|
Categorization
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identifying spam emails and deciding whether to give someone a driving license. As well as 'category', synonyms or near-synonyms for 'class' include 'type', 'species', 'order', 'concept', 'taxon', 'group', 'identification' and 'division'. The meaning of the word 'classification' (and its synonyms) may take on one of several related meanings. It may encompass both classification and the creation of classes, as for example in 'the task of categorizing pages in Wikipedia'; this overall activity is listed under taxonomy. It may refer exclusively to the underlying scheme of classes (which otherwise may be called a taxonomy). Or it may refer to the label given to an object by the classifier. Classification is a part of many different kinds of acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Categorization
Categorization is a type of cognition involving conceptual differentiation between characteristics of conscious experience, such as objects, events, or ideas. It involves the abstraction and differentiation of aspects of experience by sorting and distinguishing between groupings, through classification or typification on the basis of traits, features, similarities or other criteria that are universal to the group. Categorization is considered one of the most fundamental cognitive abilities, and it is studied particularly by psychology and cognitive linguistics. Categorization is sometimes considered synonymous with classification (cf., Classification synonyms). Categorization and classification allow humans to organize things, objects, and ideas that exist around them and simplify their understanding of the world. Categorization is something that humans and other organisms ''do'': "doing the right thing with the right ''kind'' of thing." The activity of categorizing things ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation of things to the classes (classification). Originally, taxonomy referred only to the Taxonomy (biology), classification of organisms on the basis of shared characteristics. Today it also has a more general sense. It may refer to the classification of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such work. Thus a taxonomy can be used to organize species, documents, videos or anything else. A taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon"). Many are hierarchy, hierarchies. One function of a taxonomy is to help users more easily find what they are searching for. This may be effected in ways that include a library classification system and a Taxonomy for search e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Classification (other)
{{disambig ...
Data classification may refer to: * Data classification (data management) * Data classification (business intelligence) * Classification (machine learning), classification of data using machine learning algorithms * Assigning a level of sensitivity to classified information * In computer science, the data type of a piece of data See also * Classification (other) * Categorization Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the data analyzing technique in which task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more Similarity measure, similar (in some specific sense defined by the analyst) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis refers to a family of algorithms and tasks rather than one specific algorithm. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier (other)
Classifier may refer to: *Classifier (linguistics), or ''measure word'', especially in East Asian languages **Classifier handshape Classifier may refer to: *Classifier (linguistics), or ''measure word'', especially in East Asian languages **Classifier handshape, in sign languages *Classifier (UML), in software engineering *Classification rule, in statistical classification, e. ..., in sign languages * Classifier (UML), in software engineering * Classification rule, in statistical classification, e.g.: ** Hierarchical classifier ** Linear classifier * Deductive classifier * Subobject classifier, in category theory *An air classifier or similar machine for sorting materials * Classifier (machine learning) See also * Finite-state machine#Classifiers * * Classification (other) * Classified (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classified (other)
Classified may refer to: General *Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive *Classified advertising or "classifieds" Music *Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper * The Classified, a 1980s American rock band featuring Steve Vai * Classified Records, an American record label Albums * ''Classified'' (Bond album), 2004 * ''Classified'' (Classified album), 2013 * ''Classified'' (Sweetbox album), 2001 *''Classified'', by James Booker, 1982 Songs *"Classified", by C. W. McCall from '' Wolf Creek Pass'', 1975 *"Classified", by the Orb from '' Metallic Spheres'', 2010 *"Classified", by Pete Townshend from the compilation '' Glastonbury Fayre'', 1972 *"Classifieds", by the Academy Is... from '' Almost Here'', 2005 Films and television * ''Classified'' (1925 film), an American silent film *'' Classified: The Edward Snowden Story'', a 2014 Canadian film *'' Classé secret'', a 2022 French Canadian TV series, also known as ''Classified Secret' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (other)
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to: Common uses not otherwise categorized * Class (biology), a taxonomic rank * Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects * Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differently from such group phenomena as "types" or "kinds" * Class (set theory), a collection of sets that can be unambiguously defined by a property that all its members share * Hazard class, a dangerous goods classification * Social class, the hierarchical arrangement of individuals in society, usually defined by wealth and occupation * Working class, can be defined by rank, income or collar Arts, entertainment, and media * "The Class" (song), 1959 Chubby Checker song * Character class in role-playing games and other genres * Class 95 (radio station), a Singaporean radio channel Films * ''Class'' (film), 1983 American film * ''The Class'' (2007 film), 2007 Estonian film * ''The Class'' (2008 film), 2008 film (''Entre les murs'') Televi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category
Category, plural categories, may refer to: General uses *Classification, the general act of allocating things to classes/categories Philosophy * Category of being * ''Categories'' (Aristotle) * Category (Kant) * Categories (Peirce) * Category (Vaisheshika) * Stoic categories * Category mistake Science *Cognitive categorization, categories in cognitive science *Statistical classification, statistical methods used to effect classification/categorization Mathematics * Category (mathematics), a structure consisting of objects and arrows * Category (topology), in the context of Baire spaces * Lusternik–Schnirelmann category, sometimes called ''LS-category'' or simply ''category'' * Categorical data, in statistics Linguistics * Lexical category, a part of speech such as ''noun'', ''preposition'', etc. *Syntactic category, a similar concept which can also include phrasal categories * Grammatical category, a grammatical feature such as ''tense'', ''gender'', etc. Other * Categor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
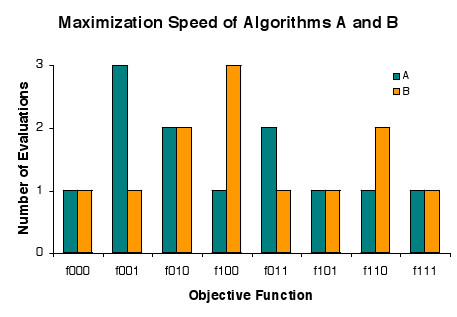
No Free Lunch In Search And Optimization
In computational complexity and optimization the no free lunch theorem is a result that states that for certain types of mathematical problems, the computational cost of finding a solution, averaged over all problems in the class, is the same for any solution method. The name alludes to the saying " no such thing as a free lunch", that is, no method offers a "short cut". This is under the assumption that the search space is a probability density function. It does not apply to the case where the search space has underlying structure (e.g., is a differentiable function) that can be exploited more efficiently (e.g., Newton's method in optimization) than random search or even has closed-form solutions (e.g., the extrema of a quadratic polynomial) that can be determined without search at all. For such probabilistic assumptions, the outputs of all procedures solving a particular type of problem are statistically identical. A colourful way of describing such a circumstance, introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
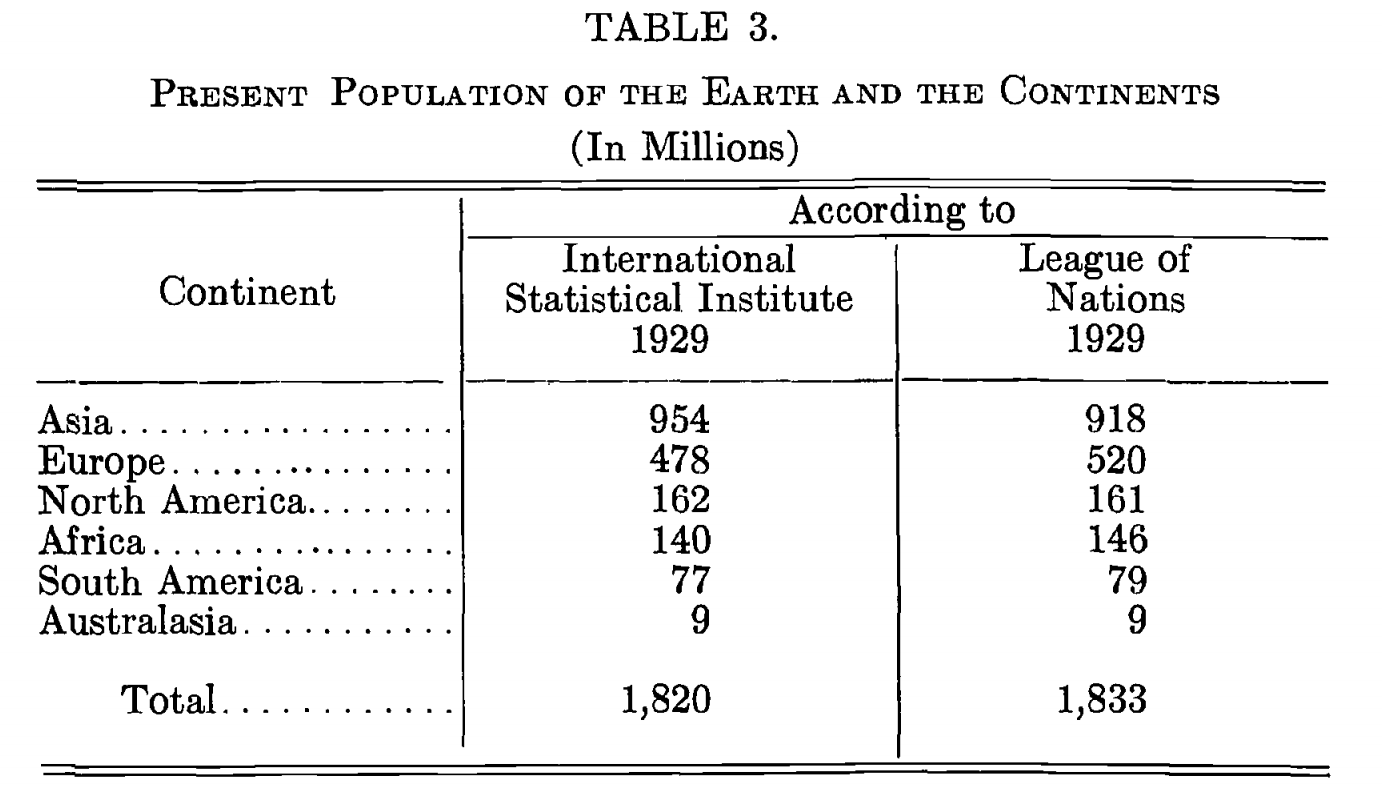
International Statistical Review
The International Statistical Institute (ISI) is a professional association of statisticians. At a meeting of the Jubilee Meeting of the Royal Statistical Society, statisticians met and formed the agreed statues of the International Statistical Institute. It was founded in 1885, although there had been international statistical congresses since 1853. The institute has about 4,000 members from government, academia, and the private sector. The affiliated associations have membership open to any professional statistician. The institute publishes a variety of books and journals, and holds an international conference every two years. The biennial convention was commonly known as the ISI Session; however, since 2011, it is now referred to as the ISI World Statistics Congress. The permanent office of the institute is located in thStatistics Netherlands (CBS)building in the Leidschenveen-Ypenburg district of The Hague, in the Netherlands. It was established in 1913 to preserve documen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision And Recall
In pattern recognition, information retrieval, object detection and classification (machine learning), precision and recall are performance metrics that apply to data retrieved from a collection, corpus or sample space. Precision (also called positive predictive value) is the fraction of relevant instances among the retrieved instances. Written as a formula: \text = \frac Recall (also known as sensitivity) is the fraction of relevant instances that were retrieved. Written as a formula: \text = \frac Both precision and recall are therefore based on relevance. Consider a computer program for recognizing dogs (the relevant element) in a digital photograph. Upon processing a picture which contains ten cats and twelve dogs, the program identifies eight dogs. Of the eight elements identified as dogs, only five actually are dogs ( true positives), while the other three are cats ( false positives). Seven dogs were missed ( false negatives), and seven cats were correctly ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |