|
Chiavette
Chiavette (plural of it, chiavetta, "little clefs") is a system of standard combinations of clefs used in polyphonic music of the 16th through 18th centuries, differing from the usual ''chiavi naturali'' (the combination of soprano, alto, tenor, and bass clefs.) Typically, these clefs place each staff line a third lower than usual. (A second possible set of clefs, ''in contrabasso,'' places each staff line a third higher; this is less common outside of Franco-Flemish compositions.) The first author to mention a standard set of high clefs is Silvestro Ganassi dal Fontego, in his 1543 ''Regula Rubertina'', chapter 22, which instructs the musician to transpose such music down a fifth. Other theorists, such as Adriano Banchieri (1601) and Picerli (1631), indicate to transpose down a fifth if there is no key signature, and a fourth if there is a flat indicated. By mid-century, Italian commentators only mention a transposition down a fourth, and still later the practice seems to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
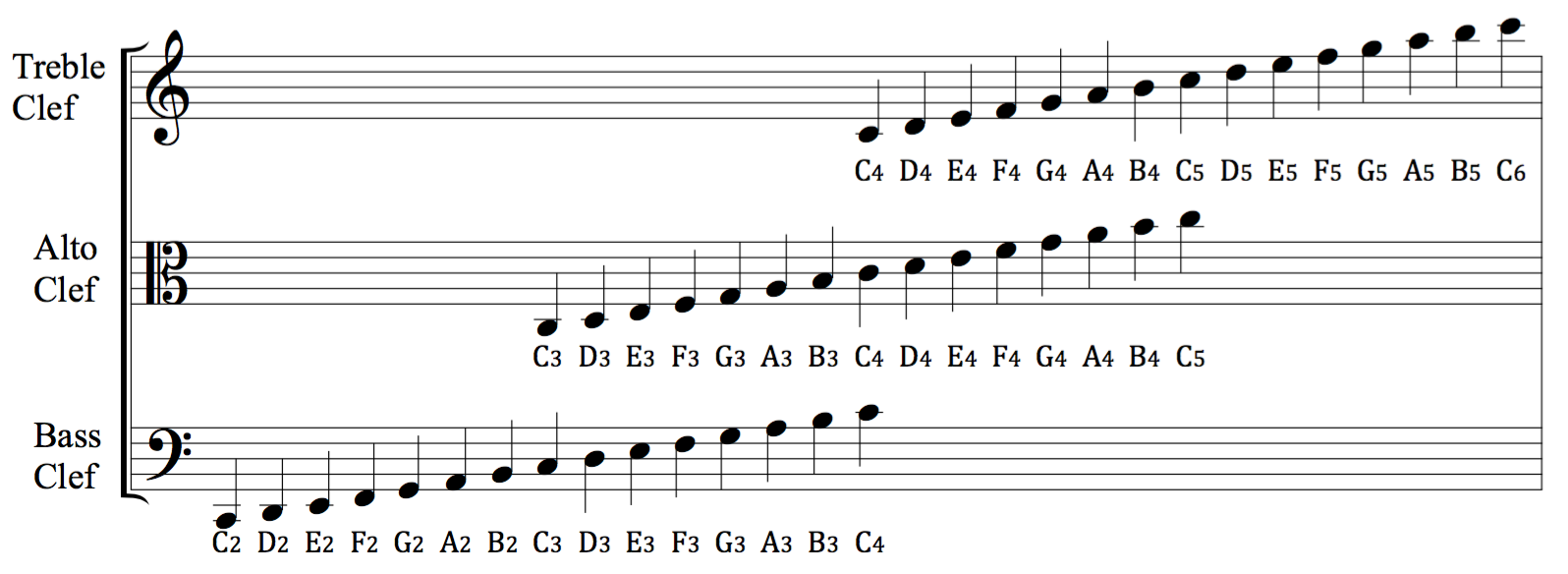
Clef
A clef (from French: 'key') is a Musical notation, musical symbol used to indicate which Musical note, notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff (music), stave. Placing a clef on a stave assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces. The three clef symbols used in modern music notation are the #G-clefs, G-clef, #F-clefs, F-clef, and #C-clefs, C-clef. Placing these clefs on a line fixes a reference note to that line—an F-clef fixes the F below middle C, a C-clef fixes middle C, and a G-clef fixes the G above middle C. In modern music notation, the G-clef is most frequently seen as treble clef (placing Scientific pitch notation, G4 on the second line of the stave), and the F-clef as bass clef (placing F3 on the fourth line). The C-clef is mostly encountered as alto clef (placing middle C on the third line) or tenor clef (middle C on the fourth line). A clef may be placed on a space ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphonic
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords, homophony. Within the context of the Western musical tradition, the term ''polyphony'' is usually used to refer to music of the late Middle Ages and Renaissance. Baroque forms such as fugue, which might be called polyphonic, are usually described instead as contrapuntal. Also, as opposed to the ''species'' terminology of counterpoint, polyphony was generally either "pitch-against-pitch" / "point-against-point" or "sustained-pitch" in one part with melismas of varying lengths in another. In all cases the conception was probably what Margaret Bent (1999) calls "dyadic counterpoint", with each part being written generally against one other part, with all parts modified if needed in the end. This point-against-point conception is opposed to "su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff (music)
In Western culture, Western musical notation, the staff (US and UK)"staff" in the Collins English Dictionary "in British English: also called: stave; plural: staffs or staves""staff" in the Merriam-Webster Dictionary /ref> or stave (UK) (#Usage and etymology, plural: staffs or staves) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, different percussion instruments. Appropriate music symbols, depending on the intended effect, are placed on the staff according to their corresponding pitch or function. Musical notes are placed by pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvestro Ganassi Dal Fontego
Silvestro di Ganassi dal Fontego, also given as Sylvestro di Ganassi dal Fontego, Silvestro Ganasi dal Fontego, and Silvestro dal Fontego (1 January 1492 – 1565) was a Venetian musician and author of two important treatises on instrumental technique. His first treatise covers recorder playing: ''Opera intitulata Fontegara'' (Venice, 1535). His second (in two volumes) is about the viola da gamba: ''Regola Rubertina'' (Venice, 1542) and ''Lettione Seconda'' (Venice, 1543). They cover both technicalities of playing and the subtleties of expression. There is also guidance on ornamentation—''passaggi''. The revival of interest in historically aware musical performance has resulted in renewed interest in Ganassi's writings. His treatises are now available in modern editions. Viol technique Ganassi's ''Regola Rubertina'' is among the earliest sources of advice to the viol player on how to hold the bow. In Chapter III, Ganassi says: You know that the bow is to be held with three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adriano Banchieri
Adriano Banchieri (Bologna, 3 September 1568 – Bologna, 1634) was an Italian composer, music theorist, organist and poet of the late Renaissance and early Baroque eras. He founded the Accademia dei Floridi in Bologna. Biography He was born and died in Bologna (then in the Papal States). In 1587 he became a monk of the Benedictine order, taking his vows in 1590, and changing his name to Adriano (from Tommaso). One of his teachers at the monastery was Gioseffo Guami, who had a strong influence on his style. Like Orazio Vecchi he was interested in converting the madrigal to dramatic purposes. Specifically, he was one of the developers of a form called "madrigal comedy" — unstaged but dramatic collections of madrigals which, when sung consecutively, told a story. Formerly, madrigal comedy was considered to be one of the important precursors to opera, but most music scholars now see it as a separate development, part of a general interest in Italy at the time in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Morley
