|
Blades
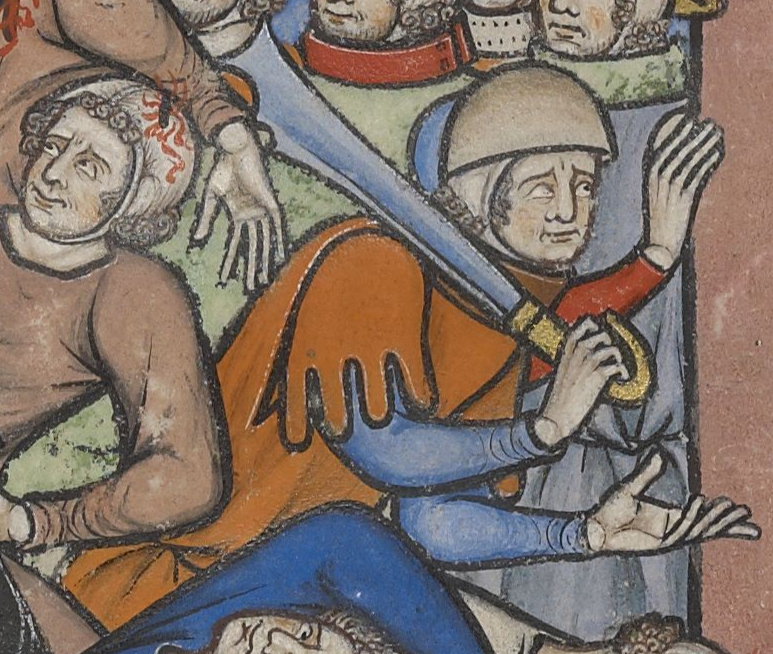
A blade is the portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with an edge that is designed to puncture, chop, slice or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are to be used on. Historically, humans have made blades from flaking stones such as flint or obsidian, and from various metal such as copper, bronze and iron. Modern blades are often made of steel or ceramic. Blades are one of humanity's oldest tools, and continue to be used for combat, food preparation, and other purposes. Blades work by concentrating force on the cutting edge. Certain blades, such as those used on bread knives or saws, are serrated, further concentrating force on the point of each tooth. Uses During food preparation, knives are mainly used for slicing, chopping, and piercing. In combat, a blade may be used to slash or puncture, and may also be thrown or otherwise propelled. The function is to sever a nerve, muscle or tendon fibers, or bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchen Knife
A kitchen knife is any knife that is intended to be used in food preparation. While much of this work can be accomplished with a few general-purpose knives – notably a large chef's knife, a tough cleaver, a small paring knife and some sort of serrated blade (such as a bread knife or serrated utility knife) – there are also many specialized knives that are designed for specific tasks. Kitchen knives can be made from several different materials. Construction Material * Carbon steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, often including other elements such as vanadium and manganese. Carbon steel commonly used in knives has around 1.0% carbon (ex. AISI 1095), is inexpensive, and holds its edge well. Carbon steel is normally easier to resharpen than many stainless steels, but is vulnerable to rust and stains. The blades should be cleaned, dried, and lubricated after each use. New carbon-steel knives may impart a metallic or "iron" flavour to acidic foods, though over time, the ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium. It is commonly found within the margins of rhyolite, rhyolitic lava flows known as obsidian flows. These flows have a high content of silicon dioxide, silica, granting them a high viscosity. The high viscosity inhibits atomic diffusion, diffusion of atoms through the lava, which inhibits the first step (nucleation) in the formation of mineral crystals. Together with rapid cooling, this results in a natural glass forming from the lava. Obsidian is hard, Brittleness, brittle, and amorphous; it therefore Fracture (mineralogy)#Conchoidal fracture, fractures with sharp edges. In the past, it was used to manufacture cutting and piercing tools, and it has been used experimentally as surgic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
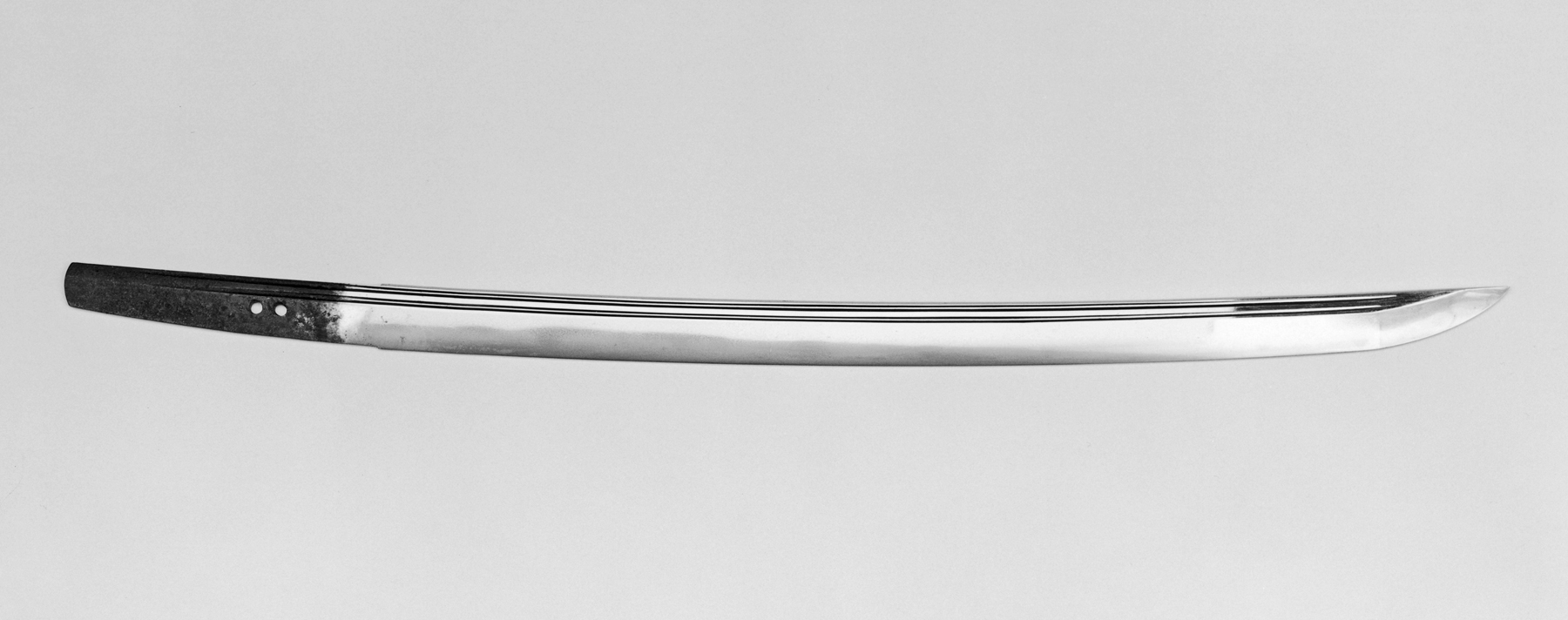
Talwar
