|
Benzoxazole
Benzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine. Although benzoxazole itself is of little practical value, many derivatives of benzoxazoles are commercially important. Being a heterocyclic compound, benzoxazole finds use in research as a starting material for the synthesis of larger, usually bioactive structures. Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable, although as a heterocycle, it has reactive sites which allow for functionalization. Occurrence and applications It is found within the chemical structures of pharmaceutical drugs such as flunoxaprofen and tafamidis. Benzoxazole derivatives are also of interest for optical brighteners in laundry detergents.E. Smulders, E. Sung "Laundry Detergents, 2. Ingredients and Products" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. Benzoxazoles belong to the group of well-known antifungal agents with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoxazoles
Benzoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure, and an odor similar to pyridine. Although benzoxazole itself is of little practical value, many derivatives of benzoxazoles are commercially important. Being a heterocyclic compound, benzoxazole finds use in research as a starting material for the synthesis of larger, usually bioactive structures. Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable, although as a heterocycle, it has reactive sites which allow for functionalization. Occurrence and applications It is found within the chemical structures of pharmaceutical drugs such as flunoxaprofen and tafamidis. Benzoxazole derivatives are also of interest for optical brighteners in laundry detergents.E. Smulders, E. Sung "Laundry Detergents, 2. Ingredients and Products" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012. Benzoxazoles belong to the group of well-known antifungal agents with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthranil
Anthranil (2,1-benzisoxazole) is an organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO, which features a fused benzene-isoxazole bicyclic ring structure. It is an isomer of the more common compounds benzoxazole and benzisoxazole, which have their oxygen atoms located in the 1-position. The locations of the heteroatoms in anthranil results in disrupted aromaticity In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to satur ..., making it by far the least stable of the 3 structural isomers. References Aromatic bases Simple aromatic rings {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flunoxaprofen
Flunoxaprofen, also known as Priaxim, is a chiral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is closely related to naproxen, which is also an NSAID. Flunoxaprofen has been shown to significantly improve the symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The clinical use of flunoxaprofen has ceased due to concerns of potential hepatotoxicity. Structure Flunoxaprofen is a two-ring heterocyclic compound derived from benzoxazole. It also contains a fluorine atom and a propanoyl group. Synthesis and preparation Synthesis of flunoxaprofen can be seehere Because flunoxaprofen has limited water-solubility, additional steps must be taken in order to prepare syrups, creams, suppositories, etc. In order to make flunoxaprofen water-soluble, yet still active and efficient, it must be mixed with lysine and then suspended in an organic solvent that is soluble in water. A salt will crystallize upon cooling. The salt must then be filtered out and dried. Pharmacological testing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tafamidis
Tafamidis, sold under the brand names Vyndaqel and Vyndamax, is a medication used to delay disease progression in adults with certain forms of transthyretin amyloidosis. It can be used to treat both hereditary forms, familial amyloid cardiomyopathy and familial amyloid polyneuropathy, as well as wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis, which formerly was called senile systemic amyloidosis. It works by stabilizing the quaternary structure of the protein transthyretin. In people with transthyretin amyloidosis, transthyretin falls apart and forms clumps called (amyloid) that harm tissues including nerves and the heart. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration considers tafamidis to be a first-in-class medication. Medical use Tafamidis is used to delay nerve damage in adults who have transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy, or heart disease in adults who have transthyretin amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy. It is taken by mouth. Women should not get pregnant while taking it and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzisoxazole
1,2-Benzisoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO containing a benzene-fused isoxazole ring structure. The compound itself has no common applications; however, functionalized benzisoxazoles and benzisoxazoyls have a variety of uses, including pharmaceutical drugs such as some antipsychotics (including risperidone, paliperidone, ocaperidone, and iloperidone) and the anticonvulsant zonisamide. Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable; however, it is only weakly basic. Synthesis Benzisoxazole may be prepared from inexpensive salicylaldehyde, via a base catalyzed room temperature reaction with hydroxylamine-''O''-sulfonic acid. : Reactions Kemp elimination First reported by Daniel S. Kemp Daniel Schaeffer Kemp (October 20, 1936May 2, 2020) was an American organic chemist, an emeritus professor of chemistry at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Kemp's work was focused on the synthesis (chemistry), synthesis and conformation ..., the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics, as if they were tennis balls for example, is not possible due to quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. The protons have a positive electric charge, the electrons have a negative electric charge, and the neutrons have no electric charge. If the number of protons and electrons are equal, then the atom is electrically neutral. If an atom has more or fewer electrons than protons, then it has an overall negative or positive charge, respectively – such atoms are called ions. The electrons of an atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Bases
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
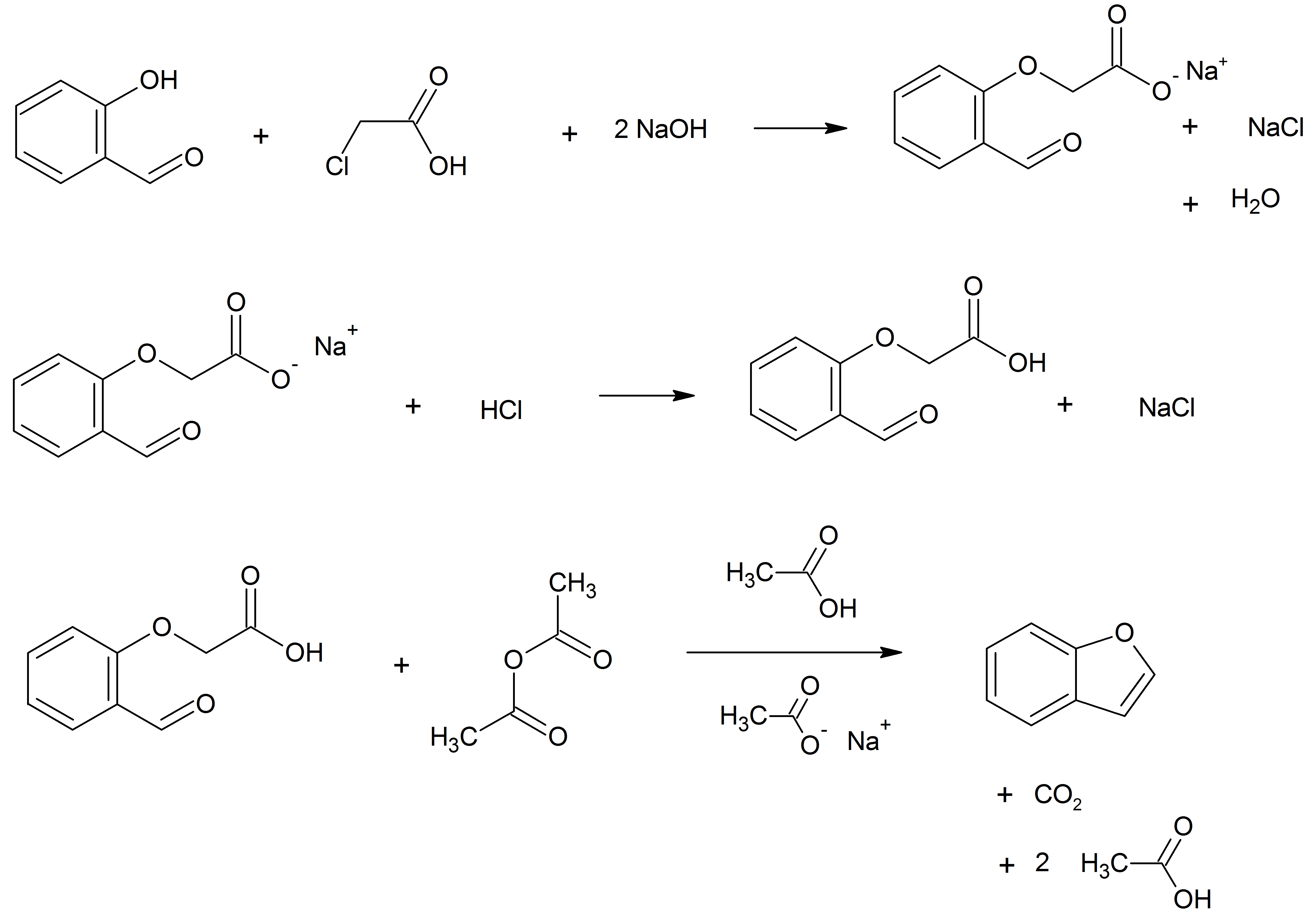
Benzofuran
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the "parent" of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants. Production Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol. Laboratory methods Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. *Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide: : *Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles: : Diels–Alder reaction yielding a substituted benzofuran, 450px * Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols: : Benzofurans via Cycloisomerization, 400px Related compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ... with the formula Carbon, C8Hydrogen, H7Nitrogen, N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by a variety of bacteria. As an Cell signaling, intercellular signal molecule, indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including Bacterial spore, spore formation, plasmid stability, drug resistance, resistance to drugs, biofilm formation, and virulence. The amino acid tryptophan is an indole derivative and the precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. General properties and occurrence Indole is a solid at room temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzothiazole
Benzothiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula . It is colorless, slightly viscous liquid. Although the parent compound, benzothiazole is not widely used, many of its derivatives are found in commercial products or in nature. Firefly luciferin can be considered a derivative of benzothiazole. Structure and preparation Benzothiazoles consist of a 5-membered 1,3-thiazole ring fused to a benzene ring. The nine atoms of the bicycle and the attached substituents are coplanar. Benzothiazoles are prepared by treatment of 2-mercaptoaniline with acid chlorides: :C6H4(NH2)SH + RC(O)Cl → C6H4(NH)SCR + HCl + H2O Uses Benzothiazole occurs naturally in some foods but is also used as a food additive. It has a sulfurous odor and meaty flavor. The European Food Safety Authority assessment had "no safety concern at estimated levels of intake as a flavouring substance". The heterocyclic core of the molecule is readily substituted at the unique methyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazole
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a colorless solid. Preparation Benzimidazole is produced by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid,. or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate: :C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH 2-substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation.Robert A. Smiley "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions Benzimidazole is a base: :C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → 6H4(NH)2CHsup>+ It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases: :C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li 6H4N2CH + H2 The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry. The most prominent benzimidazole complex features ''N''-ribosyl-dimethylbenzimidazole as found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)