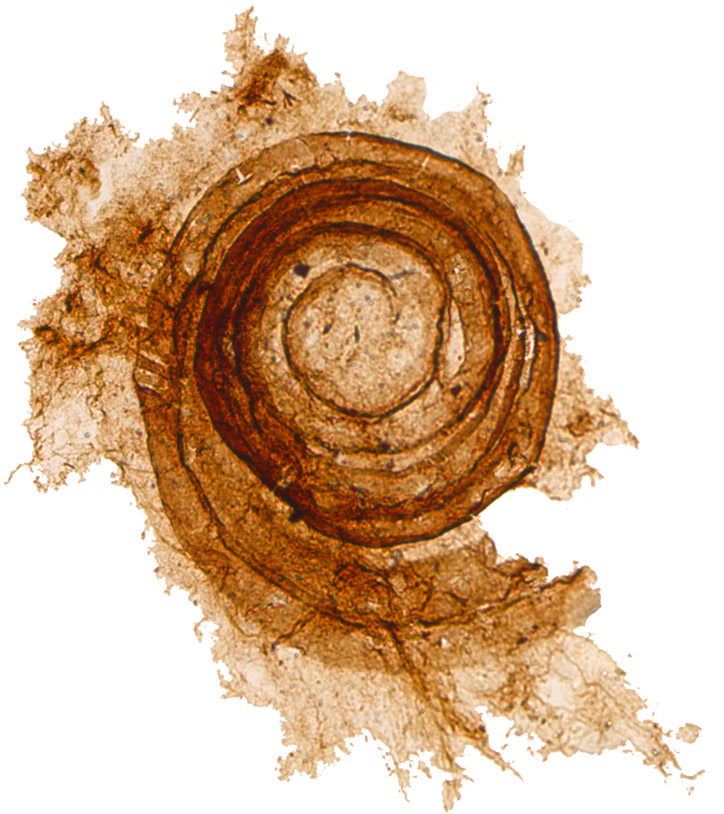
Chitinozoan
Chitinozoa (singular: chitinozoan, plural: chitinozoans) are a group of flask-shaped, organic walled marine microfossils produced by an as yet unknown organism. Common from the Ordovician to Devonian periods (i.e. the mid-Paleozoic), the millimetre-scale organisms are abundant in almost all types of marine sediment across the globe. This wide distribution, and their rapid pace of evolution, makes them valuable biostratigraphic markers. Their bizarre form has made classification and ecological reconstruction difficult. Since their discovery in 1931, suggestions of protist, plant, and fungal affinities have all been entertained. The organisms have been better understood as improvements in microscopy facilitated the study of their fine structure, and it has been suggested that they represent either the eggs or juvenile stage of a marine animal. However, recent research has suggested that they represent the hard shell of a group of protists with uncertain affinities. Chitinozoan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfossil
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, is referred to as a macrofossil. Microfossils are a common feature of the geological record, from the Precambrian to the Holocene. They are most common in deposits of marine environments, but also occur in brackish water, fresh water and terrestrial sedimentary deposits. While every kingdom of life is represented in the microfossil record, the most abundant forms are protist skeletons or microbial cysts from the Chrysophyta, Pyrrhophyta, Sarcodina, acritarchs and chitinozoans, together with pollen and spores from the vascular plants. Overview A microfossil is a descriptive term applied to fossilized plants and animals whose size is just at or below the level at which the fossil can be analyzed by the naked eye. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Eisenack
Alfred Eisenack (born 13 May 1891 in Altfelde, West Prussia, died 19 April 1982 in Reutlingen) was a German paleontologist. He was a pioneer of micropaleontology and palynology. His botanical and mycological author abbreviation is "Eisenack". Eisenack took his photographs using a Leitz monocular microscope, to which he attached a box camera fashioned from a biscuit tin and furnished with glass negatives. He first described chitinozoans and many species of acritarchs, dinoflagellate cysts and graptolites. In 1973 he became an honorary member of the Paleontological Society. Biography Eisenack went to school in Elbing and graduated in 1911 at the University of Jena and in 1913 at the University of Königsberg and began a Ph.D. thesis with Sven Tornquist about the stratigraphy of the Portlandium on Garda Lake. He was not able to finish, as his studies were interrupted by the First World War. He volunteered, and after the Battle of Łódź he was taken as a prisoner of war by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially basidiomycetes and filamentous fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfishes and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radially Symmetrical
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a plane of symmetry down its centre, or a pine cone with a clear symmetrical spiral pattern. Internal features can also show symmetry, for example the tubes in the human body (responsible for transporting gases, nutrients, and waste products) which are cylindrical and have several planes of symmetry. Biological symmetry can be thought of as a balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. Importantly, unlike in mathematics, symmetry in biology is always approximate. For example, plant leaves – while considered symmetrical – rarely match up exactly when folded in half. Symmetry is one class of patterns in nature whereby there is near-repetition of the pattern element, either by reflection or rotatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix " micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test (biology)
In biology, a test is the hard shell of some spherical marine animals and protists, notably sea urchins and microorganisms such as testate foraminiferans, radiolarians, and testate amoebae. The term is also applied to the covering of scale insects. The related Latin term testa is used for the hard seed coat of plant seeds. Etymology The anatomical term "test" derives from the Latin ''testa'' (which means a rounded bowl, amphora or bottle). Structure The test is a skeletal structure, made of hard material such as calcium carbonate, silica, chitin or composite materials. As such, it allows the protection of the internal organs and the attachment of soft flesh. In sea urchins The test of sea urchins is made of calcium carbonate, strengthened by a framework of calcite monocrystals, in a characteristic "stereomic" structure. These two ingredients provide sea urchins with a great solidity and a moderate weight, as well as the capacity to regenerate the mesh from the cuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyte, Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyte, Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and Fern ally, their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and '' protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |