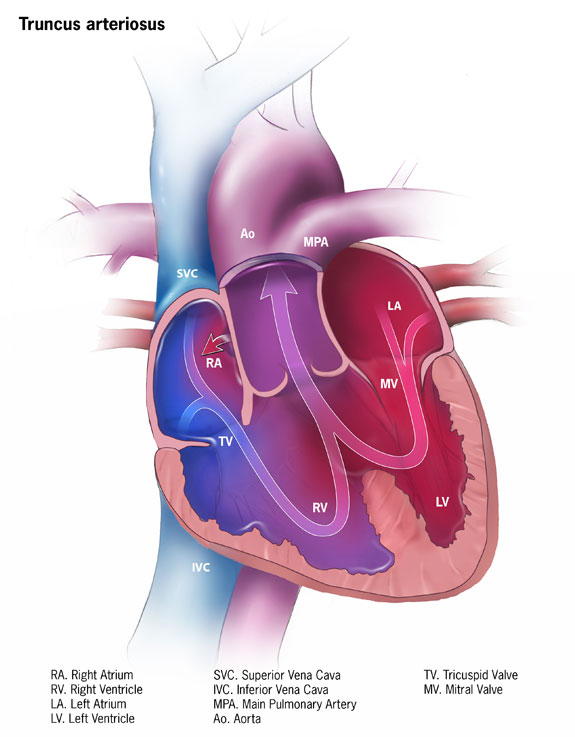
|
Blue Baby
Blue baby syndrome can refer to conditions that cause cyanosis, or blueness of the skin, in babies as a result of low oxygen levels in the blood. This term has traditionally been applied to cyanosis as a result of: #Cyanotic heart disease, which is a category of congenital heart defect that results in low levels of oxygen in the blood. This can be caused by either reduced blood flow to the lungs or mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. # Methemoglobinemia, which is a disease defined by high levels of methemoglobin in the blood. Increased levels of methemoglobin prevent oxygen from being released into the tissues and result in hypoxemia. Although these are the most common causes of cyanosis, there are other potential factors that can cause a blue tint to a baby's skin or mucous membranes. These factors include hypoventilation, perfusion or ventilation differences in the lungs, and poor cardiac output of oxygenated blood, among others. The blue baby syndrome or cyanosis occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotic
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations where the skin is thinner, including the mucous membranes, lips, nail beds, and ear lobes. Some medications containing amiodarone or silver, Mongolian spots, large birth marks, and the consumption of food products with blue or purple dyes can also result in the bluish skin tissue discoloration and may be mistaken for cyanosis. Cyanosis is further classified into central cyanosis vs. peripheral cyanosis. Pathophysiology The mechanism behind cyanosis is different depending on whether it is central or peripheral. Central cyanosis Central cyanosis is caused by a decrease in arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) and begins to show once the concentration of deoxyhemoglobin in the blood reaches a concentration of ≥ 5.0 g/dL (≥ 3.1 mmol/L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection
Anomalous pulmonary venous connection (or anomalous pulmonary venous drainage or anomalous pulmonary venous return) is a congenital defect of the pulmonary veins. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection ''Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection'', also known as total ''anomalous pulmonary venous return'', is a rare cyanotic congenital heart defect in which all four pulmonary veins are malpositioned and make anomalous connections to the systemic venous circulation. (Normally, pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium where it can then be pumped to the rest of the body). A patent foramen ovale, patent ductus arteriosus or an atrial septal defect ''must'' be present, or else the condition is fatal due to a lack of systemic blood flow. In some cases, it can be detected prenatally. There are four variants: Supracardiac (50%): blood drains to one of the innominate veins (brachiocephalic veins) or the superior vena cava; Cardiac (20%), where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CO-oximeter
A CO-oximeter is a device that measures the oxygen carrying state of hemoglobin in a blood specimen, including oxygen-carrying hemoglobin (O2Hb), non-oxygen-carrying but normal hemoglobin (HHb) (formerly, but incorrectly, referred to as 'reduced' hemoglobin), as well as the dyshemoglobins such as carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) and methemoglobin (MetHb). The use of 'CO' rather than 'Co' or 'co' is more appropriate since this designation represents a device that measures carbon monoxide (CO) bound to hemoglobin, as distinguished from simple oximetry which measures hemoglobin bound to molecular oxygen—O2Hb—or hemoglobin capable of binding to molecular oxygen—HHb. Simpler oximeters may report oxygen saturation alone, i.e. the ratio of oxyhemoglobin to total 'bindable' hemoglobin (i.e. oxyhemoglobin + deoxyhemoglobin-HHb). CO-oximetry is useful in defining the causes for hypoxemia, or hypoxia, ( oxygen deficiency at the tissue level). Mechanism A CO-oximeter measures the absorption o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances (such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia), inadequate coronary artery blood flow (such as myocardial ischemia and myocardial infarction), and electrolyte disturbances (such as hypokalemia and hyperkalemia). Traditionally, "ECG" usually means a 12-lead ECG taken while lying down as discussed below. However, other devices can record the electrical activity of the heart such as a Holter monitor but also s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Radiograph
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine. Like all methods of radiography, chest radiography employs ionizing radiation in the form of X-rays to generate images of the chest. The mean radiation dose to an adult from a chest radiograph is around 0.02 mSv (2 mrem) for a front view (PA, or posteroanterior) and 0.08 mSv (8 mrem) for a side view (LL, or latero-lateral). Together, this corresponds to a background radiation equivalent time of about 10 days. Medical uses Conditions commonly identified by chest radiography * Pneumonia * Pneumothorax * Interstitial lung disease * Heart failure * Bone fracture * Hiatal hernia Chest radiographs are used to diagnose many conditions involving the chest wall, including its bones, and also structures contained within the thoracic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachypnea
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing. In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea being any rate above that. Children have significantly higher resting ventilatory rates, which decline rapidly during the first three years of life and then steadily until around 18 years. Tachypnea can be an early indicator of pneumonia and other lung diseases in children, and is often an outcome of a brain injury. Distinction from other breathing terms Different sources produce different classifications for breathing terms. Some of the public describe tachypnea as any rapid breathing. Hyperventilation is then described as increased ventilation of the alveoli (which can occur through increased rate or depth of breathing, or a mix of both) where there is a smaller rise in metabolic carbon dioxide relative to this increase in ventilation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
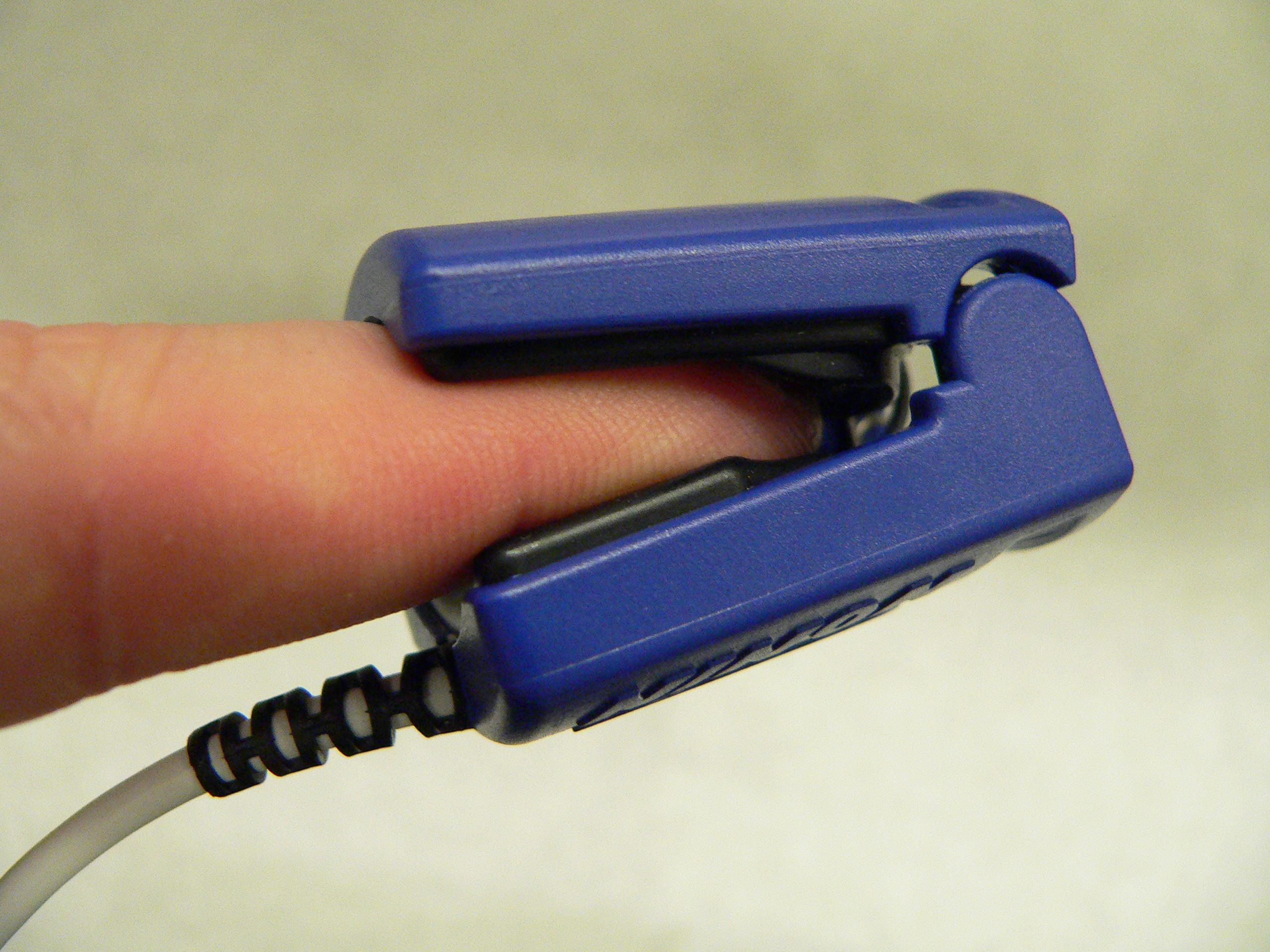
Pulse Oximeter
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring a person's oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) from arterial blood gas analysis. But the two are correlated well enough that the safe, convenient, noninvasive, inexpensive pulse oximetry method is valuable for measuring oxygen saturation in clinical use. The most common approach is ''transmissive pulse oximetry''. In this approach, a sensor device is placed on a thin part of the patient's body, usually a fingertip or earlobe, or an infant's foot. Fingertips and earlobes have higher blood flow rates than other tissues, which facilitates heat transfer. The device passes two wavelengths of light through the body part to a photodetector. It measures the changing absorbance at each of the wavelengths, allowing it to determine the absorbances due to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extend of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and oftentimes determines supply options. Categories The parameters for water quality are determined by the intended use. Work in the area of water quality tends to be focused on water that is treated for potability, industrial/domestic use, or restoration (of an environment/ecosystem, generally for health of human/aquatic life). Human consumption Contaminants that may be in untreated water include microorganisms such as viruses, protozoa and bacteria; inorganic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Latrine
A pit latrine, also known as pit toilet, is a type of toilet that collects human feces in a hole in the ground. Urine and feces enter the pit through a drop hole in the floor, which might be connected to a toilet seat or squatting pan for user comfort. Pit latrines can be built to function without water (dry toilet) or they can have a water seal (pour-flush pit latrine). When properly built and maintained, pit latrines can decrease the spread of disease by reducing the amount of human feces in the environment from open defecation. This decreases the transfer of pathogens between feces and food by flies. These pathogens are major causes of infectious diarrhea and intestinal worm infections. Infectious diarrhea resulted in about 700,000 deaths in children under five years old in 2011 and 250 million lost school days. Pit latrines are a low-cost method of separating feces from people. A pit latrine generally consists of three major parts: a hole in the ground, a concrete slab o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well Water
A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn up by a pump, or using containers, such as buckets or large water bags that are raised mechanically or by hand. Water can also be injected back into the aquifer through the well. Wells were first constructed at least eight thousand years ago and historically vary in construction from a simple scoop in the sediment of a dry watercourse to the qanats of Iran, and the stepwells and sakiehs of India. Placing a lining in the well shaft helps create stability, and linings of wood or wickerwork date back at least as far as the Iron Age. Wells have traditionally been sunk by hand digging, as is still the case in rural areas of the developing world. These wells are inexpensive and low-tech as they use mostly manual labour, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |