|
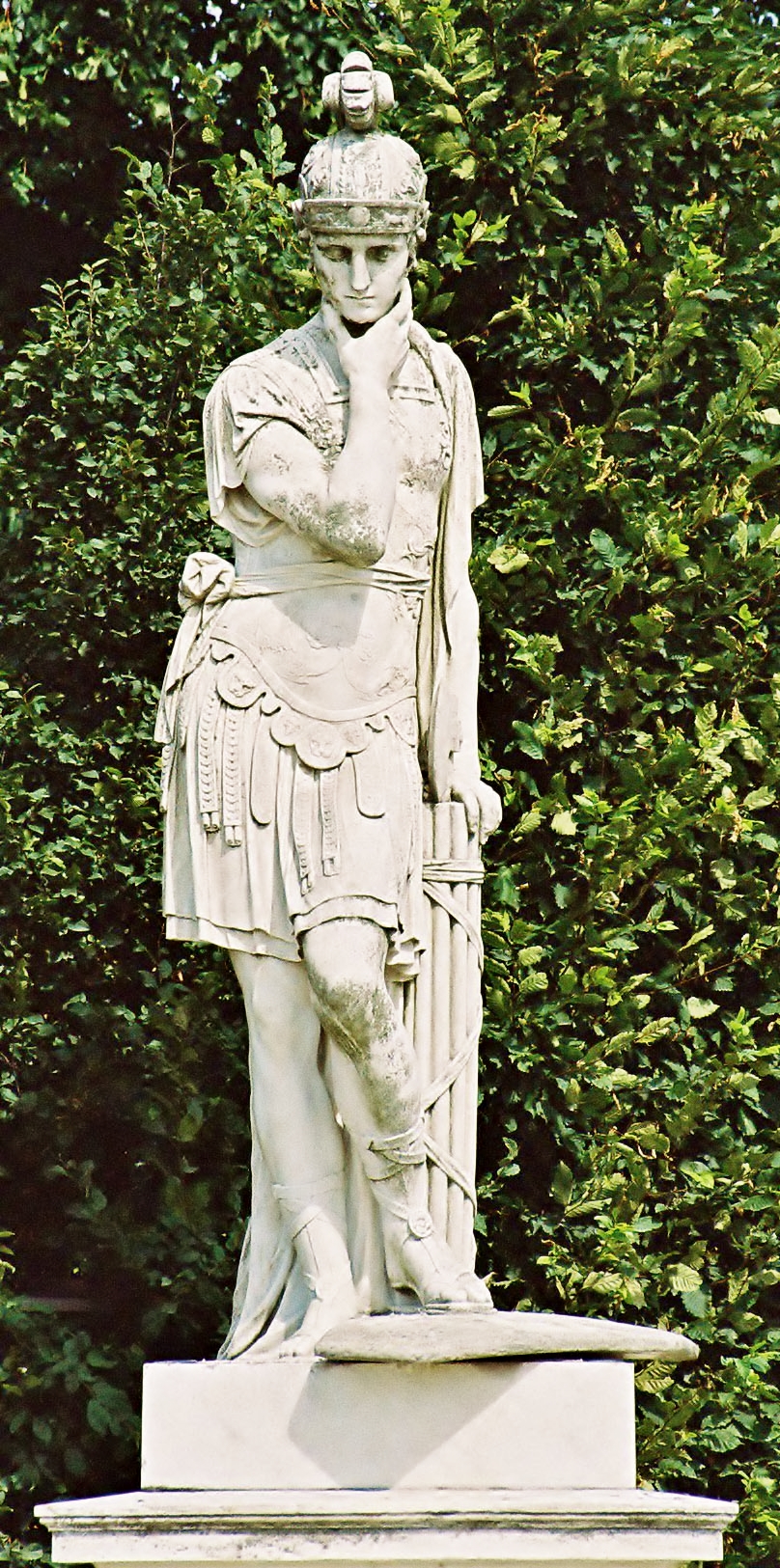
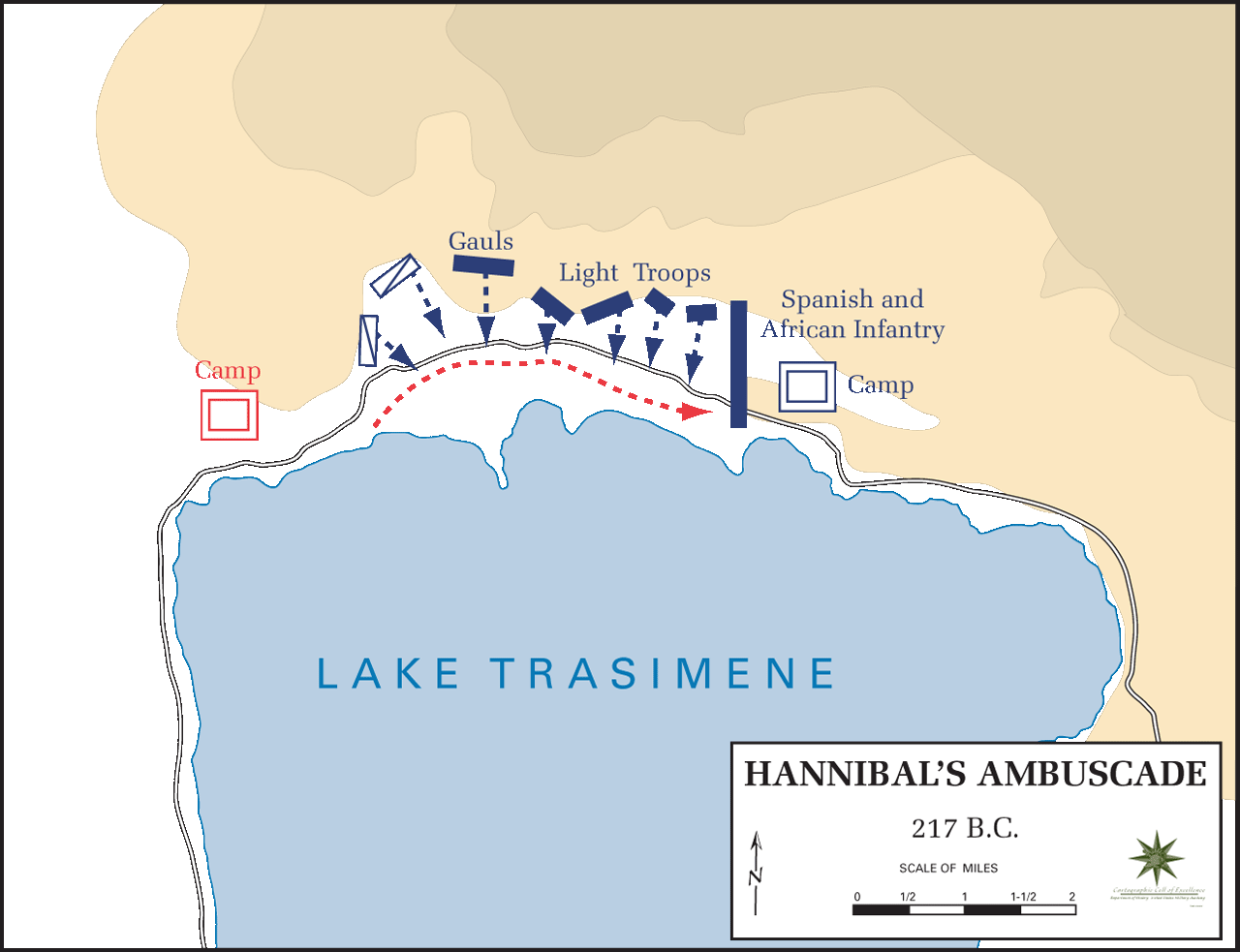
Gaius Flaminius (consul 223 BC)
Gaius Flaminius (c. 275 BC217 BC) was a leading Roman politician in the third century BC. Twice consul, in 223 and 217, Flaminius is notable for the ''Lex Flaminia'', a land reform passed in 232, the construction of the Circus Flaminius in 221, and his death at the hands of Hannibal's army at the Battle of Lake Trasimene in 217, during the Second Punic War. Flaminius is celebrated by ancient sources as being a skilled orator and a man possessed of great piety, strength, and determination. He is, however, simultaneously criticised by ancient writers such as Cicero and Livy for his popular policies and disregard of Roman traditions, particularly during the terms of his tribunate and second consulship. Tribunate and the ''Lex Flaminia'', 232 BC Flaminius was elected as tribune of the plebs in 232 BC. Cicero writes that Flaminius was an accomplished orator before the people, a skill that likely helped him achieve the tribunate. During his term Flaminius proposed the ''Lex Flaminia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducarius
Ducarius was a Gallic nobleman from the Insubres who fought for Hannibal at the Battle of Lake Trasimene on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War, and, according to Livy, slew the Roman commander Gaius Flaminius. As described by Livy: {{blockquote, text=For almost three hours the fighting went on; everywhere a desperate struggle was kept up, but it raged with greater fierceness round the consul. He was followed by the pick of his army, and wherever he saw his men hard pressed and in difficulties he at once went to their help. Distinguished by his armour he was the object of the enemy's fiercest attacks, which his comrades did their utmost to repel, until an Insubrian horseman who knew the consul by sight — his name was Ducarius — cried out to his countrymen, "Here is the man who slew our legions and laid waste our city and our lands! I will offer him in sacrifice to the shades of my foully murdered countrymen." Digging spurs into his horse he charged into the dense mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senones
The Senones or Senonii (Gaulish: "the ancient ones") were an ancient Gallic tribe dwelling in the Seine basin, around present-day Sens, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Part of the Senones settled in the Italian peninsula, where they ousted the Umbrians between Ariminum (modern-day Rimini) and Ancona. They are described in classical sources as the leaders of the Gallic war-band that captured Rome during the Battle of the Allia in 390 BCE. They remained a constant threat until Rome eventually subjugated them in 283 BCE, after which they disappeared from Italy. Name They are mentioned as ''Sḗnōnes'' (Σήνωνες) and ''Sḗnōnas'' (Σήνωνας) by Polybius (2nd c. BC), ''Senonii'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Sénnōnes'' (Σέννωνες) by Diodorus Siculus (1st c. BC), ''Sénōnes'' (Σένωνες) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), ''Senones'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), ''Sénones'' (Σένονες) by Ptolemy (2nd c. AD), and as ''Senones'' by Ammnianus (4th c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ager Romanus
The Ager Romanus (literally, "the field of Rome"') is the geographical rural area (part plains, part hilly) that surrounds the city of Rome. Politically and historically, it has represented the area of influence of Rome's municipal government. It is limited to the south by the Monti Prenestini range, Alban hills and Pontine Marshes; to the west by the Tyrrhenian Sea; to the north by the hills surrounding Lake Bracciano and to the east by the Monti Tiburtini range. History Ancient Rome The Rome of Romulus and his immediate successors possessed a very restricted territory, as did neighbouring Latin cities such as Praeneste. Such territories were marked by boundary stones, or cippi, used to define and limit the legitimate area of influence of cities, and the boundaries of private landholdings. According to tradition, Rome rapidly outgrew the ''ager'' established by its founder, and rather than accept its confinement, Tullus Hostilius razed the Latin city of Alba Longa ca. 635 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobiles
The ''nobiles'' ( ''nobilis'') were members of a social rank in the Roman Republic indicating that one was "well known". This may have changed over time: in Cicero's time, one was notable if one descended from a person who had been elected Roman consul, consul. In earlier periods and more broadly, this may have included a larger group consisting of those who were Patrician (ancient Rome), patricians, were descended from patricians who had become plebeians via ''transitio ad plebem'', or were descended from plebeians who had held Curule seat#Ancient Rome, curule offices. History The ''nobiles'' emerged after the Conflict of the Orders established legal equality between patricians and plebeians, allowing plebeians to hold all the Roman magistrate, magistracies; the state of being "known" was connected to the ''nobiless rights to funeral masks ( la, imagines) and actors in aristocratic funeral processions. However, the term is largely unattested to in the middle Republic, having been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius Gracchus
Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus ( 163 – 133 BC) was a Roman politician best known for his agrarian law, agrarian reform law entailing the transfer of land from the Roman state and wealthy landowners to poorer citizens. He had also served in the Roman army, fighting in the Third Punic War and in Spain. Against substantial opposition in the Roman Senate, senate, his land reform bill was carried through during his term as tribune of the plebs in 133 BC. Fears of Tiberius' popularity and willingness to break political norms, incited by his standing for a second and consecutive term as tribune, led to his being killed, along with many supporters, in a riot instigated by his enemies. A decade later, his younger brother Gaius Gracchus, Gaius proposed similar and more radical reformist legislation and suffered a similar fate. The date of his death marks the traditional start of the Roman republic's decline and eventual collapse. Background Tiberius Sempronii, Sempronius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietas
''Pietas'' (), translated variously as "duty", "religiosity" or "religious behavior", "loyalty", "devotion", or "filial piety" (English "piety" derives from the Latin), was one of the chief virtues among the ancient Romans. It was the distinguishing virtue of the founding hero Aeneas, who is often given the adjectival epithet ''pius'' ("religious") throughout Virgil's epic ''Aeneid''. The sacred nature of ''pietas'' was embodied by the divine personification Pietas, a goddess often pictured on Roman coins. The Greek equivalent is ''eusebeia'' (εὐσέβεια). Cicero defined ''pietas'' as the virtue "which admonishes us to do our duty to our country or our parents or other blood relations." The man who possessed ''pietas'' "performed all his duties towards the deity and his fellow human beings fully and in every respect," as the 19th-century classical scholar Georg Wissowa described it. Cicero suggests people should have awareness of our own honor, we must always attempt to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maiestas Law
The law of majestas, or ''lex maiestatis'', encompasses several ancient Roman laws (''leges maiestatis'') throughout the Republican and Imperial periods dealing with crimes against the Roman people, state, or Emperor. Description In Roman law, the offences originally falling under the head of treason were almost exclusively those committed in military service. The very name ''perduellio'', the name of the crime in the older Roman law, is evidence of this. ''Perduelles'' were, strictly, public enemies who bore arms against the state; and traitors were regarded as having no more rights than public enemies. The Twelve Tables made it punishable with death to communicate with the enemy or to betray a citizen to the enemy. Other kinds of ''perduellio'' were punished by "interdiction of fire and water" (''aquae et ignis interdictio''), in other words, banishment. The crime was tried before a special tribunal (''quaestio'') by two officials (''duumviri perduellionis''), which was perhaps t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gracchi
The Gracchi brothers were two Roman brothers, sons of Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus who was consul in 177 BC. Tiberius, the elder brother, was tribune of the plebs in 133 BC and Gaius, the younger brother, was tribune a decade later in 123–122 BC. They attempted to redistribute the ''ager publicus'' – the public land hitherto controlled principally by aristocrats – and military veterans, in addition to other social and constitutional reforms. After achieving some early success, both were assassinated by the Early lives Their father was the elderly Tiberius Sempronius Gracchus, who had served as tribune of the plebs, praetor, consul, and censor. Their mother was Cornelia, daughter of Scipio Africanus, himself considered a hero by the Roman people for his part in the war against Carthage. Their parents had 12 children; only one daughter – who later married Scipio Aemilianus – and two sons, Tiberius and Gaius, survived to adulthood. After the boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populares
Optimates (; Latin for "best ones", ) and populares (; Latin for "supporters of the people", ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated academic discussion" as to whether Romans would have recognised an ideological content or political split in the label. Among other things, ''optimates'' have been seen as supporters of the continued authority of the senate, politicians who operated mostly in the senate, or opponents of the ''populares''. The ''populares'' have also been seen as focusing on operating before the popular assemblies, generally in opposition to the senate, using "the populace, rather than the senate, as a means or advantage. References to optimates (also called ''boni'', "good men") and ''populares'' are found among the writings of Roman authors of the 1st century BC. The distinction between the terms is most clearly established in Cicero's ''Pro Sestio'', a speec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerius Maximus
Valerius Maximus () was a 1st-century Latin writer and author of a collection of historical anecdotes: ''Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX'' ("Nine books of memorable deeds and sayings", also known as ''De factis dictisque memorabilibus'' or ''Facta et dicta memorabilia''). He worked during the reign of Tiberius (14 AD to 37 AD). During the Middle Ages, Valerius Maximus was one of the most copied Latin prose authors, second only to Priscian. More than 600 medieval manuscripts of his books have survived as a result.Briscoe, ''Valerius Maximus'', p. 15. Biography Nothing is known of his life except that his family was poor and undistinguished, and that he owed everything to Sextus Pompeius (consul AD 14), proconsul of Asia, whom he accompanied to the East in 27. Pompeius was the center of a literary circle to which Ovid belonged; he was also an intimate friend of the most literary prince of the imperial family, Germanicus. Although he shared the same name as a prestigious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus
Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator ( 280 – 203 BC), was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times (233, 228, 215, 214, and 209 BC) and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was censor in 230 BC. His agnomen, ''Cunctator'', usually translated as "the delayer", refers to the strategy that he employed against Hannibal's forces during the Second Punic War. Facing an outstanding commander with superior numbers, he pursued a then-novel strategy of targeting the enemy's supply lines, and accepting only smaller engagements on favourable ground, rather than risking his entire army on direct confrontation with Hannibal himself. As a result, he is regarded as the originator of many tactics used in guerrilla warfare. Beginnings Born at Rome c. 280 BC, Fabius was a descendant of the ancient patrician Fabia gens. He was the son or grandson of Quintus Fabius Maximus Gurges, three times consul and ''princeps senatus'', and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians. Illyrians spoke the Illyrian language, an Indo-European language, which in ancient times perhaps also had speakers in some parts of Southern Italy. The geographical term Illyris (distinct from ''Illyria'') was sometimes used to define approximately the area of northern and central Albania down to the Aoös valley (modern Vjosa), including in most periods much of the lakeland area. In Roman times the terms Illyria / Illyris / Illyricum were extended from the territory that was roughly located in the area of the south-eastern Adriatic coast (modern Albania and Montenegro) and its hinterland, to a broader region stretching between the Adriatic Sea and the Danube, and from the upper reaches of the Adriatic down to the Ardiaei. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |