|
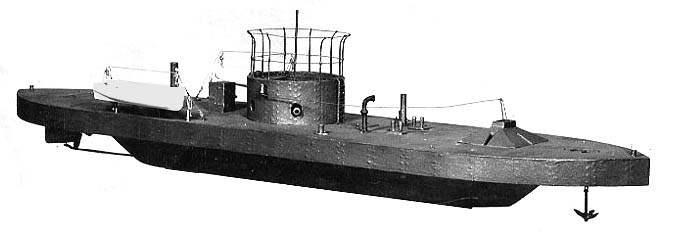
Breastwork Monitor
A breastwork monitor was a modification of the monitor, a warship which was first built in the United States in 1861, designed by John Ericsson and distinguished by the first rotating gun turret, designed by Theodore Timby. The modified design known as a breastwork monitor was introduced by Sir Edward Reed, the Chief Constructor of the Royal Navy between 1863 and 1870. The original monitors were very stable, and difficult to damage by gunfire, because of their very low freeboard. This, however, caused them to behave, some said, as a "half-tide rock", with the ever-present risk of being swamped in a sea should water gain access to the interior through hatches, turret bases or other openings in the deck. Reed proposed to overcome this risk by the addition of an armoured breastwork. This was an armoured superstructure of moderate height ( in ), centrally placed on the ship and containing within its armoured circumference the gun turrets, bridge, funnels and all other upper dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
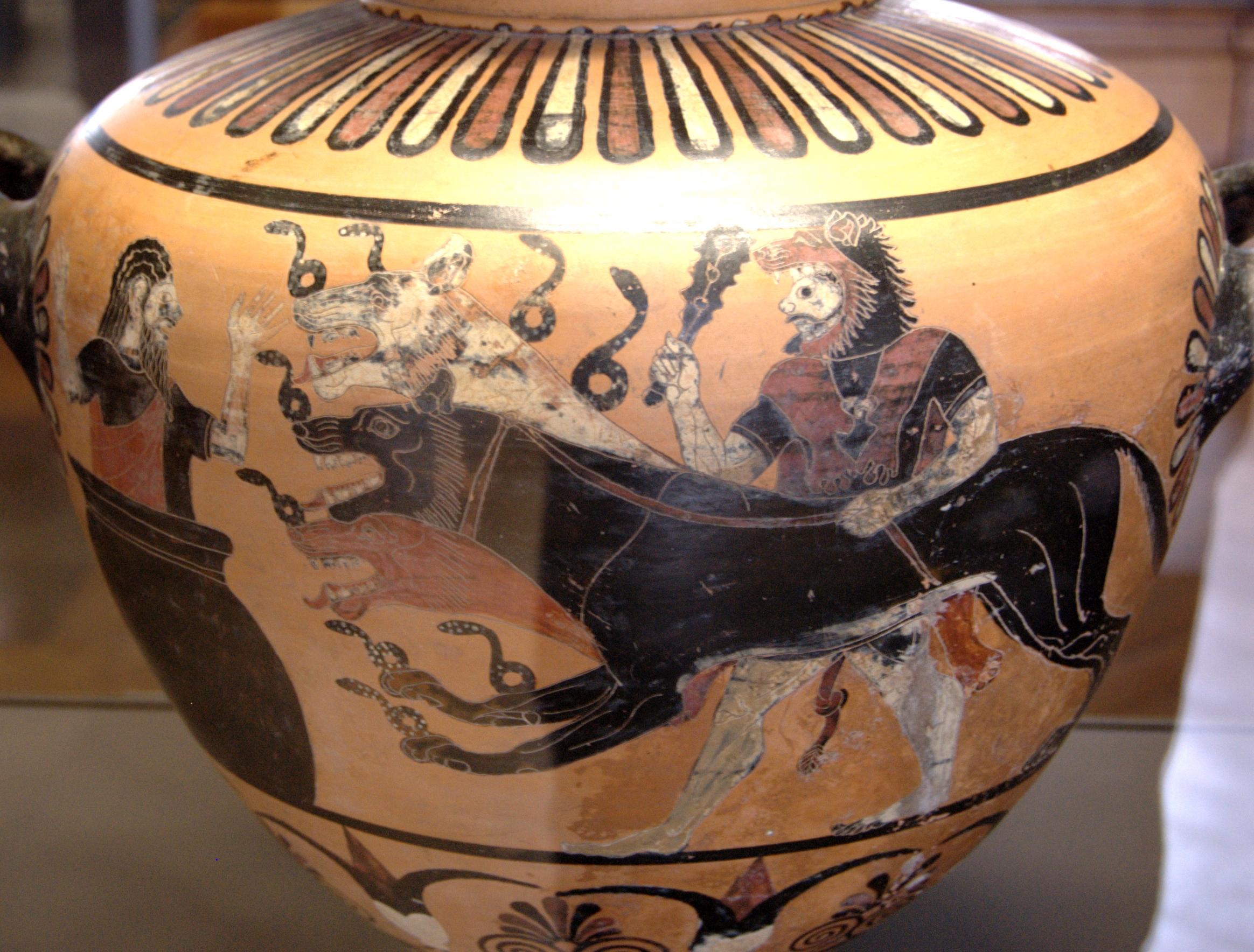
Cerberus (AWM 300036)
In Greek mythology, Cerberus (; grc-gre, Κέρβερος ''Kérberos'' ), often referred to as the hound of Hades, is a multi-headed dog that guards the gates of the Underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. He was the offspring of the monsters Echidna and Typhon, and was usually described as having three heads, a serpent for a tail, and snakes protruding from multiple parts of his body. Cerberus is primarily known for his capture by Heracles, the last of Heracles' twelve labours. Descriptions Descriptions of Cerberus vary, including the number of his heads. Cerberus was usually three-headed, though not always. Cerberus had several multi-headed relatives. His father was the multi snake-headed Typhon, and Cerberus was the brother of three other multi-headed monsters, the multi-snake-headed Lernaean Hydra; Orthrus, the two-headed dog who guarded the Cattle of Geryon; and the Chimera, who had three heads: that of a lion, a goat, and a snake. And, like these close relatives, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship which is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine warcraft, known as river monitors. During the Vietnam War these much s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ericsson
John Ericsson (born Johan Ericsson; July 31, 1803 – March 8, 1889) was a Swedish-American inventor. He was active in England and the United States. Ericsson collaborated on the design of the railroad steam locomotive ''Novelty'', which competed in the Rainhill Trials on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which were won by inventor George Stephenson's (1781-1848), ''Rocket''. In North America, he designed the United States Navy's first screw-propelled steam-frigate , in partnership with Captain (later Commodore) Robert F. Stockton (1795-1866), who unjustly blamed him for a fatal accident. A new partnership with Cornelius H. DeLamater (1821-1889), of the DeLamater Iron Works in New York City resulted in the first armoured ironclad warship equipped with a rotating gun turret, , which dramatically saved the U.S. ( Union Navy) naval blockading squadron from destruction by an ironclad Confederate States naval vessel, , at the famous Battle of Hampton Roads at the souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Timby
Theodore Ruggles Timby (5 April 1819 – 9 November 1909) is credited as the inventor of the revolving gun turret that was used on the USS ''Monitor'', the ironclad warship that fought in the American Civil War. He was born in Dutchess County, New York on April 5, 1819. Early in life, living in Cato Four Corners (later Meridian, in Cayuga County, New York), at the age of 16, he invented a method for raising ships out of the water for repairs by sinking a water-filled box beneath it, then forcing the water out through pumps in order to raise the ship. Throughout the 1840s, Timby perfected a revolving gun turret for use on land or water. He constructed a model and brought it to Washington but met with little success, as war was not imminent. However, with the outbreak of the Civil War, Timby brought his model to the Abraham Lincoln White House, and this time met with a much warmer reception. Meanwhile, a Swedish-born architect named John Ericsson had submitted a proposal to bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward James Reed
Sir Edward James Reed, KCB, FRS (20 September 1830 – 30 November 1906) was a British naval architect, author, politician, and railroad magnate. He was the Chief Constructor of the Royal Navy from 1863 until 1870. He was a Liberal politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1874 to 1906. Early life Edward Reed was born in Sheerness, Kent and was the son of John and Elizabeth Reed. He was a naval apprentice at Sheerness and subsequently entered the School of Mathematics and Naval Construction at Portsmouth. In 1851 he married Rosetta, the sister of Nathaniel Barnaby. Barnaby was at that time a fellow student; he would subsequently succeed Reed as Chief Constructor. In 1852 he entered employment at Sheerness Dockyard, but resigned after a disagreement with the management. He then worked in journalism, including editing the ''Mechanics' Magazine''. In 1860, Reed was appointed secretary of the newly formed Institute of Naval Architects. Naval architect In 1863, at the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Director Of Naval Construction
The Director of Naval Construction (DNC) also known as the Department of the Director of Naval Construction and Directorate of Naval Construction and originally known as the Chief Constructor of the Navy was a senior principal civil officer responsible to the Board of Admiralty for the design and construction of the warships of the Royal Navy. From 1883 onwards he was also head of the Royal Corps of Naval Constructors, the naval architects who staffed his department from 1860 to 1966. The (D.N.C.'s) modern equivalent is Director Ships in the Defence Equipment and Support organisation of the Ministry of Defence. History The post evolved from the office of the ''Assistant Surveyor of the Navy'' (1832-1859) In 1860 the ''Assistant Surveyor'' was renamed ''Chief Constructor'' the post lasted until 1875 when it was renamed to the ''Director of Naval Construction''. The chief constructor was originally head of the Royal Corps of Naval Constructors and members of the corps were respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeboard (nautical)
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relative to the ship's load line, regardless of deck arrangements, is the mandated and regulated meaning. In yachts, a low freeboard is often found on racing boats, for increased speed (by reducing weight and therefore drag). A higher freeboard will give more room in the cabin, but will increase weight and drag, compromising speed. A higher freeboard, such as used on ocean liners, also helps weather waves and so reduce the likelihood of being washed over by full water waves. A low-freeboard vessel is susceptible to taking in water in rough seas. Freighter ships and warships use high freeboard designs to increase internal volume, which also allows them to satisfy International Maritime Organization The International Maritime Organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breastwork (fortification)
A breastwork is a temporary fortification, often an earthwork thrown up to breast height to provide protection to defenders firing over it from a standing position. A more permanent structure, normally in stone, would be described as a parapet or the battlement of a castle wall. In warships, a breastwork is the armored superstructure in the ship that did not extend all the way out to the sides of the ship. It was generally only used in ironclad turret ships designed between 1865 and 1880. See also *List of established military terms (Fortifications A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''face ...) Fortifications by type {{Fort-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Breastwork Monitors Of The Royal Navy
The breastwork monitor was developed during the 1860s by Sir Edward Reed, Chief Constructor of the Royal Navy, as an improvement of the basic monitor design developed by John Ericsson during the American Civil War. Reed gave these ships a superstructure to increase seaworthiness and raise the freeboard of the gun turrets so they could be worked in all weathers. The superstructure was armoured to protect the bases of the turrets, the funnels and the ventilator ducts in what he termed a breastwork. The ships were conceived as harbour defence ships with little need to leave port. This meant that they could dispense with the masts, sails and rigging needed to supplement their coal-fired steam engines over any distance. Reed took advantage of the lack of masts and designed the ships with one twin-gun turret at each end of the superstructure, each able to turn and fire in a 270° arc. These ships were described by Admiral George Alexander Ballard as being like "full-armoured knights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Types
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)