|
Battle Of Mirebeau
The Battle of Mirebeau was a battle in 1202 between the House of Lusignan-Breton alliance and the Kingdom of England. King John of England successfully smashed the Lusignan army by surprise. Background After Richard I's death on 6 April 1199 there were two potential claimants to the Angevin throne: John, whose claim rested on being the sole surviving son of Henry II, and Arthur I of Brittany, who held a claim as the son of Geoffrey, John's elder brother. Richard appeared to have started to recognise John as his legitimate heir in the final years before his death, but the matter was not clear-cut and medieval law gave little guidance as to how the competing claims should be decided. With Norman law favouring John as the only surviving son of Henry II and Angevin law favouring Arthur as the heir of Henry's elder son, the matter rapidly became an open conflict. John was supported by the bulk of the English and Norman nobility and was crowned at Westminster Abbey, backed by hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur I, Duke Of Brittany
Arthur I ( br, Arzhur 1añ; french: link=no, Arthur 1er de Bretagne) (29 March 1187 – presumably 1203) was 4th Earl of Richmond and Duke of Brittany between 1196 and 1203. He was the posthumous son of Geoffrey II, Duke of Brittany, and Constance, Duchess of Brittany. His father, Geoffrey, was the son of Henry II, King of England. In 1190 Arthur was designated heir to the throne of England and its French territory by his uncle, Richard I, the intent being that Arthur would succeed Richard in preference to Richard's younger brother John. Nothing is recorded of Arthur after his incarceration in Rouen Castle in 1203, and while his precise fate is unknown, it is generally believed he was killed by John. Early life Arthur was born in 1187, the son of Duchess Constance and Duke Geoffrey II of Brittany, who died before he was born. As an infant, Arthur was second in line to the succession of his paternal grandfather King Henry II of England, after his uncle Richard. King Henry died wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin king of England. King Louis VII of France made him Duke of Normandy in 1150. Henry became Count of Anjou and Maine upon the death of his father, Count Geoffrey V, in 1151. His marriage in 1152 to Eleanor of Aquitaine, former spouse of Louis VII, made him Duke of Aquitaine. He became Count of Nantes by treaty in 1158. Before he was 40, he controlled England; large parts of Wales; the eastern half of Ireland; and the western half of France, an area that was later called the Angevin Empire. At various times, Henry also partially controlled Scotland and the Duchy of Brittany. Henry became politically involved by the age of 14 in the efforts of his mother Matilda, daughter of Henry I of England, to claim the English throne, then occupied b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the Côte d'Opale, a touristic stretch of French coast on the English Channel between Calais and Normandy, and the most visited location in the region after the Lille conurbation. Boulogne is its department's second-largest city after Calais, and the 183rd-largest in France.Téléchargement du fichier d'ensemble des populations légales en 2017 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaud I, Count Of Dammartin