The talwar (), also spelled ''talwaar'' and ''tulwar'', is a type of curved sword or sabre from the Indian subcontinent. Etymology and classification The word ''talwar'' originated from the Sanskrit word ''taravāri'' ( sa, तरवारि) which means "one-edged sword". It is the word for ''sword'' in several related languages, such as Hindustani (Urdu and Hindi), Nepali, Marathi, Gujarati, Punjabi, etc. and as () in Bengali. Like many swords from around the world with an etymology derived from a term meaning simply 'sword', the talwar has in scholarship, and in museum and collector usage, acquired a more specific meaning. Unfortunately, South Asian swords, while showing a rich diversity of forms, suffer from relatively poor dating (so developmental history is obscure) and a lack of precise nomenclature and classification. The typical talwar is a type of sabre, characterised by a curved blade (without the radical curve of some Persian swords), possessing an all-metal hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kukri
The kukri () or khukuri ( ne, खुकुरी, ) is a type of machete with a distinct recurve in its blade. It serves multiple purposes as a melee weapon and also as a regular cutting tool throughout most of South Asia. The ''kukri'', ''khukri'', and ''kukkri'' spellings are of Indian English origin, with the original Nepalese English spelling being ''khukuri''. Originating from the Indian subcontinent, the kukri is the national weapon of Nepal, traditionally serving the role of a basic utility knife for the Nepali-speaking Gurkhas, and consequently is a characteristic weapon of the Nepali Army. There have been, and still are many myths surrounding the kukri since its earliest recorded use in the 7th century—most notably that a traditional custom revolves around the blade in which it must draw blood, owing to its sole purpose as a fighting weapon, before being sheathed. However, they are frequently used as regular utility tools. History Researchers trace the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were pottery objects (''pots,'' ''vessels or vases'') or figurines made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened and sintered in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as in semiconductors. The word "'' ceramic''" comes from the Greek word (), "of pottery" or "for pottery", from (), "potter's clay, tile, pottery". The earliest kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Knife
A ballistic knife is a knife with a detachable blade that can be ejected to a distance of several meters/yards by pressing a trigger or operating a lever or switch on the handle.Crawford, Steve, ''Deadly fighting skills of the world'', New York: Thomas Dunne Books, St. Martin's Press, (1999), pp. 45-46: The minimum standard demanded of ''Spetsnaz'' recruits when throwing a knife from six feet is three consecutive hits on target; five hits is considered excellent. Spring-powered ballistic knives first appeared in books and press reports on Soviet and Eastern Bloc armed forces in the late 1970s. Commercially-produced ballistic knives briefly gained notoriety in the United States in the mid-1980s after they were marketed and sold in the United States and other Western countries. Since then, the marketing and sale of ballistic knives to civilians has been restricted or prohibited by law in several nations. Usage In its spring-propelled form, the blade of a ballistic knife is theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapier
A rapier () or is a type of sword with a slender and sharply-pointed two-edged blade that was popular in Western Europe, both for civilian use (dueling and self-defense) and as a military side arm, throughout the 16th and 17th centuries. Important sources for rapier fencing include the Italian Bolognese group, with early representatives such as Antonio Manciolino and Achille Marozzo publishing in the 1530s, and reaching the peak of its popularity with writers of the early 1600s (Salvator Fabris, Ridolfo Capo Ferro). In Spain, rapier fencing came to be known under the term of ("dexterity") in the second half of the 16th century, based on the theories of Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza in his work ("The Philosophy of Arms and of their Dexterity and of Aggression and the Christian Defence"), published in 1569. The best known treatise of this tradition was published in French, by Girard Thibault, in 1630. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fires. It occurs chiefly as nodules and masses in sedimentary rocks, such as chalks and limestones.''The Flints from Portsdown Hill'' Inside the nodule, flint is usually dark grey, black, green, white or brown in colour, and often has a glassy or waxy appearance. A thin layer on the outside of the nodules is usually different in colour, typically white and rough in texture. The nodules can often be found along s and |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carbon, other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khopesh
The ''khopesh'' ('; also vocalized khepesh) is an Egyptian sickle-shaped sword that evolved from battle axes. Description A typical ''khopesh'' is 50–60 cm (20–24 inches) in length, though smaller examples also exist. The inside curve of the weapon could be used to trap an opponent's arm, or to pull an opponent's shield out of the way. These weapons changed from bronze to iron in the New Kingdom period. The earliest known depiction of a ''khopesh'' is from the Stele of the Vultures, depicting King Eannatum of Lagash wielding the weapon; this would date the ''khopesh'' to at least 2500 BC. The blade is only sharpened on the outside portion of the curved end. The ''khopesh'' evolved from the epsilon or similar crescent-shaped axes that were used in warfare. History The ''khopesh'' fell out of use around 1300 BC. However, on the 196 BC Rosetta Stone, it is referenced as the "sword" determinative in a hieroglyph block, with the spelled letters of k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falchion
A falchion (; Old French: ''fauchon''; Latin: ''falx'', "sickle") is a one-handed, single-edged sword of European origin. Falchions are found in different forms from around the 13th century up to and including the 16th century. In some versions, the falchion looks rather like the seax and later the sabre, and in other versions more like a machete with a crossguard. Types The blade designs of falchions varied widely across the continent and over time. They almost always included a single edge with a slight curve on the blade towards the point on the end and most were also affixed with a quilloned crossguard for the hilt in the manner of the contemporary arming swords. Unlike the double-edged swords of Europe, few actual swords of this type have survived to the present day; fewer than a dozen specimens are currently known. A number of weapons superficially similar to the falchion existed in Western Europe, including the Messer, hanger and the backsword. Two basic types of fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |