|
Boat-tail Bullet
External ballistics or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or in the vacuum of space, but most certainly flying under the influence of a gravitational field. Gun-launched projectiles may be unpowered, deriving all their velocity from the propellant's ignition until the projectile exits the gun barrel. However, exterior ballistics analysis also deals with the trajectories of rocket-assisted gun-launched projectiles and gun-launched rockets; and rockets that acquire all their trajectory velocity from the interior ballistics of their on-board propulsion system, either a rocket motor or air-breathing engine, both during their boost phase and after motor burnout. External ballistics is also concerned with the free-flight of other projectiles, such as balls, arrows etc. Forces acting on the projectile Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullet Wiki
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and constructions (depending on the intended applications), including specialized functions such as hunting, target shooting, training and combat. Bullets are often tapered, making them more aerodynamic. Bullet sizes are expressed by their weights and diameters (referred to as "calibers") in both imperial and metric measurement systems. For example: 55 grain .223 caliber bullets are of the same weight and caliber as 3.56 gram 5.56mm caliber bullets. Bullets do not normally contain explosives but strike or damage the intended target by transferring kinetic energy upon impact and penetration. Bullets shot by firearms can be used for target practice or hunting. Description The term ''bullet'' is from Middle French, originating as the diminutive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Gun
The Paris Gun (german: Paris-Geschütz / Pariser Kanone) was the name given to a type of German long-range siege gun, several of which were used to bombard Paris during World War I. They were in service from March to August 1918. When the guns were first employed, Parisians believed they had been bombed by a high-altitude Zeppelin, as the sound of neither an airplane nor a gun could be heard. They were the largest pieces of artillery used during the war by barrel length, and qualify under the (later) formal definition of large-calibre artillery. Also called the "''Kaiser Wilhelm Geschütz''" (" Kaiser Wilhelm Gun"), they were often confused with Big Bertha, the German howitzer used against Belgian forts in the Battle of Liège in 1914; indeed, the French called them by this name as well.For an instance of war-time naming of this gun as "Big Bertha", see They were also confused with the smaller "Langer Max" (Long Max) cannon, from which they were derived; although the famous Krup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, and to make predictions about behavior. Elements of a mathematical model Mathematical models can take many forms, including dynamical systems, statisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photography Of Bow Shock Waves Around A Brass Bullet, 1888
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication. Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which is electronically processed and stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result with photographic emulsion is an invisible latent image, which is later chemically "developed" into a visible image, either negative or positive, depending on the purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-blank Range
Point-blank range is any distance over which a certain firearm can hit a target without the need to compensate for bullet drop, and can be adjusted over a wide range of distances by sighting in the firearm. If the bullet leaves the barrel parallel to the sight, the bullet, like any object in flight, is pulled downwards by gravity, so for distant targets, the shooter must point the firearm above the target to compensate. But if the target is close enough, bullet drop will be negligible so the shooter can aim the gun straight at the target. If the sights are set so that the barrel has a small upward tilt, the bullet starts by rising and later drops. This results in a weapon that hits too low for very close targets, too high for intermediate targets, too low for very far targets, and point blank at two distances in between. For a .270 Winchester, as an example, the bullet first crosses the line of sight at about 23 metres (25 yards) as it is rising and has a maximum impact above th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Table
A ballistic table or ballistic chart is a tool which predicts the trajectory of a projectile, and is used to compensate for physical effects in order to increase the probability of the projectile reaching the intended target. Ballistic tables are used in hunting, sport shooting, military and scientific applications. Corrections in ballistic tables are given relative to a zero range. Ballistic charts are often given in angular measurements, with units in either milliradians (mil) or minutes of arc (moa). The tables are usually generated using specifically designed computer programs built on mathematical functions, known as ballistic calculators. The number of inputs to the ballistic calculator can sometimes vary depended on the specific generator, or the user may choose to only input certain variables. For example, a very simple drop table can be made using inputs for the sight adjustment value (in mil or moa), the zero range, intended target ranges, muzzle velocity, caliber, bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Trajectory
Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an object or particle (a projectile) that is projected in a gravitational field, such as from Earth's surface, and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity only. In the particular case of projectile motion of Earth, most calculations assume the effects of air resistance are passive and negligible. The curved path of objects in projectile motion was shown by Galileo to be a parabola, but may also be a straight line in the special case when it is thrown directly upwards. The study of such motions is called ballistics, and such a trajectory is a ballistic trajectory. The only force of mathematical significance that is actively exerted on the object is gravity, which acts downward, thus imparting to the object a downward acceleration towards the Earth’s center of mass. Because of the object's inertia, no external force is needed to maintain the horizontal velocity component of the object's motion. Taking other f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sighting In
In ranged weapons such as firearms and artillery pieces, sighting in or sight-in is a preparatory or corrective calibration of the sights with the goal that the projectile (e.g. bullet or shell) may be placed at a predictable impact position within the sight picture. The principle of sighting-in is to shift the line of aim until it intersects the parabolic projectile trajectory at a designated point of reference, so when the gun is fired in the future (provided there is reliable precision) it will repeatably hit where it aims at identical distances of that designated point. Because when using a telescopic sight, the crosshair lines geometrically resemble the X- and Y-axis of the Cartesian coordinate system where the reticle center is analogous to the origin point ( i.e. coordinate ,0, the designated sighting-in point is known as a zero, and the act of sighting-in is therefore also called zeroing. A gunsight that remains true to its designated zero after repeated usage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
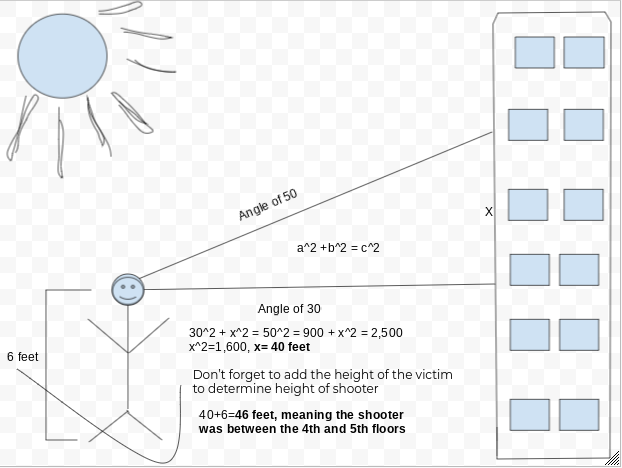
How Forensic Investigators Use The Evidence From A Shooting To Locate Bullet Trajectory
How may refer to: * How (greeting), a word used in some misrepresentations of Native American/First Nations speech * How, an interrogative word in English grammar Art and entertainment Literature * ''How'' (book), a 2007 book by Dov Seidman * ''HOW'' (magazine), a magazine for graphic designers * H.O.W. Journal, an American art and literary journal Music * "How", a song by The Cranberries from ''Everybody Else Is Doing It, So Why Can't We?'' * "How", a song by Maroon 5 from ''Hands All Over'' * "How", a song by Regina Spektor from ''What We Saw from the Cheap Seats'' * "How", a song by Daughter from ''Not to Disappear'' * "How?" (song), by John Lennon Other media * HOW (graffiti artist), Raoul Perre, New York graffiti muralist * ''How'' (TV series), a British children's television show * ''How'' (video game), a platform game People * How (surname) * HOW (graffiti artist), Raoul Perre, New York graffiti muralist Places * How, Cumbria, England * How, Wisco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force may be applied to cause a linear acceleration without an angular acceleration. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass. It is a hypothetical point where the entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualise its motion. In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton's laws of motion. In the case of a single rigid body, the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body, and if the body has uniform density, it will be located at the centroid. The center of mass may be located outside the physical body, as is sometimes the case for hollow or open-shaped objects, such as a horseshoe. In the case of a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Pressure (fluid Mechanics)
In fluid mechanics, the center of pressure is the point where the total sum of a pressure field acts on a body, causing a force to act through that point. The total force vector acting at the center of pressure is the surface integral of the pressure vector field across the surface of the body. The resultant force and center of pressure location produce an equivalent force and moment on the body as the original pressure field. Pressure fields occur in both static and dynamic fluid mechanics. Specification of the center of pressure, the reference point from which the center of pressure is referenced, and the associated force vector allows the moment generated about any point to be computed by a translation from the reference point to the desired new point. It is common for the center of pressure to be located on the body, but in fluid flows it is possible for the pressure field to exert a moment on the body of such magnitude that the center of pressure is located outside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)