Renaud de Dammartin (Reginald of Boulogne) (c. 1165 – 1227) was Count of Boulogne from 1190, Count of Dammartin from 1200 to 1214 and Count of Aumale from 1204 to 1214. He was son of Alberic III of Dammartin and Mathilde of Clermont. Brought up at the French court, he was a childhood friend of Philip Augustus. At his father's insistence he fought for the Plantagenets. Received back into Philip's favour, he married Marie de Châtillon, daughter of Guy II de Châtillon and Adèle of Dreux, a royal cousin. In 1191, Renaud's father, Alberic, kidnapped and had Renaud marry Ida, Countess of Boulogne. The County of Boulogne thereby became vassal to the French king, rather than the count of Flanders. While this marriage made Renaud a power, it also made enemies in the Dreux family and that of the count of Guînes, who had been betrothed to Ida. In 1203, Renaud and his wife gave a merchant's charter to Boulogne. This was probably made for financial consideration. Philip made Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
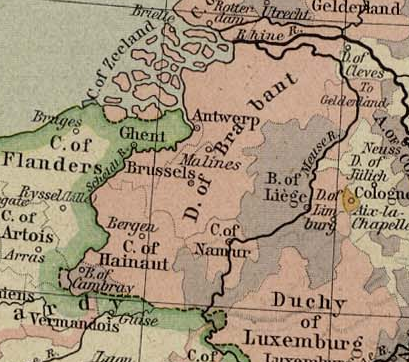
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Brabant an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin IX
Baldwin I ( nl, Boudewijn; french: Baudouin; July 1172 – ) was the first Emperor of the Latin Empire of Constantinople; Count of Flanders (as Baldwin IX) from 1194 to 1205 and Count of Hainaut (as Baldwin VI) from 1195-1205. Baldwin was one of the most prominent leaders of the Fourth Crusade, which resulted in the sack of Constantinople in 1204, the conquest of large parts of the Byzantine Empire, and the foundation of the Latin Empire. He lost his final battle to Kaloyan, the emperor of Bulgaria, and spent his last days as his prisoner. Early life and family history Baldwin was the son of Count Baldwin V of Hainaut and Countess Margaret I of Flanders.. When the childless Count Philip I of Flanders left on the last of his personal crusades in 1177, he designated Baldwin, his brother-in-law, as his heir. When Philip returned in 1179 after an unsuccessful siege of Harim during a joint campaign on behalf of the Principality of Antioch, he was designated as the chief adviser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Hertogenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brabançons
The Brabançons or Brabanters ( la, Brabantiones) were ''routiers'' (mercenary troops) originally from the Duchy of Brabant active between 1166 and 1214. Origins Brabant was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. The social origins of the Brabançons are uncertain. Some were the younger sons of the knightly class who had received formal military training. Others were drawn from the lower classes and had little or no such training. There were some women in their ranks. They mostly fought as infantry, possessing few horses. They were feared because of their ruthlessness, but probably had less of a tactical impact than the ''routiers'' of the later Middle Ages. Despite their name, the Brabançons came to be drawn from all across northern Europe. Walter Map in his ''De nugis curialium'' written about 1180 described the origins of the Brabançons thus: A new and particularly noxious sect of heretics arose. The fighters of these ''rotten'' were protected from head to foot by a leather jerkin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château Gaillard
Château Gaillard () is a medieval castle ruin overlooking the River Seine above the commune of Les Andelys, in the French department of Eure, in Normandy. It is located some north-west of Paris and from Rouen. Construction began in 1196 under the auspices of Richard the Lionheart, who was simultaneously King of England and feudal Duke of Normandy. The castle was expensive to build, but the majority of the work was done in an unusually short period of time. It took just two years and, at the same time, the town of Petit Andely was constructed. Château Gaillard has a complex and advanced design, and uses early principles of concentric fortification; it was also one of the earliest European castles to use machicolations. The castle consists of three enclosures separated by dry moats, with a keep in the inner enclosure. Château Gaillard was captured in 1204 by the king of France, Philip II, after a lengthy siege. In the mid-14th century, the castle was the residence of the exil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tours
Tours ( , ) is one of the largest cities in the region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Indre-et-Loire. The Communes of France, commune of Tours had 136,463 inhabitants as of 2018 while the population of the whole functional area (France), metropolitan area was 516,973. Tours sits on the lower reaches of the Loire, between Orléans and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. Formerly named Caesarodunum by its founder, Roman Augustus, Emperor Augustus, it possesses one of the largest amphitheaters of the Roman Empire, the Tours Amphitheatre. Known for the Battle of Tours in 732 AD, it is a National Sanctuary with connections to the Merovingian dynasty, Merovingians and the Carolingian dynasty, Carolingians, with the Capetian dynasty, Capetians making the kingdom's currency the Livre tournois. Martin of Tours, Saint Martin, Gregory of Tours and Alcuin were all from Tours. Tours was once part of Tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
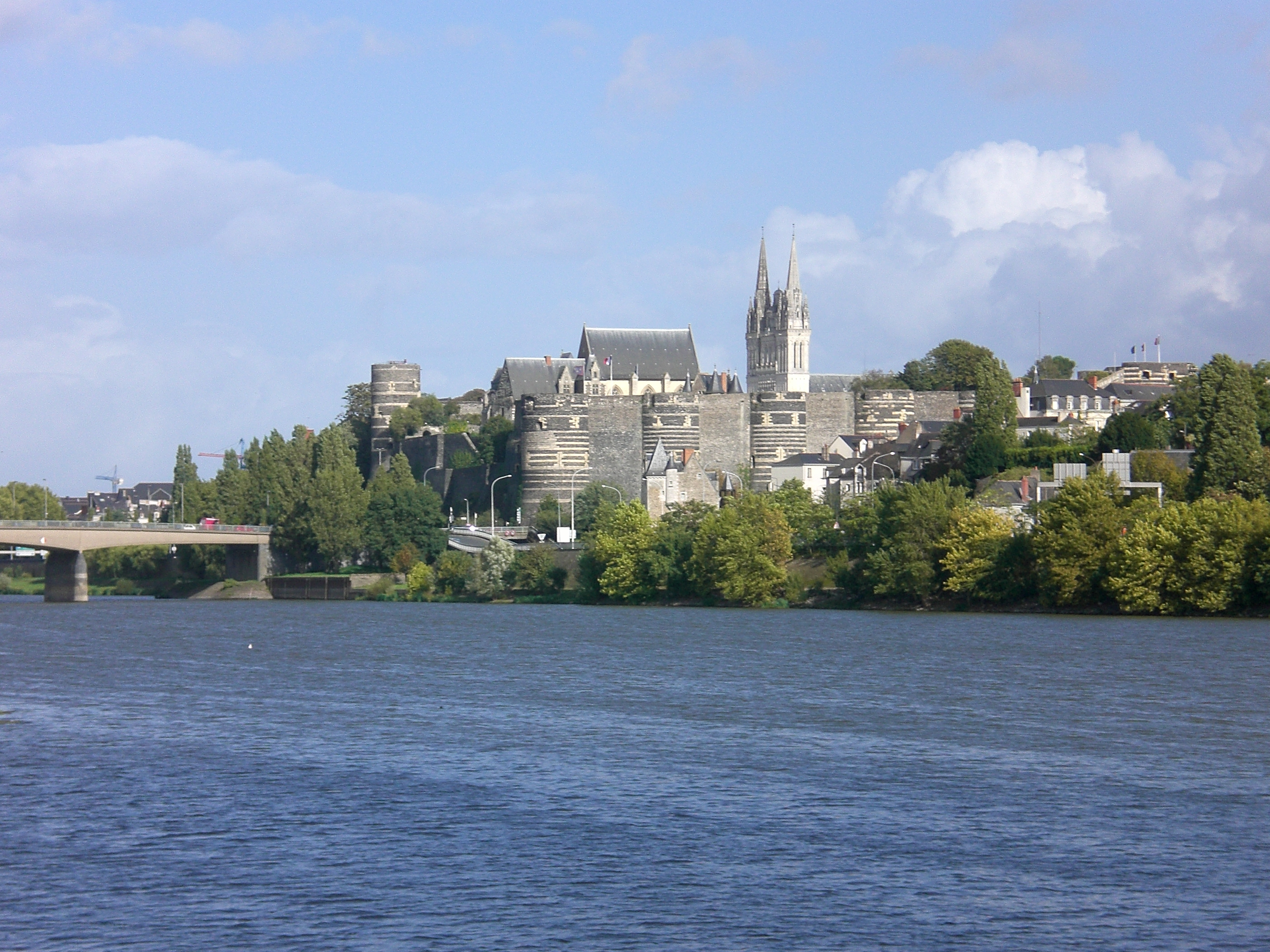
Angers
Angers (, , ) is a city in western France, about southwest of Paris. It is the prefecture of the Maine-et-Loire department and was the capital of the province of Anjou until the French Revolution. The inhabitants of both the city and the province are called ''Angevins'' or, more rarely, ''Angeriens''. Angers proper covers and has a population of 154,508 inhabitants, while around 432,900 live in its metropolitan area (''aire d'attraction''). The Angers Loire Métropole is made up of 29 communes covering with 299,500 inhabitants (2018).Comparateur de territoire INSEE Not including the broader metropolitan area, Angers is the third most populous |