Thomas Morley (1557 – early October 1602) was an English composer, theorist, singer and organist of the Renaissance. He was one of the foremost members of the English Madrigal School. Referring to the strong Italian influence on the English madrigal, ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' states that Morley was "chiefly responsible for grafting the Italian shoot on to the native stock and initiating the curiously brief but brilliant flowering of the madrigal that constitutes one of the most colourful episodes in the history of English music." Living in London at the same time as Shakespeare, Morley was the most famous composer of secular music in Elizabethan England. He and Robert Johnson are the composers of the only surviving contemporary settings of verse by Shakespeare. Morley was active in church music as a singer, composer and organist at St Paul's Cathedral. He was also involved in music publishing. From 1598 up to his death he held a printing patent (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as ''Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Sadie
Stanley John Sadie (; 30 October 1930 – 21 March 2005) was an influential and prolific British musicologist, music critic, and editor. He was editor of the sixth edition of the '' Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (1980), which was published as the first edition of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians''. Along with Thurston Dart, Nigel Fortune and Oliver Neighbour he was one of Britain's leading musicologists of the post-World War II generation. Career Born in Wembley, Sadie was educated at St Paul's School, London, and studied music privately for three years with Bernard Stevens. At Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge he read music under Thurston Dart. Sadie earned Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Music degrees in 1953, a Master of Arts degree in 1957, and a PhD in 1958. His doctoral dissertation was on mid-eighteenth-century British chamber music. After Cambridge, he taught at Trinity College of Music, London (1957–1965). Sadie then turned to musi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tyrrell (musicologist)
John Tyrrell (17 August 1942 – 4 October 2018) was a British musicologist. He published several books on Leoš Janáček, including an authoritative and largely definitive two-volume biography. Early life Tyrrell was born in Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia (now Harare, Zimbabwe), he studied at the universities of Cape Town, Oxford and Brno. He pursued his Bachelor of Music at the University of Cape Town following which he moved to Oxford University to pursue a doctoral degree under the supervision of Edmund Rubbra Career Tyrrell started his career working in an editorial capacity at The Musical Times. He was a Lecturer in Music at the University of Nottingham (1976), becoming Reader in Opera Studies (1987) and Professor (1996). From 1996 to 2000 he was Executive Editor of the second edition of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (2001). From 2000-08, he was Research Professor at Cardiff University. He received numerous awards and honours throughout his career. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Notation
Music notation or musical notation is any system used to visually represent aurally perceived music played with instruments or sung by the human voice through the use of written, printed, or otherwise-produced symbols, including notation for durations of absence of sound such as rests. The types and methods of notation have varied between cultures and throughout history, and much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time period, such as in the 2010s, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods; for example, for professional classical music performers, sheet music using staves and noteheads is the most common way of notating music, but for professional country music session musicians, the Nashville Number System is the main method. The symbols used include ancient symbols and modern symbols made upon any media such as symbols cut into stone, made in clay tablets, made using a pen on papyrus or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th Century In Music
16 (sixteen) is the natural number following 15 and preceding 17. 16 is a composite number, and a square number, being 42 = 4 × 4. It is the smallest number with exactly five divisors, its proper divisors being , , and . In English speech, the numbers 16 and 60 are sometimes confused, as they sound very similar. Sixteen is the fourth power of two. For this reason, 16 was used in weighing light objects in several cultures. The British have 16 ounces in one pound; the Chinese used to have 16 ''liangs'' in one ''jin''. In old days, weighing was done with a beam balance to make equal splits. It would be easier to split a heap of grains into sixteen equal parts through successive divisions than to split into ten parts. Chinese Taoists did finger computation on the trigrams and hexagrams by counting the finger tips and joints of the fingers with the tip of the thumb. Each hand can count up to 16 in such manner. The Chinese abacus uses two upper beads to represent the 5s and 5 low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |