|
Big Bounce
The Big Bounce is a hypothesized cosmological model for the origin of the known universe. It was originally suggested as a phase of the ''cyclic model'' or ''oscillatory universe'' interpretation of the Big Bang, where the first cosmological event was the result of the collapse of a previous universe. It receded from serious consideration in the early 1980s after inflation theory emerged as a solution to the horizon problem, which had arisen from advances in observations revealing the large-scale structure of the universe. In the early 2000s, inflation was found by some theorists to be problematic and unfalsifiable in that its various parameters could be adjusted to fit any observations, so that the properties of the observable universe are a matter of chance. Alternative pictures including a Big Bounce may provide a predictive and falsifiable possible solution to the horizon problem, and are under active investigation as of 2017. Expansion and contraction The concept of the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Model
Physical cosmology is a branch of cosmology concerned with the study of cosmological models. A cosmological model, or simply cosmology, provides a description of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and allows study of fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate.For an overview, see Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed those physical laws to be understood. Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond the Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gamow
George Gamow (March 4, 1904 – August 19, 1968), born Georgiy Antonovich Gamov ( uk, Георгій Антонович Гамов, russian: Георгий Антонович Гамов), was a Russian-born Soviet and American polymath, theoretical physicist and cosmologist. He was an early advocate and developer of Lemaître's Big Bang theory. He discovered a theoretical explanation of alpha decay by quantum tunneling, invented the liquid drop model and the first mathematical model of the atomic nucleus, and worked on radioactive decay, star formation, stellar nucleosynthesis and Big Bang nucleosynthesis (which he collectively called nucleocosmogenesis), and molecular genetics. In his middle and late career, Gamow directed much of his attention to teaching and wrote popular books on science, including '' One Two Three... Infinity'' and the ''Mr Tompkins'' series of books (1939–1967). Some of his books are still in print more than a half-century after their original publicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
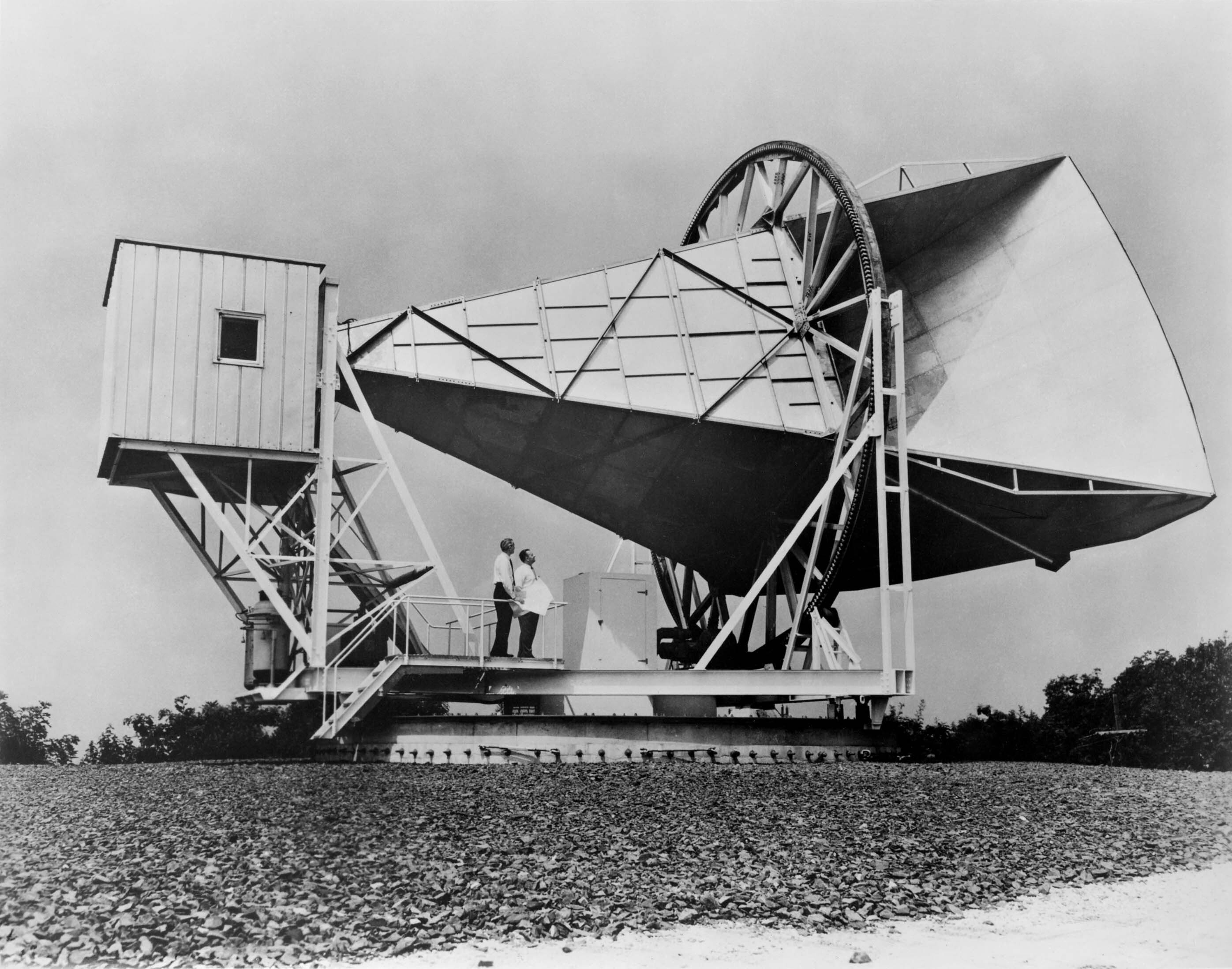
Robert Woodrow Wilson
Robert Woodrow Wilson (born January 10, 1936) is an American astronomer who, along with Arno Allan Penzias, discovered cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) in 1964. The pair won the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery. While doing tests and experiments with the Holmdel Horn Antenna at Bell Labs in Holmdel Township, New Jersey, Wilson and Penzias discovered a source of noise in the atmosphere that they could not explain. After removing all potential sources of noise, including pigeon droppings on the antenna, the noise was finally identified as CMB, which served as important corroboration of the Big Bang theory. In 1970, Wilson led a team that made the first detection of a rotational spectral line of carbon monoxide (CO) in an astronomical object, the Orion Nebula, and eight other galactic sources. Subsequently, CO observations became the standard method of tracing cool molecular interstellar gas, and detection of CO was the foundational event for the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arno Penzias
Arno Allan Penzias (; born April 26, 1933) is an American physicist, radio astronomer and Nobel laureate in physics. Along with Robert Woodrow Wilson, he discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation, which helped establish the Big Bang theory of cosmology. Early life and education Penzias was born in Munich, Germany, the son of Justine (née Eisenreich) and Karl Penzias, who ran a leather business. His grandparents had come to Munich from Poland and were among the leaders of the Reichenbach Strasse Shul. At age six, he and his brother Gunther were among the Jewish children evacuated to Britain as part of the Kindertransport rescue operation. Some time later, including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1978 ''The Origin of Elements'' his parents also fled Nazi Germany for the U.S., and the family settled in the Garment District of New York City in 1940. In 1946, Penzias became a naturalized citizen of the United States. He graduated from Brooklyn Technical High School in 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space. It is an important source of data on the early universe because it is the oldest electromagnetic radiation in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination when the first atoms were formed. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark (see: Olbers' paradox). However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background brightness, or glow, almost uniform, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elmore Leonard
Elmore John Leonard Jr. (October 11, 1925August 20, 2013) was an American novelist, short story writer, and screenwriter. His earliest novels, published in the 1950s, were Westerns, but he went on to specialize in crime fiction and suspense thrillers, many of which have been adapted into motion pictures. Among his best-known works are ''Get Shorty'', ''Out of Sight'', '' Swag'', '' Hombre'', ''Mr. Majestyk'', and ''Rum Punch'' (adapted as the film ''Jackie Brown''). Leonard's writings include short stories that became the films '' 3:10 to Yuma'' and ''The Tall T'', as well as the FX television series '' Justified''. Early life and education Leonard was born in New Orleans, Louisiana, the son of Flora Amelia (née Rive) and Elmore John Leonard. Because his father worked as a site locator for General Motors, the family moved frequently for several years. In 1934, the family settled in Detroit. He graduated from the University of Detroit Jesuit High School in 1943 and, after bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Big Bounce (novel)
''The Big Bounce'' is a crime novel written by Elmore Leonard, published in 1969. The author's first attempt at the crime genre after having met success with westerns, it was adapted twice into film. It is also Leonard's first book starring the character of Jack Ryan (no relation to Tom Clancy's character of the same name), who would return eight years later in '' Unknown Man No. 89''. Plot summary Jack Ryan, a drifter and small-time delinquent, arrives at the Thumb area of Michigan as a seasonal farm laborer, picking pickles for food tycoon Ray Ritchie. He soon gets involved with Nancy, a young seductress, currently Ray Ritchie's girlfriend, though she is also cheating on him with another man, Bob Jr. For a while, Ryan and Nancy get their thrills smashing windows and breaking and entering, but Ryan soon gets a shot at settling down with the help of justice of the peace Mr. Majestyk, who hires Jack as a handyman at his beach resort. When Nancy grows bored with housebreaking a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eternal Inflation
Eternal inflation is a hypothetical inflationary universe model, which is itself an outgrowth or extension of the Big Bang theory. According to eternal inflation, the inflationary phase of the universe's expansion lasts forever throughout most of the universe. Because the regions expand exponentially rapidly, most of the volume of the universe at any given time is inflating. Eternal inflation, therefore, produces a hypothetically infinite multiverse, in which only an insignificant fractal volume ends inflation. Paul Steinhardt, one of the original researchers of the inflationary model, introduced the first example of eternal inflation in 1983, and Alexander Vilenkin showed that it is generic. Alan Guth's 2007 paper, "Eternal inflation and its implications", states that under reasonable assumptions "Although inflation is generically eternal into the future, it is not eternal into the past." Guth detailed what was known about the subject at the time, and demonstrated that eternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Principle
In modern physical cosmology, the cosmological principle is the notion that the spatial distribution of matter in the universe is homogeneous and isotropic when viewed on a large enough scale, since the forces are expected to act uniformly throughout the universe, and should, therefore, produce no observable irregularities in the large-scale structuring over the course of evolution of the matter field that was initially laid down by the Big Bang. Definition Astronomer William Keel explains: The cosmological principle is usually stated formally as 'Viewed on a sufficiently large scale, the properties of the universe are the same for all observers.' This amounts to the strongly philosophical statement that the part of the universe which we can see is a fair sample, and that the same physical laws apply throughout. In essence, this in a sense says that the universe is knowable and is playing fair with scientists. The cosmological principle depends on a definition of "observer", an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotropic
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence ''anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe situations where properties vary systematically, dependent on direction. Isotropic radiation has the same intensity regardless of the direction of measurement, and an isotropic field exerts the same action regardless of how the test particle is oriented. Mathematics Within mathematics, ''isotropy'' has a few different meanings: ; Isotropic manifolds: A manifold is isotropic if the geometry on the manifold is the same regardless of direction. A similar concept is homogeneity. ; Isotropic quadratic form: A quadratic form ''q'' is said to be isotropic if there is a non-zero vector ''v'' such that ; such a ''v'' is an isotropic vector or null vector. In complex geometry, a line through the origin in the direction of an isotropic vector is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Heterogeneous Mixtures, in chemistry, is where certain elements are unwillingly combined and, when given the option, will separate. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', “same”) and ἕτερος (''heteros'', “other, another, different”) respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', “kind”); - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |