|
Bioregionalists
Bioregionalism is a philosophy that suggests that political, cultural, and economic systems are more sustainable and just if they are organized around naturally defined areas called bioregions, similar to ecoregions. Bioregions are defined through physical and environmental features, including watershed boundaries and soil and terrain characteristics. Bioregionalism stresses that the determination of a bioregion is also a cultural phenomenon, and emphasizes local populations, knowledge, and solutions. Bioregionalism asserts "that a bioregion's environmental components (geography, climate, plant life, animal life, etc.) directly influence ways for human communities to act and interact with each other which are, in turn, optimal for those communities to thrive in their environment. As such, those ways to thrive in their totalityŌĆöbe they economic, cultural, spiritual, or politicalŌĆöwill be distinctive in some capacity as being a product of their bioregional environment." B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascadia (independence Movement)
The Cascadia independence movement is a bioregional movement based in the Cascadia bioregion of western North America. Potential boundaries differ, with some drawn along existing political state and provincial lines, and others drawn along larger ecological, cultural, political, and economic boundaries. The proposed country or region largely would consist of the Canadian province of British Columbia and the US States of Washington and Oregon, including major cities Seattle, Vancouver, and Portland. When all parts of the bioregion are included, Cascadia would stretch from coastal Alaska in the north into Northern California in the south, and inland to include parts of Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Utah, Wyoming, and Yukon. More conservative advocates propose borders that include the land west of the crest of Cascade Range, and the western side of British Columbia. As measured only by the combination of present Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia statistics, Cascadia would be h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
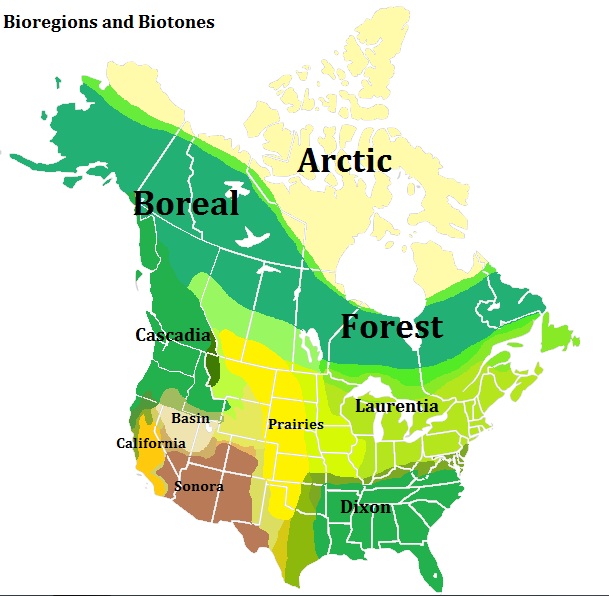
Bioregions And Biotones Of North America
A bioregion is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a biogeographic realm, but larger than an ecoregion or an ecosystem, in the World Wide Fund for Nature classification scheme. There is also an attempt to use the term in a rank-less generalist sense, similar to the terms "biogeographic area" or "biogeographic unit". It may be conceptually similar to an ecoprovince. It is also differently used in the environmentalist context, being coined by Berg and Dasmann (1977). WWF bioregions The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) scheme divides some of the biogeographic realms into bioregions, defined as "geographic clusters of ecoregions that may span several habitat types, but have strong biogeographic affinities, particularly at taxonomic levels higher than the species level (genus, family)." The WWF bioregions are as follows: *Afrotropical realm **Western Africa and Sahel **Central Africa **Eastern and Southern Africa **Horn of Africa **MadagascarŌĆōInd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Of Canada
, settlement_type = Region of British Columbia , image_skyline = , nickname = "The Coast" , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Canada , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = British Columbia , parts_type = Principal cities , p1 = Vancouver , p2 = Surrey , p3 = Burnaby , p4 = Richmond , p5 = Abbotsford , p6 = Coquitlam , p7 = Delta , p8 = Nanaimo , p9 = Victoria , p10 = Chilliwack , p11 = Maple Ridge , p12 = New Westminster , p13 = Port Coquitlam , p14 = North Vancouver , area_blank1_title = 15 Districts , area_blank1_km2 = 244,778 , area_footnotes = , elevation_max_m = 4019 , elevation_min_m = 0 , elevation_max_footnotes = M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkpatrick Sale
Kirkpatrick Sale (born June 27, 1937) is an American author who has written prolifically about political decentralism, environmentalism, luddism and technology. He has been described as having a "philosophy unified by decentralism" and as being "a leader of the Neo-Luddites,"Kevin KellyInterview with the Luddite ''Wired Magazine'', 1995. an "anti-globalization leftist,"Schwenkler, John (2008-11-03 States ''The American Conservative'' and "the theoretician for a new secessionist movement." Peter ApplebomeA Vision of a Nation No Longer in the U.S. ''The New York Times'', October 18, 2007. Life and work Sale grew up in Cayuga Heights, Ithaca, New York, and would later say of the village that he "spent most of my first twenty years there, and that has made an imprint on meŌĆöon my philosophy, social attitudes, certainly on my politicsŌĆöthat has lasted powerfully for the rest of my life." He graduated from Cornell University, majoring in English and history, in 1958. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond F
Raymond is a male given name. It was borrowed into English from French (older French spellings were Reimund and Raimund, whereas the modern English and French spellings are identical). It originated as the Germanic ßÜ▒ßÜ©ßÜĘßøüßÜŠßøŚßÜóßÜŠßø× (''Raginmund'') or ßÜ▒ßø¢ßÜĘßøüßÜŠßøŚßÜóßÜŠßø× (''Reginmund''). ''Ragin'' (Gothic) and ''regin'' (Old German) meant "counsel". The Old High German ''mund'' originally meant "hand", but came to mean "protection". This etymology suggests that the name originated in the Early Middle Ages, possibly from Latin. Alternatively, the name can also be derived from Germanic Hraidmund, the first element being ''Hraid'', possibly meaning "fame" (compare ''Hrod'', found in names such as Robert, Roderick, Rudolph, Roland, Rodney and Roger) and ''mund'' meaning "protector". Despite the German and French origins of the English name, some of its early uses in English documents appear in Latinized form. As a surname, its first recorded appearance in Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Berg (bioregionalist)
Peter Stephen Berg (October 1, 1937 ŌĆō July 28, 2011) was an environmental writer, best known as an advocate of the concept of bioregionalism. In the early 1960s, he was a member of the San Francisco Mime Troupe and the Diggers (theater), Diggers. He is the founder of the Planet Drum Foundation. Early life and education Born on October 1, 1937, in Jamaica, Queens, New York, Berg was raised in Florida after moving there at age six, which was where he first became interested in the environment as a child. He began attending the University of Florida at age 16, after winning a scholarship to study psychology. He dropped out at age 17, hitchhiked to San Francisco, and then enlisted and served in the army. After his discharge, he moved back to New York. After becoming active in the civil rights movement, he hitchhiked to San Francisco in 1964. In San Francisco, he joined the San Francisco Mime Troupe and met Judy Goldhaft. He also became a founder of the Artists Liberation Fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Localism
Localism describes a range of political philosophies which prioritize the local. Generally, localism supports local production and consumption of goods, local control of government, and promotion of local history, local culture and local identity. Localism can be contrasted with regionalism and centralized government, with its opposite being found in the unitary state. Localism can also refer to a systematic approach to organizing a central government so that local autonomy is retained rather than following the usual pattern of government and political power becoming centralized over time. On a conceptual level, there are important affinities between localism and deliberative democracy. This concerns mainly the democratic goal of engaging citizens in decisions that affect them. Consequently, localism will encourage stronger democratic and political participatory forums and widening public sphere connectivity. History Localists assert that throughout the world's history, mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commission For Environmental Cooperation
The Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC; es, Comisi├│n para la Cooperaci├│n Ambiental; french: Commission de coop├®ration environnementale) was established by Canada, Mexico, and the United States to implement the North American Agreement on Environmental Cooperation (NAAEC), the environmental side accord to the North American Free Trade Agreement. The CEC's mission is to facilitate cooperation and public participation to foster conservation, protection and enhancement of the North American environment for the benefit of present and future generations, in the context of increasing economic, trade and social links among Canada, Mexico and the United States. Origins and structure The Commission for Environmental Cooperation was created in 1994 by Canada, Mexico and the United States, under the NAAEC. The NAAEC was implemented in parallel to the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and complements the environmental provisions of NAFTA. It signified a commitment tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the World Wildlife Fund, which remains its official name in Canada and the United States. WWF is the world's largest conservation organization, with over five million supporters worldwide, working in more than 100 countries and supporting around 3,000 conservation and environmental projects. They have invested over $1 billion in more than 12,000 conservation initiatives since 1995. WWF is a foundation with 65% of funding from individuals and bequests, 17% from government sources (such as the World Bank, DFID, and USAID) and 8% from corporations in 2020. WWF aims to "stop the degradation of the planet's natural environment and to build a future in which humans live in harmony with nature." The Living Planet Report has been published every two y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named after the Kansas River, which in turn was named after the Kansa Native Americans who lived along its banks. The tribe's name (natively ') is often said to mean "people of the (south) wind" although this was probably not the term's original meaning. For thousands of years, what is now Kansas was home to numerous and diverse Native American tribes. Tribes in the eastern part of the state generally lived in villages along the river valleys. Tribes in the western part of the state were semi-nomadic and hunted large herds of bison. The first Euro-American settlement in Kansas occurred in 1827 at Fort Leavenworth. The pace of settlement accelerated in the 1850s, in the midst of political wars over the slavery debate. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ßÄŻßĦßÄ│ßÄ░ßÄ╣, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage language, a Dhegiha Siouan language, and referred to their relatives, the Quapaw people. The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta. Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 34th most populous state, with a population of just over 3 million at the 2020 census. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock, in the central part of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, including the FayettevilleŌĆōSpringdaleŌ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |