|
Battle Of Silva Litana
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army of 25,000 men under the consul-elect Lucius Postumius Albinus and destroyed the Roman army, with only ten men surviving the ambush, a few prisoners were taken by the Gauls and Postumius was killed, his corpse was decapitated and his skull was covered with gold and used as a ceremonial cup by the Boii. News of this military disaster, reaching Rome probably after the election of consuls for 215 BC in Spring 215 BC or after the defeat at Cannae in the fall of 216 BC, triggered a renewed panic in Rome and forced the Romans to postpone military operations against the Gauls until the conclusion of the Second Punic War. Rome decided to focus on defeating Hannibal and sent only two legions to guard against any possible Gallic attack, however, the Boii and Insubres did not attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides the Carthaginians were defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. The First Punic War had ended in a Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbrian
Umbrian is an extinct Italic language formerly spoken by the Umbri in the ancient Italian region of Umbria. Within the Italic languages it is closely related to the Oscan group and is therefore associated with it in the group of Osco-Umbrian languages, a term generally replaced by Sabellic in modern scholarship. Since that classification was first formulated, a number of other languages in ancient Italy were discovered to be more closely related to Umbrian. Therefore, a group, the Umbrian languages, was devised to contain them. Corpus Umbrian is known from about 30 inscriptions dated from the 7th through 1st centuries BC. The largest cache by far is the Iguvine Tablets, sevenThe tradition born in the 17th century that the tablets were originally nine, and that two, sent to Venice, never came back, must be considered spurious. Paolucci (1966), p. 44 inscribed bronze tablets found in 1444 near the village of Scheggia or, according to another tradition, in an underground chamber a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaesatae
The Gaesatae or Gaesati (Greek Γαισάται) were a group of Gallic mercenary warriors who lived in the Alps near the river Rhône and fought against the Roman Republic at the Battle of Telamon in 225 BC., s.v. ''Gaesatae''. According to some scholars, the Gaesatae may be identified with the Allobroges, who first appeared in the same region only a few years later in connection with Hannibal's crossing of the Alps in 218 BC. Etymology The Gaulish name ''Gaisatai'' literally means '(armed) with javelins' or 'spearmen', and derives from the Celtic noun ''*gaisos'', meaning 'spear, javelin'. It is cognate with the Old Irish ''gaiscedach'' ('armed person, warrior, champion'), from ''gaisced'' ('weapons, arms'), itself from ''gáe'' ('spear, javelin'). The stem ''gaisat''- can also be found in the Gaulish proper nouns ''Gaesatus'', ''Gesatus'', ''Gesatius'', or ''Gesatia'', as well as in the compound ''Gesato-rix'', meaning 'king-spear', or 'king-javelin'. The Greek historian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
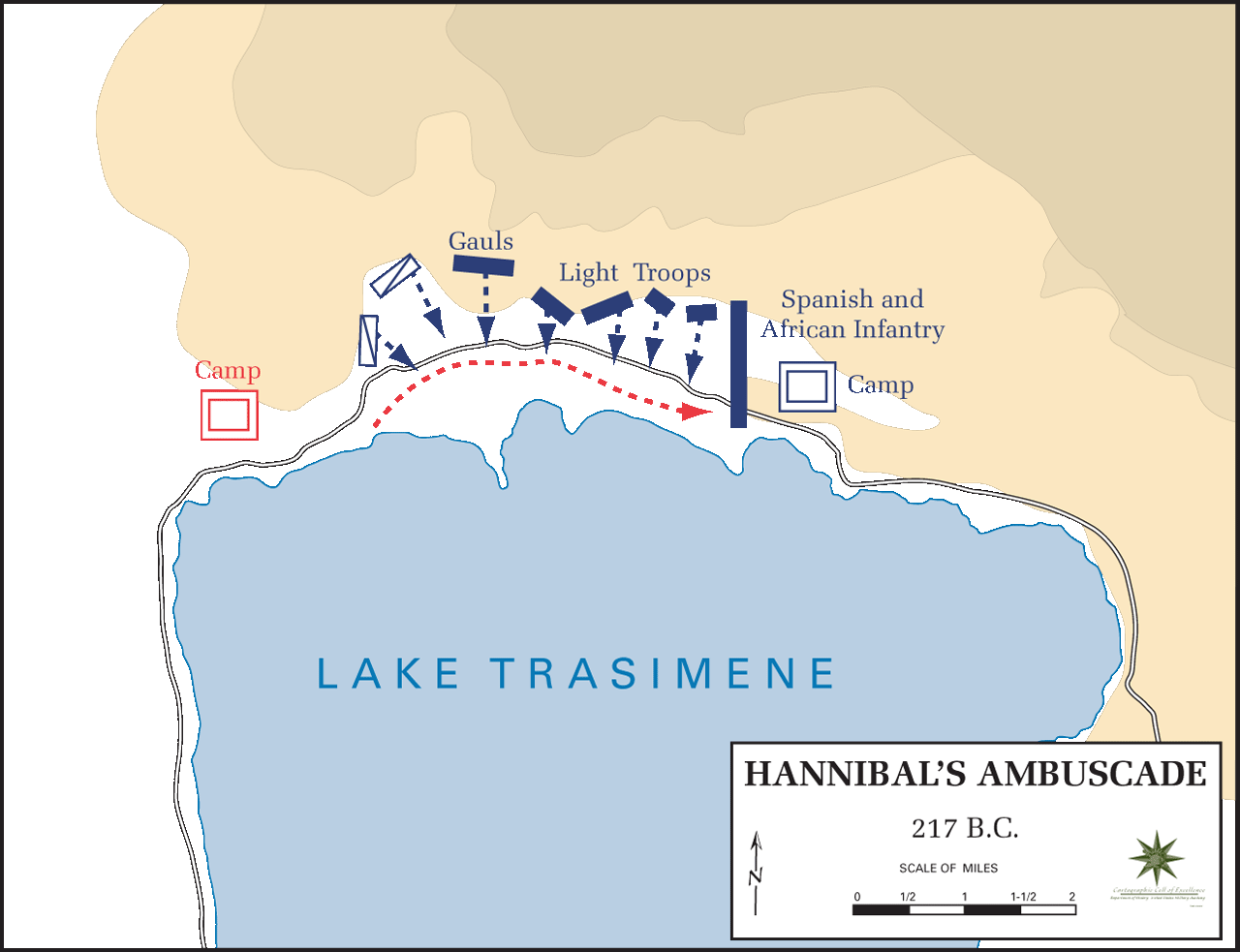
Gaius Flaminius (consul 223 BC)
Gaius Flaminius (c. 275 BC217 BC) was a leading Roman politician in the third century BC. Twice consul, in 223 and 217, Flaminius is notable for the ''Lex Flaminia'', a land reform passed in 232, the construction of the Circus Flaminius in 221, and his death at the hands of Hannibal's army at the Battle of Lake Trasimene in 217, during the Second Punic War. Flaminius is celebrated by ancient sources as being a skilled orator and a man possessed of great piety, strength, and determination. He is, however, simultaneously criticised by ancient writers such as Cicero and Livy for his popular policies and disregard of Roman traditions, particularly during the terms of his tribunate and second consulship. Tribunate and the ''Lex Flaminia'', 232 BC Flaminius was elected as tribune of the plebs in 232 BC. Cicero writes that Flaminius was an accomplished orator before the people, a skill that likely helped him achieve the tribunate. During his term Flaminius proposed the ''Lex Flaminia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermo
Fermo (ancient: Firmum Picenum) is a town and ''comune'' of the Marche, Italy, in the Province of Fermo. Fermo is on a hill, the Sabulo, elevation , on a branch from Porto San Giorgio on the Adriatic coast railway. History The oldest human remains from the area are funerary remains from the 9th–8th centuries BC, belonging to the Villanovan culture or the proto-Etruscan civilization. The ancient Firmum Picenum was founded as a Latin colony, consisting of 6000 men, in 264 BC, after the conquest of the Picentes, as the local headquarters of the Roman power, to which it remained faithful. It was originally governed by five quaestors. It was made a colony with full rights after the battle of Philippi, the 4th Legion being settled there. It lay at the junction of roads to Pausulae, Urbs Salvia, and Asculum, connected to the coast road by a short branch road from Castellum Firmanum (Porto S. Giorgio). According to Plutarch's ''Parallel Lives'', Cato the Elder thought highly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picentes
The name Picentes or Picentini refers to the population of Picenum, on the northern Adriatic coastal plain of ancient Italy. Their endonym, if any, is not known for certain. There is linguistic evidence that the Picentini comprised two different ethnicities: a group known to scholars as the "South Picenes" (or South Picenians) were an Italic tribe,Philip Baldi, 1999, ''The Foundations of Latin'', The Hague, Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 134–6, 152–3. while the "North Picenes" (or North Picenians) appear to have had closer links to non-Italic peoples. Usage of the toponym Picenum depends on the time period. The region between the Apennines and the Adriatic Sea south of Ancona was in Picenum during the entire early historic period. Between Ancona and Rimini to the north the population was multi-ethnic. In the Roman Republic it was Gallia Togata, but the Gauls were known to have combined or supplanted earlier populations. The ''ager Gallicus'', as it was called, was considered both Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sena Gallica
Sena may refer to: Places * Sanandaj or Sena, city in northwestern Iran * Sena (state constituency), represented in the Perlis State Legislative Assembly * Sena, Dashtestan, village in Bushehr Province, Iran * Sena, Huesca, municipality in Huesca province, Spain * Sena, Iran, village in Bushehr Province, Iran * Sena, a Medieval Catalan exonym for Siena, Italy * Sena, Yemen * Seňa, village and municipality in the Kosice Region, Slovakia * Vila de Sena or Sena, Mozambique People *Balthasar Seña (1590–1614), Spanish Jesuit missionary * Dominic Sena (born 1949), American movie director * Suzanne Sena (born 1963), American television host * Maryam Sena, wife of Sarsa Dengel, the Emperor of Ethiopia *Lady Tsukiyama also known as Sena (瀬名), Japanese samurai-class woman. * , Japanese snowboarder (born 1999) Fictional characters * Robin Sena from ''Witch Hunter Robin'' * Sena Kobayakawa from ''Eyeshield 21'' * Sena Hayami from ''Mashin Sentai Kiramager'' * Kaito Sena from ''Tortur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ager Gallicus
The expression Ager Gallicus defines the territory of the Senone Gauls after it was devastated and conquered by Rome in 284 BC or 283 BC, either after the Battle of Arretium or the Battle of Lake Vadimon. Destruction of the Ager Gallicus According to Polybius, unspecified Gauls besieged the city of Arretium ( Arezzo, in north-eastern Tuscany) and defeated a Roman force which had come to the aid of the city. Their commander, the praetor Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter died in the battle. This would place the battle in 283 BC because Denter was a consul in 284 BC. Denter was replaced by Manius Curius Dentatus, who sent envoys to negotiate the release of Roman hostages, but they were killed. The Romans marched on Gaul and they were met by the Senones who were defeated in a pitched battle. Polybius used the highly generic term Gaul. He meant Gallia Cisalpina (Gaul this side of the Alp from the Roman geographical viewpoint) which was the name the Romans gave the area of the Gauls o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lake Vadimo (283 BC)
The second Battle of Lake Vadimo was fought in 283 BC between Rome and the combined forces of the Etruscans and the Gallic tribes of the Boii and the Senones. The Roman army was led by consul Publius Cornelius Dolabella. The result of the battle was a Roman victory. History The previous battle was fought in 310 BC during the Second Samnite War (327-304 BC) between the Romans and a large coalition of Etruscan city-states. It was said to have been the largest battle between the two nations. Unfortunately, this battle occurred in a period for which the books in The History of Rome by Livy, the most thorough ancient historian who wrote Roman history, have been lost and we do not have his thorough coverage. The best text is by Polybius, but this lacks important details. A fragment from Appian is confusing. There are many details about how the battle was fought. According to Polybius, the battle followed events which started with the siege of Arretium (Arezzo, in north-eastern Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sentinum
The Battle of Sentinum was the decisive battle of the Third Samnite War, fought in 295 BC near Sentinum (next to the modern town of Sassoferrato, in the Marche region of Italy), in which the Romans overcame a formidable coalition of Samnites, Etruscans, and Umbrians and Senone Gauls. The Romans won a decisive victory that broke up the tribal coalition (the Etruscans, Umbrians, and Senones pulled out of the war) and paved the way for the Romans' complete victory over the Samnites. The Romans involved in the battle of Sentinum were commanded by consuls Publius Decius Mus and Quintus Fabius Maximus Rullianus. Background The Third Samnite War started when envoys from Lucania asked Rome for help against an attack on them by the Samnites. Rome intervened and the war started. Just prior to and during the first year of this, Rome was also facing a war with the Etruscans. In 297 BC the Romans received news that the Etruscans were considering suing for peace. As a result, both Roman con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire. Definition Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on which resided the tribe of the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins or Latians. It was located on the left bank (east and south) of the Tiber, River Tiber, extending northward to the Aniene, River Anio (a left-bank tributary of the Tiber) and southeastward to the Pomptina Palus (Pontine Marshes, now the Pontine Fields) as far south as the Cape Circeo, Circeian promontory. The right bank of the Tiber was occupied by the Etruscan city of Veii, and the other borders were occupied by Ancient Italic people, Italic tribes. Subsequently, Rome defeated Veii and then its Italic neighbours, expanding its dominions over Southern Etruria and to the south, in a partly marshy and partly mountainous region. The latter saw the creation of numerous Roman and Latin co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Allia
The Battle of the Allia was a battle fought between the Senones – a Gallic tribe led by Brennus, who had invaded Northern Italy – and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought at the confluence of the Tiber and Allia rivers, 11 Roman miles (16 km, 10 mi) north of Rome. The Romans were routed and subsequently Rome was sacked by the Senones. According to scholar Piero Treves, "the absence of any archaeological evidence for a destruction-level of this date suggests that hissack of Rome was superficial only." The date of the battle has been traditionally given as 390 BC in the Varronian chronology, based on an account of the battle by the Roman historian Livy. Plutarch noted that the battle took place "just after the summer solstice when the moon was near the full ..a little more than three hundred and sixty years from the founding f Rome" or shortly after 393 BC.Plut. Cam. 19.1Plut. Cam. 22.1 The Greek historian Polybius used a Greek dating system to der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


