|
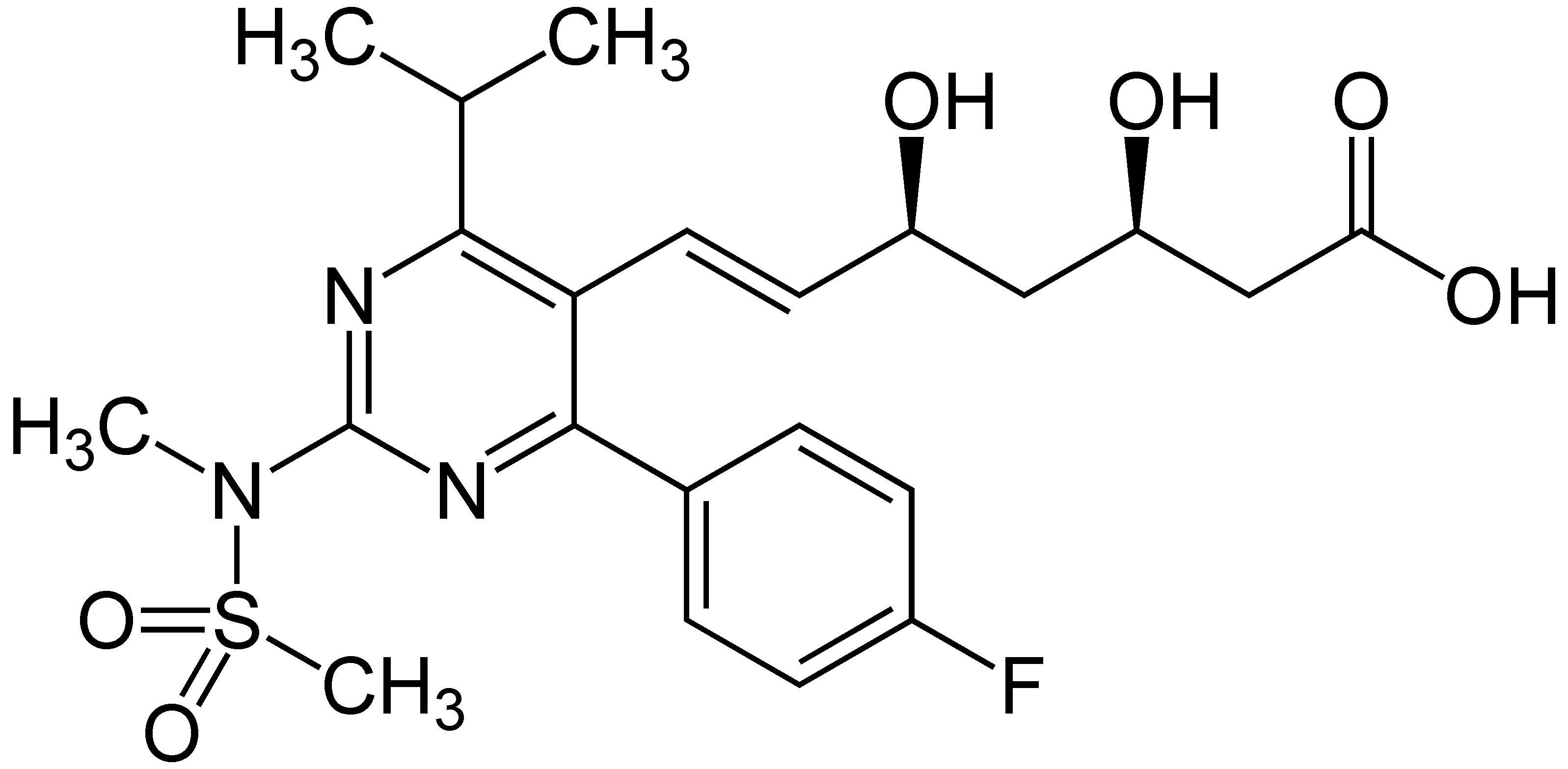
Bosentan
Bosentan, sold under the brand name Tracleer and Safebo among others, is a dual endothelin receptor antagonist medication used in the treatment of pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH). Bosentan is available as film-coated tablets (62.5 mg or 125 mg) or as dispersable tablets for oral suspension (32 mg). Medical uses Bosentan is used to treat people with moderate pulmonary arterial hypertension and to reduce the number of digital ulcers — open wounds on especially on fingertips and less commonly the knuckles — in people with systemic scleroderma. Bosentan causes harm to fetuses and pregnant women must not take it, and women must not become pregnant while taking it (Pregnancy Category X). It may render hormonal contraceptives ineffective so other forms of birth control must be used. In the US it is only available from doctors who follow an FDA-mandated risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) with respect to risks to fetuses and its risks of causing liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin
Endothelins are peptides with receptor (biochemistry), receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when gene expression, overexpressed, they contribute to high blood pressure (hypertension), heart disease, and potentially other diseases. Endothelins are 21-amino acid vasoconstriction, vasoconstricting peptides produced primarily in the endothelium having a key role in smooth muscle, vascular homeostasis. Endothelins are implicated in vascular diseases of several organ systems, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, and brain. As of 2018, endothelins remain under extensive basic research, basic and clinical research to define their roles in several organ systems. Etymology Endothelins derived the name from their isolation in cultured endothelial cells. Isoforms There are three isoforms of the peptide (identified as ET-1, -2, -3), each encoded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
Endothelins are peptides with receptors and effects in many body organs. Endothelin constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. The endothelins are normally kept in balance by other mechanisms, but when overexpressed, they contribute to high blood pressure ( hypertension), heart disease, and potentially other diseases. Endothelins are 21-amino acid vasoconstricting peptides produced primarily in the endothelium having a key role in vascular homeostasis. Endothelins are implicated in vascular diseases of several organ systems, including the heart, lungs, kidneys, and brain. As of 2018, endothelins remain under extensive basic and clinical research to define their roles in several organ systems. Etymology Endothelins derived the name from their isolation in cultured endothelial cells. Isoforms There are three isoforms of the peptide (identified as ET-1, -2, -3), each encoded by a separate gene, with varying regions of expression and binding to at least four know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidines
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drugs
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP3A4 Inducers
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme. While many drugs are deactivated by CYP3A4, there are also some drugs which are ''activated'' by the enzyme. Some substances, such as some drugs and furanocoumarins present in grapefruit juice, interfere with the action of CYP3A4. These substances will therefore either amplify or weaken the action of those drugs that are modified by CYP3A4. CYP3A4 is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of oxidizing enzymes. Several other members of this family are also involved in drug metabolism, but CYP3A4 is the most common and the most versatile one. Like all members of this family, it is a hemoprotein, i.e. a protein containing a heme group with an iron atom. In humans, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitaxentan
Sitaxentan sodium (TBC-11251) is a medication for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). It was marketed as Thelin by Encysive Pharmaceuticals until Pfizer purchased Encysive in February 2008. In 2010, Pfizer voluntarily removed sitaxentan from the market due to concerns about liver toxicity.Citing liver damage, Pfizer withdraws Thelin Associated Press, December 12, 2010 Mechanism of action Sitaxentan is a that blocks the action of |
Darusentan
Darusentan (LU-135252; HMR-4005) is an endothelin receptor antagonist. Gilead Colorado, a subsidiary of Gilead Sciences Gilead Sciences, Inc. () is an American biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Foster City, California, that focuses on researching and developing antiviral drugs used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, influenza, and C ..., under license from Abbott Laboratories, is developing darusentan for the potential treatment of uncontrolled hypertension. In June 2003, Myogen licensed the compound from Abbott for its application in the cancer field. In May 2007, a randomized, double-blind, active control, parallel assignment, safety and efficacy phase III trial was initiated in subjects who had completed the maintenance period of the DAR-312 study, but was terminated because the study did not reach its primary endpoints. See also * Ambrisentan References Endothelin receptor antagonists Barbiturates Experimental drugs Lactims Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambrisentan
Ambrisentan (U.S. trade name Letairis; E.U. trade name Volibris; India trade name Pulmonext by MSN labs) is a drug indicated for use in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. The peptide endothelin constricts muscles in blood vessels, increasing blood pressure. Ambrisentan, which relaxes those muscles, is an endothelin receptor antagonist, and is selective for the type A endothelin receptor (ETA). Ambrisentan significantly improved exercise capacity (6-minute walk distance) compared with placebo in two double-blind, multicenter trials (ARIES-1 and ARIES-2). Like all endothelin receptor antagonists, Ambrisentan is contraindicated in pregnant women as well as those who are trying to become pregnant, due to the potential for teratogenic effects on the fetus. Patients who are on the Ambrisentan must enroll in the Ambrisentan (Letairis) REMS Program. Ambrisentan was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and designated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OATP
Members of the Organo Anion Transporter (OAT) Family (organic-anion-transporting polypeptides, OATP) are membrane transport proteins or 'transporters' that mediate the transport of mainly organic anions across the cell membrane. Therefore, OATPs are present in the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane, acting as the cell's gatekeepers. OATPs belong to the Solute Carrier Family (SLC) and the major facilitator superfamily. The generalized transport reactions catalyzed by members of the OAT family are: Anion (in) → Anion (out) Anion1 (in) + Anion2 (out) → Anion1 (out) + Anion2 (in) Function Proteins of the OAT family catalyze the Na+-independent facilitated transport of fairly large amphipathic organic anions (and less frequently neutral or cationic drugs), such as bromosulfobromophthalein, prostaglandins, conjugated and unconjugated bile acids (taurocholate and cholate), steroid conjugates, thyroid hormones, anionic oligopeptides, drugs, toxins and other xenobiotics. One fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP2C19
Cytochrome P450 2C19 (abbreviated CYP2C19) is an enzyme protein. It is a member of the CYP2C subfamily of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system. This subfamily includes enzymes that catalyze metabolism of xenobiotics, including some proton pump inhibitors and antiepileptic drugs. In humans, it is the ''CYP2C19'' gene that encodes the CYP2C19 protein. CYP2C19 is a liver enzyme that acts on at least 10% of drugs in current clinical use, most notably the antiplatelet treatment clopidogrel (Plavix), drugs that treat pain associated with ulcers, such as omeprazole, antiseizure drugs such as mephenytoin, the antimalarial proguanil, and the anxiolytic diazepam. CYP2C19 has been annotated as (R)-limonene 6-monooxygenase and (S)-limonene 6-monooxygenase in UniProt. Function The gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. Enzymes in the CYP2C subfamily, including CYP2C19, account for approximately 20% of cytochrome P450 in the adult liver. These pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |