|
Bethanechol
Bethanechol is a parasympathomimetic choline carbamate that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors without any effect on nicotinic receptors. Unlike acetylcholine, bethanechol is not hydrolyzed by cholinesterase and will therefore have a long duration of action. Bethanechol is sold under the brand names Duvoid (Roberts), Myotonachol (Glenwood), Urecholine (Merck Frosst) and Urocarb (Hamilton). The name bethanechol refers to its structure as the urethane of beta-methylcholine. Medical uses Bethanechol alleviates dry mouth and is sometimes given orally or subcutaneously to treat urinary retention resulting from general anesthetic, diabetic neuropathy of the bladder, or a side effect of antidepressants; or to treat gastrointestinal lack of muscular tone. The muscarinic receptors in the bladder and gastrointestinal tract stimulate contraction of the bladder and expulsion of urine, and increased gastrointestinal motility, respectively. Bethanechol should be used to treat th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system. Muscarinic receptors are so named because they are more sensitive to muscarine than to nicotine. Their counterparts are nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), receptor ion channels that are also important in the autonomic nervous system. Many drugs and other substances (for example pilocarpine and scopolamine) manipulate these two distinct receptors by acting as selective agonists or antagonists. Function Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter found in the brain, neuromuscular junctions and the autonomic ganglia. Muscarinic receptors are used in the following roles: Recovery receptors ACh is always used as the neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
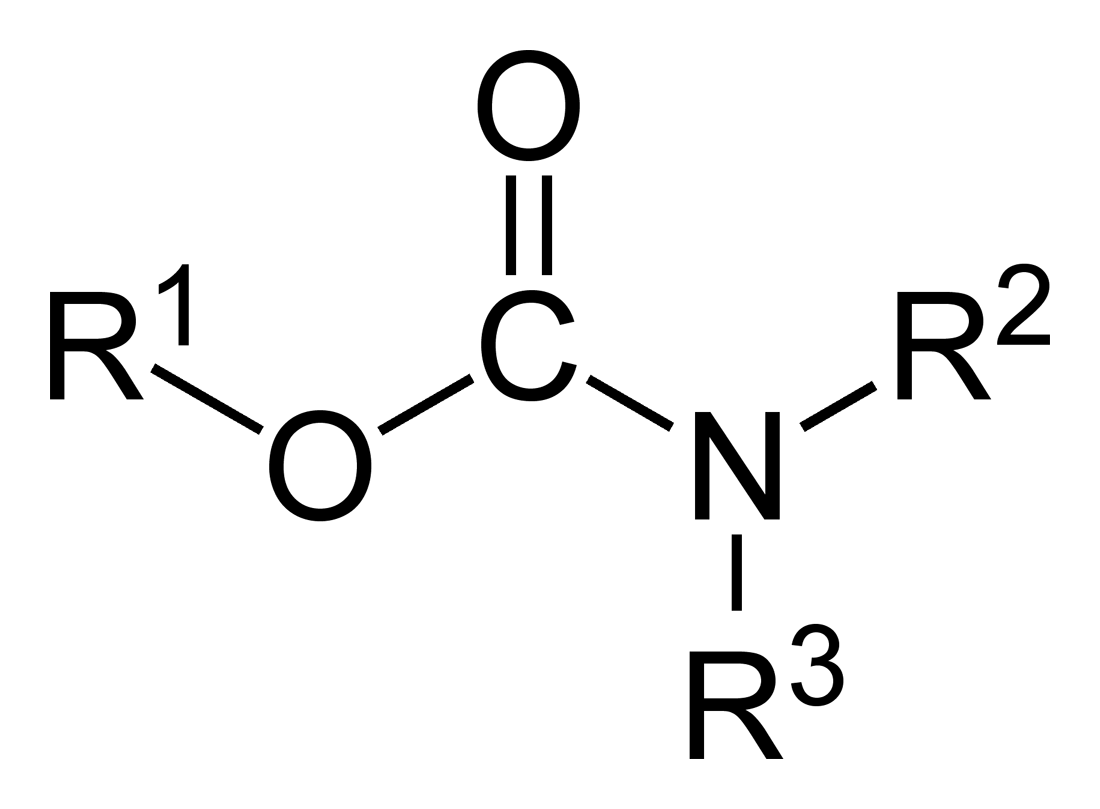
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate immediately, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choline Esters
Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts (X− in the depicted formula is an undefined counteranion). Humans are capable of some ''de novo synthesis'' of choline but require additional choline in the diet to maintain health. Dietary requirements can be met by choline per se or in the form of choline phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine. Choline is not formally classified as a vitamin despite being an essential nutrient with an amino acid–like structure and metabolism. In most animals, choline phospholipids are necessary components in cell membranes, in the membranes of cell organelles, and in very low-density lipoproteins. Choline is required to produce acetylcholine – a neurotransmitter – and ''S''-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a universal methyl donor. Upon methylation SAM is transformed into homocysteine. Symptomatic choline deficiency causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and muscle dama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthesis Quaternary ammonium compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating and not passing gas. Mechanical obstruction is the cause of about 5 to 15% of cases of severe abdominal pain of sudden onset requiring admission to hospital. Causes of bowel obstruction include adhesions, hernias, volvulus, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, appendicitis, tumors, diverticulitis, ischemic bowel, tuberculosis and intussusception. Small bowel obstructions are most often due to adhesions and hernias while large bowel obstructions are most often due to tumors and volvulus. The diagnosis may be made on plain X-rays; however, CT scan is more accurate. Ultrasound or MRI may help in the diagnosis of children or pregnant women. The condition may be treated conserva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
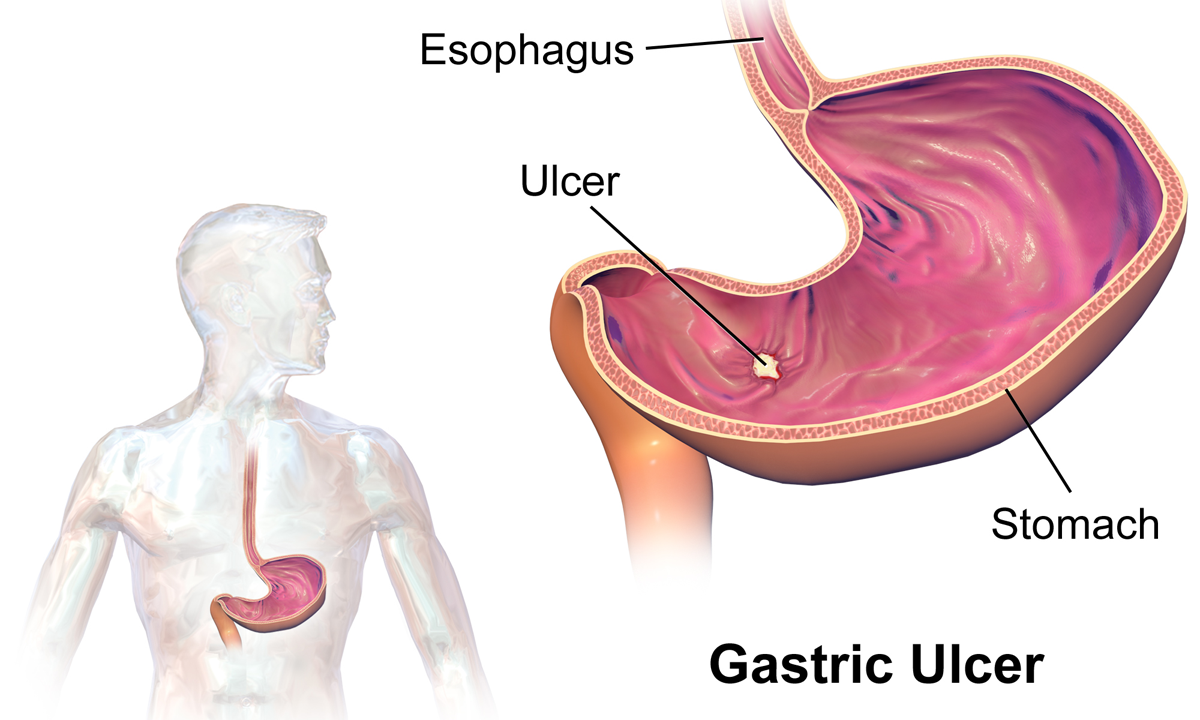
Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
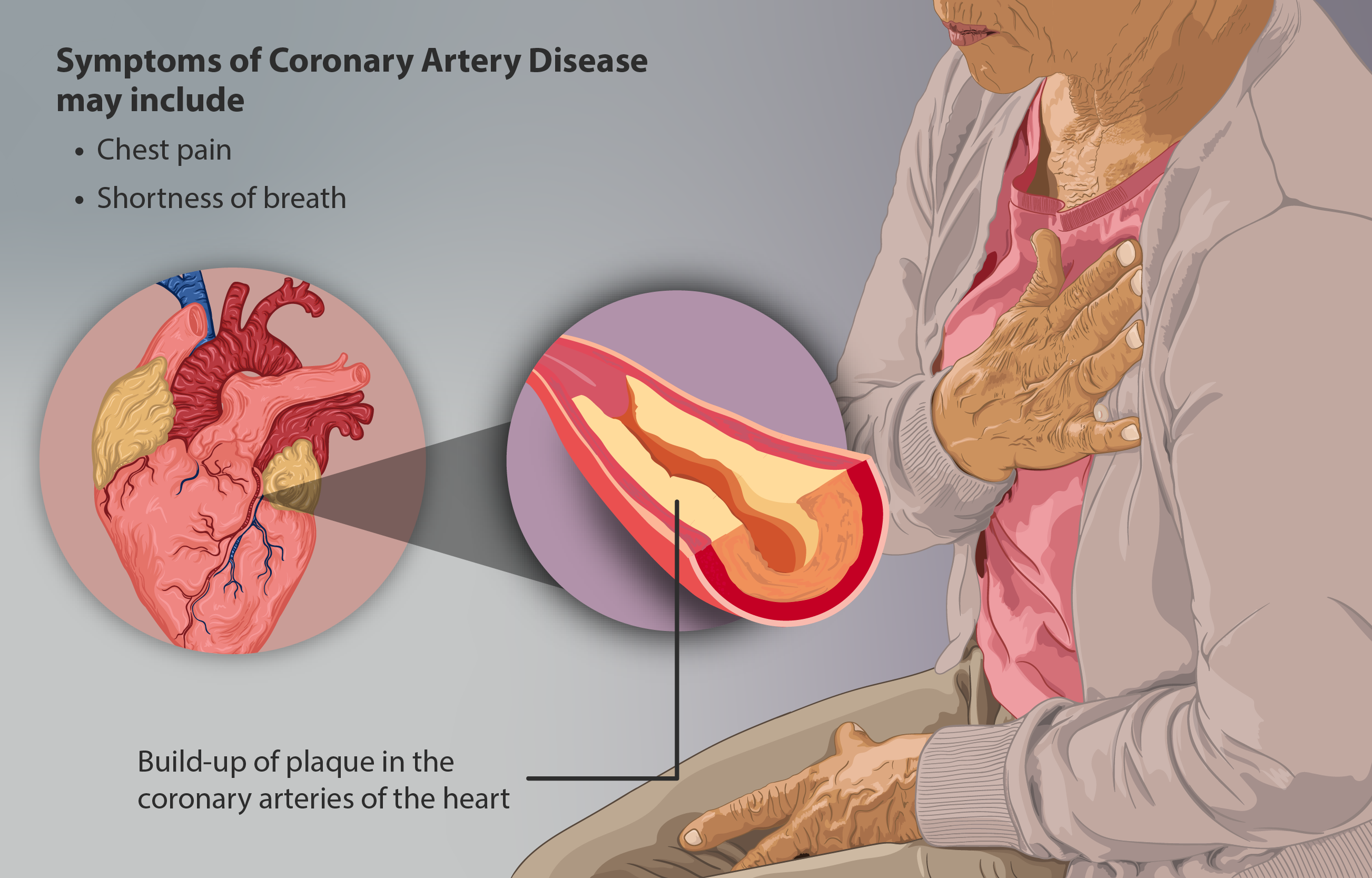
Coronary Insufficiency
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Stress (psychological), stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atopic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, and speaking. Often, babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl or walk as early as other children of their age. Other symptoms include seizures and problems with thinking or reasoning, which each occur in about one-third of people with CP. While symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, underlying problems do not worsen over time. Cerebral palsy is caused by abnormal development or damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and posture. Most often, the problems occur during pregnancy, but they may also occur during childbirth or shortly after birth. Often, the cause is unknown. Risk factors include preterm birth, being a twin, certain infections during pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |