|
Centaur (astronomy)
In planetary astronomy, a centaur is a small Solar System body with either a perihelion or a semi-major axis between those of the outer planets (between Jupiter and Neptune). Centaurs generally have unstable orbits because they cross or have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets; almost all their orbits have dynamic lifetimes of only a few million years, but there is one known centaur, 514107 Kaʻepaokaʻawela, which may be in a stable (though retrograde) orbit. Centaurs typically exhibit the characteristics of both asteroids and comets. They are named after the mythological centaurs that were a mixture of horse and human. Observational bias toward large objects makes determination of the total centaur population difficult. Estimates for the number of centaurs in the Solar System more than 1 km in diameter range from as low as 44,000 to more than 10,000,000. The first centaur to be discovered, under the definition of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
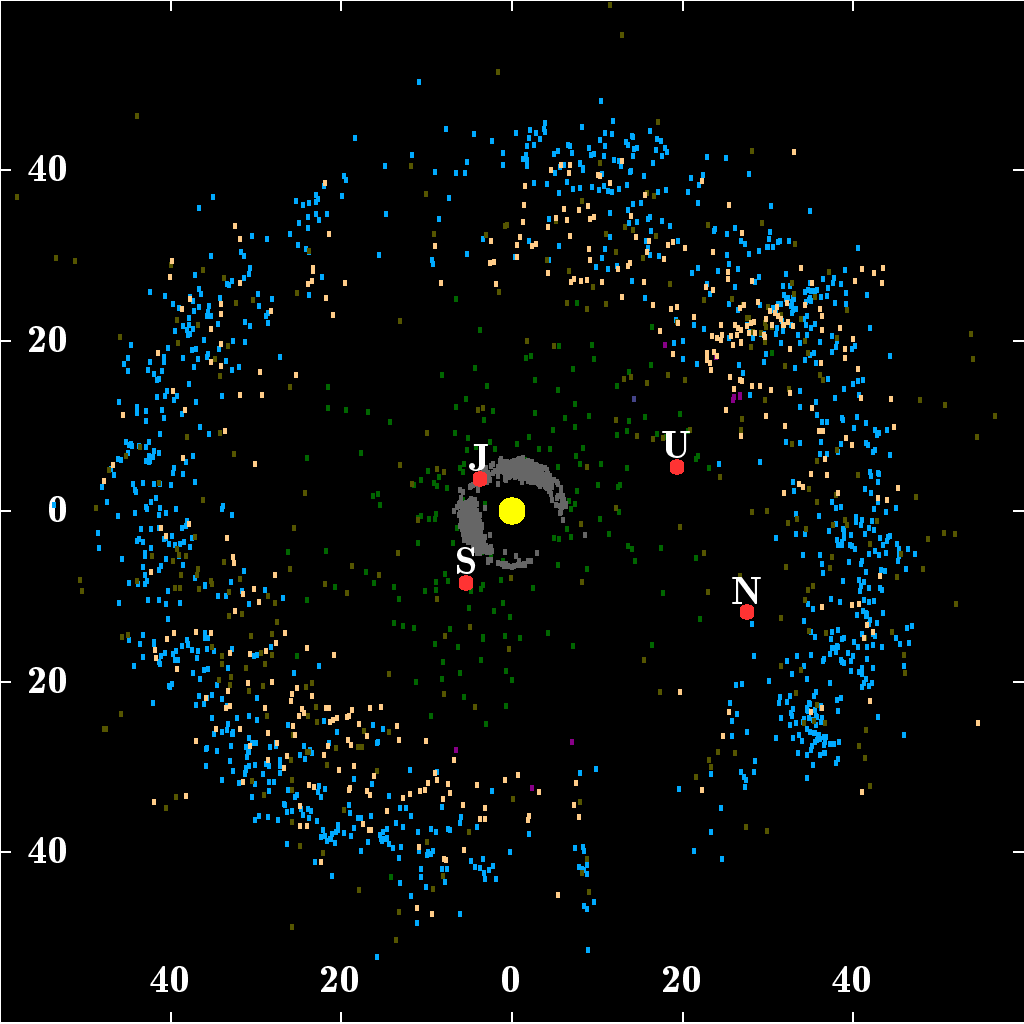
Kuiper Belt Plot Objects Of Outer Solar System
Kuiper is a Dutch occupational surname meaning cooper. Common spelling variants include Kuyper, Kuipers, Kuijper, Kuijpers, Kuypers, and De Kuyper. Notable people with the name include: Kuiper *Adrian Kuiper (born 1959), South African cricketer *Barend Klaas Kuiper (1877–1961), Dutch-American historian * David Kuiper (born 1980), Dutch rower * Duane Kuiper (born 1950), American baseball player * Edith Kuiper (born 1960), Dutch economist *Franciscus Bernardus Jacobus Kuiper (1907–2003), Dutch Indologist * Gerard Kuiper (1905–1973), Dutch-American astronomer after whom the Kuiper belt was named * Glen Kuiper (born 1963) American broadcaster * Hennie Kuiper (born 1949), Dutch cyclist * J. P. Kuiper (1922–1985), Dutch professor of social medicine *Michael Kuiper (born 1989), Dutch martial artist * Nick Kuiper (born 1982), Canadian ice hockey player *Nicky Kuiper (born 1989), Dutch footballer *Nicolaas Kuiper (1920–1994), Dutch mathematician, known for Kuiper's test, Kuip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2060 Chiron
2060 Chiron is a small Solar System body in the outer Solar System, orbiting the Sun between Saturn and Uranus. Discovered in 1977 by Charles Kowal, it was the first-identified member of a new class of objects now known as centaurs—bodies orbiting between the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt.944 Hidalgo, discovered in 1920, also fits this definition, but was not identified as belonging to a distinct population. Although it was initially called an asteroid and classified only as a minor planet with the designation "2060 Chiron", in 1989 it was found to exhibit behavior typical of a comet. Today it is classified as both a minor planet and a comet, and is accordingly also known by the cometary designation 95P/Chiron. Chiron is named after the centaur Chiron in Greek mythology. History Discovery Chiron was discovered on 1 November 1977 by Charles Kowal from images taken on 18 October at Palomar Observatory. It was given the temporary designation of . It was found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60558 Echeclus
60558 Echeclus is a centaur, approximately in diameter, located in the outer Solar System. It was discovered by Spacewatch in 2000 and initially classified as a minor planet with provisional designation (also written 2000 EC98). Research in 2001 by Rousselot and Petit at the Besançon observatory in France indicated that it was not a comet, but in December 2005 a cometary coma was detected. In early 2006 the Committee on Small Bodies Nomenclature (CSBN) gave it the cometary designation 174P/Echeclus. It last came to perihelion in April 2015, and was expected to reach about apparent magnitude 16.7 near opposition in September 2015. Name ''Echeclus'' is a centaur in Greek mythology. 60558 Echeclus is only the second comet (after Chiron) that was named as a minor planet, rather than after the name of its discoverer. Chiron is also a centaur; other centaurs are being observed for signs of a cometary coma. Besides Echeclus, eight other objects are cross-listed as both comet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma (cometary)
The coma is the nebulous envelope around the nucleus of a comet, formed when the comet passes close to the Sun on its highly elliptical orbit; as the comet warms, parts of it sublimate. This gives a comet a "fuzzy" appearance when viewed in telescopes and distinguishes it from stars. The word ''coma'' comes from the Greek "kome" (κόμη), which means "hair" and is the origin of the word ''comet'' itself. The coma is generally made of ice and comet dust. Water composes up to 90% of the volatiles that outflow from the nucleus when the comet is within 3-4 AU of the Sun. The H2O parent molecule is destroyed primarily through photodissociation and to a much smaller extent photoionization. The solar wind plays a minor role in the destruction of water compared to photochemistry. Larger dust particles are left along the comet's orbital path while smaller particles are pushed away from the Sun into the comet's tail by light pressure. On 11 August 2014, astronomers release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceres (dwarf Planet)
Ceres (; minor-planet designation: 1 Ceres) is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the first asteroid discovered, on 1 January 1801, by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily and announced as a new planet. Ceres was later classified as an asteroid and then a dwarf planetthe only one always inside Neptune's orbit. Ceres's small size means that even at its brightest, it is too dim to be seen by the naked eye, except under extremely dark skies. Its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.7 to 9.3, peaking at opposition (when it is closest to Earth) once every 15- to 16-month synodic period. As a result, its surface features are barely visible even with the most powerful telescopes, and little was known about it until the robotic NASA spacecraft ''Dawn'' approached Ceres for its orbital mission in 2015. ''Dawn'' found Ceres's surface to be a mixture of water ice, and hydrated minerals such as carbonates and cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8405 Asbolus
8405 Asbolus is a centaur orbiting in the outer Solar System between the orbits of Jupiter and Neptune. It was discovered on 5 April 1995, by James Scotti and Robert Jedicke of Spacewatch (credited) at Kitt Peak Observatory in Arizona, United States. It is named after Asbolus, a centaur in Greek mythology and measures approximately 80 kilometers in diameter. Orbit and classification Centaurs have short dynamical lifetimes due to perturbations by the giant planets. ''Asbolus'' is estimated to have an orbital half-life of about 860 kiloannum. ''Asbolus'' is currently ''classified'' as a SN centaur since Saturn is considered to control the perihelion and Neptune controls the aphelion. It currently has a perihelion of 6.8 AU, so is also influenced by Jupiter. Centaurs with a perihelion less than 6.6 AU are very strongly influenced by Jupiter and for classification purposes are considered to have a perihelion under the control of Jupiter. In about ten thousand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, may have originated in the region. The Kuiper belt was named after Dutch astronomer Gerard Kuiper, although he did not predict its existence. In 1992, minor planet (15760) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its rings and natural satellites. The Flagship-class robotic spacecraft comprised both NASA's ''Cassini'' space probe and ESA's ''Huygens'' lander, which landed on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. ''Cassini'' was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit, where it stayed from 2004 to 2017. The two craft took their names from the astronomers Giovanni Cassini and Christiaan Huygens. Launched aboard a Titan IVB/Centaur on October 15, 1997, ''Cassini'' was active in space for nearly 20 years, with 13 years spent orbiting Saturn and studying the planet and its system after entering orbit on July 1, 2004. The voyage to Saturn included flybys of Venus (April 1998 and July 1999), Earth (August 1999), the asteroid 2685 Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
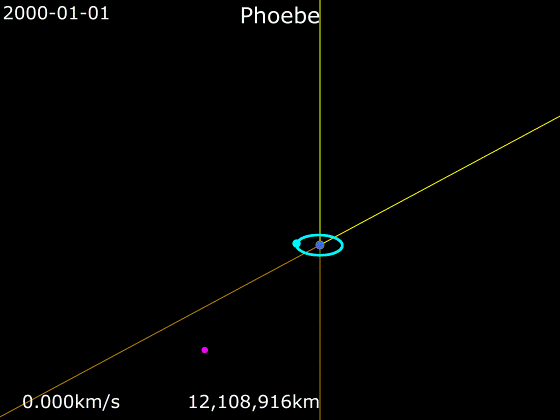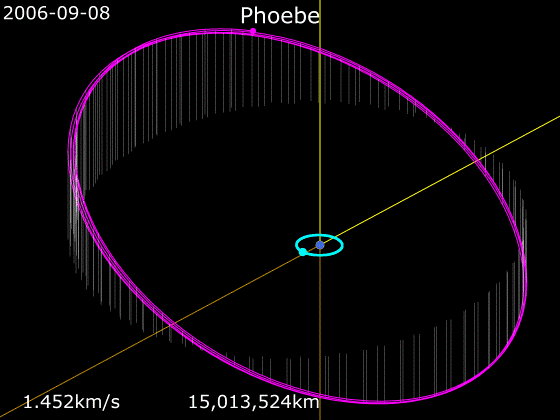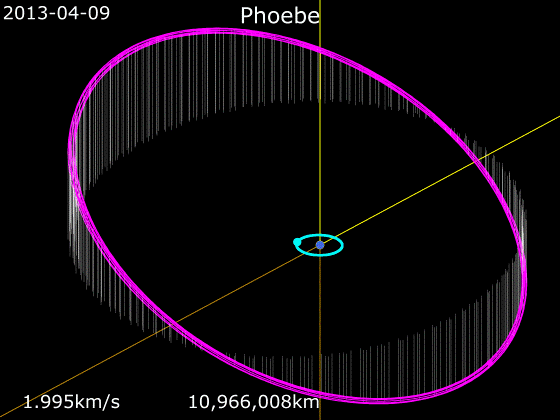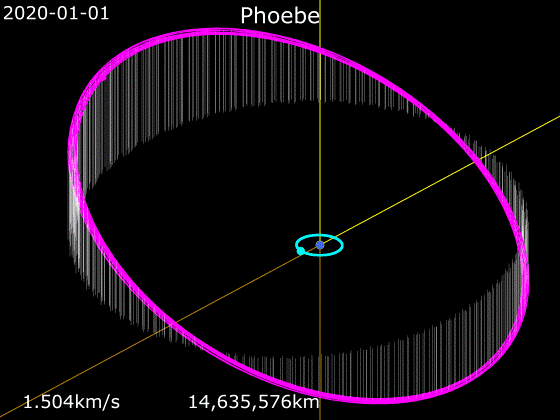
Phoebe (moon)
Phoebe ( ) is an irregular satellite of Saturn with a mean diameter of . It was discovered by William Henry Pickering on March 18, 1899 from photographic plates that had been taken starting on 16 August 1898 at the Boyden Station of the Carmen Alto Observatory near Arequipa, Peru, by DeLisle Stewart. It was the first satellite to be discovered photographically. Phoebe was the first target encountered upon the arrival of the '' Cassini'' spacecraft in the Saturn system in 2004, and is thus unusually well-studied for an irregular satellite of its size. ''Cassinis trajectory to Saturn and time of arrival were specifically chosen to permit this flyby. After the encounter and its insertion into orbit, ''Cassini'' did not go much beyond the orbit of Iapetus. Phoebe is roughly spherical and has a differentiated interior. It was spherical and hot early in its history and was battered out of roundness by repeated impacts. It is believed to be a captured centaur that originated in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; however, with its larger volume, Saturn is over 95 times more massive. Saturn's interior is most likely composed of a core of iron–nickel alloy, iron–nickel and rock (silicon and oxygen compounds). Its core is surrounded by a deep layer of metallic hydrogen, an intermediate layer of liquid hydrogen and liquid helium, and finally, a gaseous outer layer. Saturn has a pale yellow hue due to ammonia crystals in its upper atmosphere. An electrical current within the metallic hydrogen layer is thought to give rise to Saturn's planetary magnetic field, which is weaker than Earth's, but which has a magnetic moment 580 times that of Earth due to Saturn's larger size. Saturn's magnetic field strength is around one-twentieth of Jupiter's. The out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |