|
Caravan City
A caravan city is a city located on and deriving its prosperity from its location on a major trans-desert trade route. The term is believed to have been coined by the great scholar of antiquity, Michael Rostovtzeff, for his work ''O Blijnem Vostoke'', published in English for the first time by the Clarendon Press in 1932 as ''Caravan Cities''. The English translation of the work dealt principally with Petra, Jerash, Palmyra and Dura in the " near east", after Rhodes, Cyprus and Mycenaean Greece were removed from the translation as not being caravan cities. Dura, too, has been later considered to be more than a caravan city.Pierre Leriche, D. N. MacKenzie"Dura Europos" ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'', December 15, 1996, last updated December 2, 2011. Other caravan cities include Aroer in Jordan, Hatra in Iraq, Oualata in Mauritania, Damascus in Syria, and Samarkand in Uzbekistan. The caravan cities of the Near East declined as the small trade states between the Roman and Persian empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Bel, Palmyra 15
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aroer
Aroer ( he, עֲרוֹעֵר, עֲרֹעֵר) is a biblical town on the north bank of the River Arnon to the east of the Dead Sea, in present-day Jordan. The town was an ancient Moabite settlement, and is mentioned in the Bible. Aroer is identified with the modern village of ' Ara'ir in Jordan. Aroer on the Arnon Location Henry Baker Tristram suggested that "Aroer, which is on the edge of the valley of Arnon" () is the place of modern 'Ara'ir on the north bank of the Wadi Mujib ravine, the biblical Arnon stream, about from the mouth of the river. The city was still standing in the time of Eusebius. This place was usually described by its situation, in order to distinguish it from other localities of the same name. Biblical mentions It appears first as having been captured from Moab by the Amorite king Sihon. After the Israelite attack on the Amorites, it was assigned as part of the territory of the tribe of Reuben, whose southern frontier it marked. This is the city mention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Cities
Type may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc. * Data type, collection of values used for computations. * File type * TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file. * Type (Unix), a command in POSIX shells that gives information about commands. * Type safety, the extent to which a programming language discourages or prevents type errors. * Type system, defines a programming language's response to data types. Mathematics * Type (model theory) * Type theory, basis for the study of type systems * Arity or type, the number of operands a function takes * Type, any proposition or set in the intuitionistic type theory * Type, of an entire function ** Exponential type Biology * Type (biology), which fixes a scientific name to a taxon * Dog type, categorization by use or function of domestic dogs Lettering * Type is a design concept for lettering used in typography which helped bring about modern textual p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the East and West. The name "Silk Road", first coined in the late 19th century, has fallen into disuse among some modern historians in favor of Silk Routes, on the grounds that it more accurately describes the intricate web of land and sea routes connecting East and Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the Middle East, East Africa and Europe. The Silk Road derives its name from the highly lucrative trade of silk textiles that were produced almost exclusively in China. The network began with the Han dynasty's expansion into Central Asia around 114 BCE, which largely pacified the once untamed region. Imperial envoy Zhang Qian was commissioned to explore the unknown lands beyond the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes covering Asia, North Africa and Southeast Europe, most notably the Silk Road. Often located along rural roads in the countryside, urban versions of caravanserais were also historically common in cities throughout the Islamic world, and were often called other names such as ''khan'', ''wikala'', or ''funduq''. Terms and etymology Caravanserai Caravanserai ( fa, کاروانسرای, ''kārvānsarāy''), is the Persian compound word variant combining ''kārvān'' "caravan" with ''-sarāy'' "palace", "building with enclosed courts". Here "caravan" means a group of traders, pilgrims or other travellers, engaged in long-distance travel. The word is also rendered as ''caravansary'', ''caravansaray'', ''caravanseray'', ''caravansara'', and ''caravan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
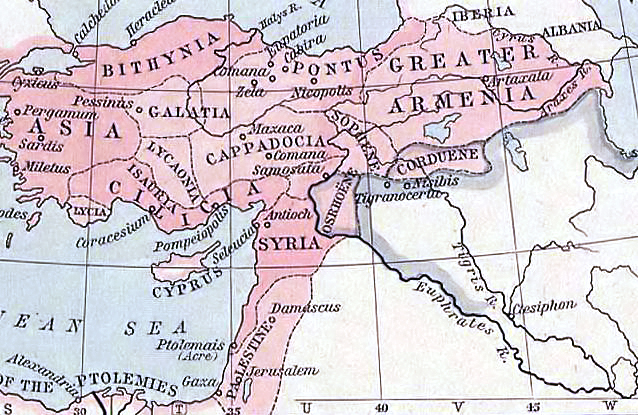
Nisibis
Nusaybin (; '; ar, نُصَيْبِيْن, translit=Nuṣaybīn; syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, translit=Nṣībīn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is predominantly Kurdish. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius ( grc, Μυγδόνιος). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac-speaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanian Defense Lines
The defense lines (or ''"limes"'') of the Sasanians were part of their military strategy and tactics. They were networks of fortifications, walls, and/or ditches built opposite the territory of the enemies. These defense lines are known from tradition and archaeological evidence. The fortress systems of the Western, Arabian, and Central Asian fronts were of both defensive and offensive functions. Mesopotamia The rivers Euphrates, Great Zab, and Little Zab acted as natural defenses for Mesopotamia (Asorestan). Sasanian development of irrigation systems in Mesopotamia further acted as water defense lines, notably the criss-crossing trunk canals in Khuzestan and the northern extension of the Nahrawan Canal, known as the ''Cut of Khusrau'', which made the Sasanian capital Ctesiphon virtually impregnable in late Sasanian period. In the early period of the Sasanian Empire, a number of buffer states existed between Persia and the Roman Empire, which played a major role in Roman-Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin, singular; plural: ) is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of Ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire, but it was not used by the Romans for that purpose. The term has been extended to refer to the frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa. The ''līmes'' is often associated with Roman forts, but the concept could apply to any adjoining area the Romans exercised loose control with military forces. Overview The Roman frontier stretched for more than from the Atlantic coast of northern Britain, through Europe to the Black Sea, and from there to the Red Sea and across North Africa to the Atlantic coast. The remains of the ''limites'' today consist of vestiges of walls, ditches, forts, fortresses, and civilian settlements. Certain elements of the frontier have been excavated, some reconstructed, and a few destroyed. The two sections of ''limes'' in Germany cover a leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarkand
fa, سمرقند , native_name_lang = , settlement_type = City , image_skyline = , image_caption = Clockwise from the top: Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, Sher-Dor Madrasah in Registan, Timur's Mausoleum Gur-e-Amir. , image_alt = , image_flag = , flag_alt = , image_seal = Emblem of Samarkand.svg , seal_alt = , image_shield = , shield_alt = , etymology = , nickname = , motto = , image_map = , map_alt = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Uzbekistan#West Asia#Asia , pushpin_map_alt = , pushpin_mapsize = 300 , pushpin_map_caption = Location in Uzbekistan , pushpin_label_position = , pushpin_relief = 1 , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious". , motto = , image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg , image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg , seal_type = Seal , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Arab world#Asia , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Damascus within Syria , pushpin_relief = 1 , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_name1 = Damascus Governorate, Capital City , government_footnotes = , government_type = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Mohammad Tariq Kreishati , parts_type = Municipalities , parts = 16 , established_title = , established_date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oualata
, settlement_type = Commune and town , image_skyline = Oualata 03.jpg , imagesize = 300px , image_caption = View of the town looking in a southeasterly direction , image_flag = , image_seal = , image_map = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Mauritania , pushpin_label_position = bottom , pushpin_mapsize = 300 , pushpin_map_caption = Location in Mauritania , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_type1 = Region , subdivision_name = Mauritania , subdivision_name1 = Hodh Ech Chargui , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name2 = , established_title = , established_date = , government_type = , leader_title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatra
Hatra ( ar, الحضر; syr, ܚܛܪܐ) was an ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia located in present-day eastern Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. The city lies northwest of Baghdad and southwest of Mosul. Hatra was a strongly fortified caravan city and capital of the small Arab Kingdom of Hatra, located between the Roman and Parthian/Persian empires. Hatra flourished in the 2nd century, and was destroyed and deserted in the 3rd century. Its impressive ruins were discovered in the 19th century. Name Hatra is known as () in Arabic. It is recorded as ''ḥṭrʾ'' (''Ḥaṭrā'') in Hatran Aramaic inscriptions, probably meaning "enclosure, hedge, fence". In Syriac, it is usually recorded in the plural form ''Ḥaṭrē''. In Roman works, it is recorded as Greek ''Átra'' and Latin ' and '. The city was officially called ''Beit ʾElāhāʾ'' "House of God", in Hatran Aramaic inscriptions and once recorded as "Enclosure of Shamash" (''ḥtrʾ d-šmš'' ) on a coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |