|
Brake Parachute
A drogue parachute is a parachute designed for deployment from a rapidly-moving object. It can be used for various purposes, such as to decrease speed, to provide control and stability, or as a pilot parachute to deploy a larger parachute. Vehicles that have used drogue parachutes include multi-stage parachutes, aircraft, and spacecraft recovery systems. The drogue parachute was invented by the Russian professor and parachute specialist Gleb Kotelnikov in 1912, who also invented the knapsack parachute. The Soviet Union introduced its first aircraft fitted with drogue parachutes during the mid 1930s; use of the technology expanded during and after the Second World War. A large number of jet-powered aircraft have been furnished with drogue parachutes, including the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress strategic bomber and the Eurofighter Typhoon multirole aircraft; they were also commonly used within crewed space vehicle recovery programmes, including Project Mercury and Project G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B52 Landing With Drogue Chute
B5, B05, B-5 may refer to: Biology * ATC code B05 (''Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions''), a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * Cytochrome ''b''5, ubiquitous electron transport hemoproteins ** Cytochrome b5, type A, a human microsomal cytochrome b5 * HLA-B5, an HLA-B serotype * Pantothenic acid (a.k.a. vitamin B5), a water-soluble vitamin * Procyanidin B5, a B type proanthocyanidin Entertainment * Alekhine's Defence (ECO code B5), a chess opening beginning with the moves e4 Nf6 * B5 (band), an R&B boy band ** ''B5'' (album), B5's self-titled debut album * ''Babylon 5'', an American science fiction television series Transport * Amadeus (airline) (IATA code: B5), an airline based in Germany (1996–2004) * B5 and B5 DOHC, models of the Mazda B engine series * B-5, the manufacturer's model number for the Blackburn Baffin biplane * B5 platform, the series designator for Audi A4 from 1994–2001 * Bundesstraße 5, a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966. Gemini's objective was the development of space travel techniques to support the Apollo mission to land astronauts on the Moon. In doing so, it allowed the United States to catch up and overcome the lead in human spaceflight capability the Soviet Union had obtained in the early years of the Space Race, by demonstrating: mission endurance up to just under 14 days, longer than the eight days required for a round trip to the Moon; methods of performing extra-vehicular activity (EVA) without tiring; and the orbital maneuvers necessary to achieve rendezvous and docking with another spacecraft. This left Apollo free to pursue its prime mission without spending time develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the two nations following World War II. The technological advantage demonstrated by spaceflight achievement was seen as necessary for national security, and became part of the symbolism and ideology of the time. The Space Race brought pioneering launches of artificial satellites, robotic space probes to the Moon, Venus, and Mars, and human spaceflight in low Earth orbit and ultimately to the Moon. Public interest in space travel originated in the 1951 publication of a Soviet youth magazine and was promptly picked up by US magazines. The competition began on July 30, 1955 when the United States announced its intent to launch artificial satellites for the International Geophysical Year. Four days later, the Soviet Union responded by declaring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
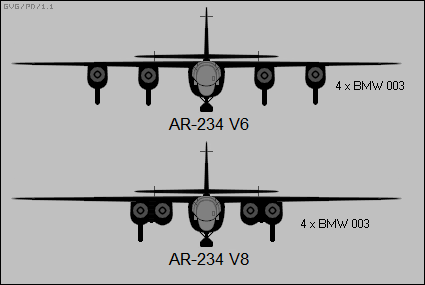
Arado Ar 234
The Arado Ar 234 ''Blitz'' (English: lightning) is a jet-powered bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the world's first operational turbojet-powered bomber, seeing service during the latter half of the Second World War. Development of the Ar 234 can be traced back to the latter half of 1940 and the request to tender from the Ministry of Aviation to produce a jet-powered high-speed reconnaissance aircraft. Arado was the only respondent with their ''E.370'' design. While its range was beneath that of the Ministry's specification, an initial order for two prototypes was promptly issued to the company, designated ''Ar 234''. While both of the prototypes had been mostly completed prior to the end of 1941, the Junkers Jumo 004 turbojet engines were not available prior to February 1943. Due to engine unreliability, the maiden flight of the Ar 234 V1 was delayed until 30 July 1943. In addition to the original reconnaissance-orientated ''Ar 23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Ice
Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object (shoals, grounded icebergs, etc.).Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Unlike fast ice, which is "fastened" to a fixed object, drift ice is carried along by winds and sea currents, hence its name. When drift ice is driven together into a large single mass (>70% coverage), it is called pack ice. Wind and currents can pile up that ice to form ridges up to tens of metres in thickness. These represent a challenge for icebreakers and offshore structures operating in cold oceans and seas. Drift ice consists of ice floes, individual pieces of sea ice or more across. Floes are classified according to size: ''small'' – to ; ''medium'' – to ; ''big'' – to ; ''vast'' – to ; and ''giant'' – more than . Drift ice affects: * Security of navigation * Climatic impact (see Polar ice packs) * Geological impact * Biosphere influence (see Ecol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Pole-1
North Pole-1 (russian: Северный полюс-1) was the world's first Soviet manned drifting station in the Arctic Ocean, primarily used for research. North Pole-1 was established on 21 May 1937 and officially opened on 6 June, some from the North Pole by the expedition into the high latitudes Sever-1, led by Otto Schmidt. The expedition had been airlifted by aviation units under the command of Mark Shevelev. "NP-1" operated for 9 months, during which the ice floe travelled . The commander of the station was Ivan Papanin. On 19 February 1938 the Soviet ice breakers '' Taimyr'' and '' Murman'' took four polar explorers off the station close to the eastern coast of Greenland. They arrived in Leningrad on 15 March on board the icebreaker ''Yermak''. The expedition members, hydrobiologist Pyotr Shirshov, geophysicist Yevgeny Fyodorov, radioman Ernst Krenkel, and the commander Ivan Papanin, were awarded the Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drifting Ice Station
A drifting ice station is a temporary or semi-permanent facility built on an ice floe. During the Cold War the Soviet Union and the United States maintained a number of stations in the Arctic Ocean on floes such as Fletcher's Ice Island for research and espionage, the latter of which were often little more than quickly constructed shacks. Extracting personnel from these stations proved difficult and in the case of the United States, employed early versions of the Fulton surface-to-air recovery system. Overview Soviet and Russian staffed drifting ice stations are research stations built on the ice of the high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean. They are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole (NP; russian: Северный полюс, translit=Severny polyus, ), followed by an ordinal number: North Pole-1, etc. NP drift stations carry out the program of complex year-round research in the fields of oceanology, ice studies, meteorology, ae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Expedition
Polar exploration is the process of exploration of the polar regions of Earth – the Arctic region and Antarctica – particularly with the goal of reaching the North Pole and South Pole, respectively. Historically, this was accomplished by explorers making often arduous travels on foot or by sled in these regions, known as a polar expedition. More recently, exploration has been accomplished with technology, particularly with satellite imagery. From 600 BC to 300 BC, Greek philosophers theorized that the planet was a Spherical Earth with North and South polar regions. By 150 AD, Ptolemy published ''Geographia'', which notes a hypothetical Terra Australis Incognita. However, due to harsh weather conditions, the poles themselves would not be reached for centuries after that. When they finally were reached, the achievement was realized only a few years apart. There are two claims, both disputed, about who was the first persons to reach the geographic North Pole. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and sea ice, ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ar 234B Drogue Chute Location
AR, Ar, or A&R may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Artists and repertoire Periodicals * ''Absolute Return + Alpha'', a hedge fund publication *''The Adelaide Review'', an Australian arts magazine * ''American Renaissance'' (magazine), a white nationalist magazine and website * ''Architectural Review'', a British architectural journal * '' Armeerundschau'', a magazine of the East German army Other media * Ar, city on the fictional planet Gor * ''a.r.'' group of Polish artists and poets, including Katarzyna Kobro * Alternate reality (other), various fictional concepts Business * Accounts receivable, abbreviated as AR or A/R * Acoustic Research, an American audio electronics manufacturer * Aerojet Rocketdyne, an American aerospace and defense manufacturer * Aerolíneas Argentinas (IATA airline code AR) * Some Alfa Romeo car models, e.g. AR51 * Toyota AR engine Language * ''Ar'', the Latin letter R when spelled out * Ar (cuneiform) The cuneifor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |