|
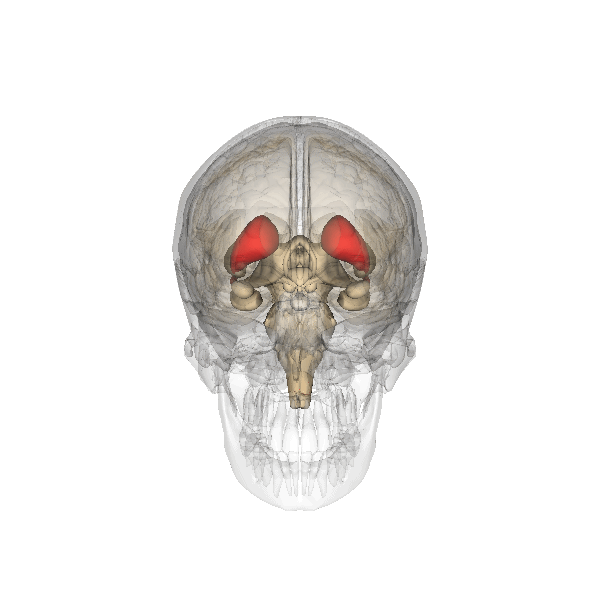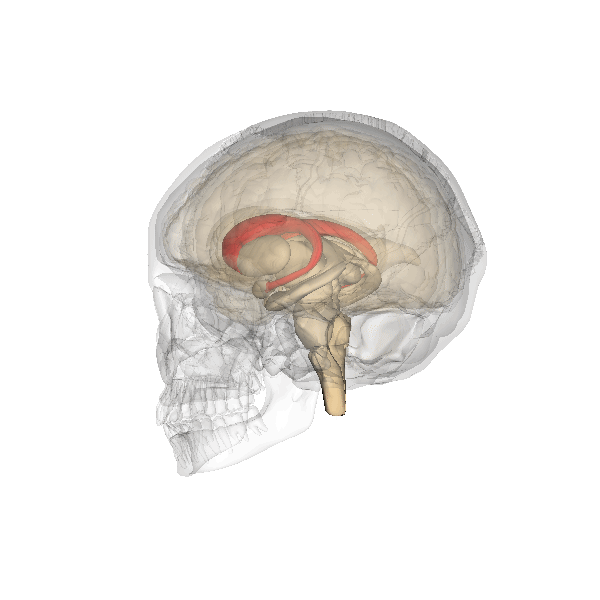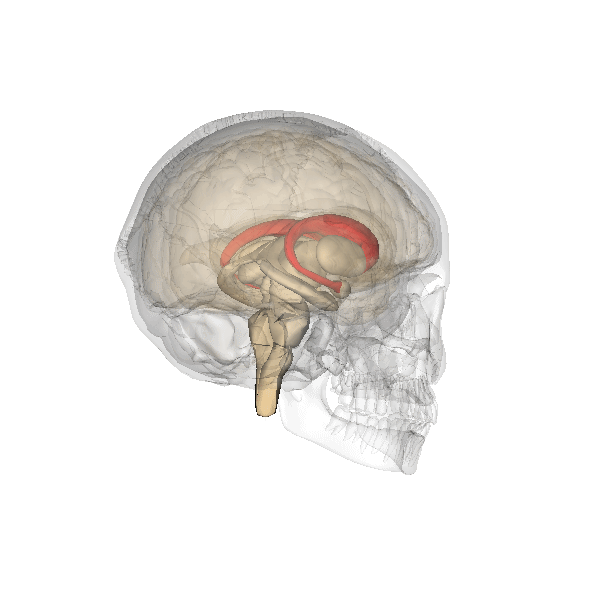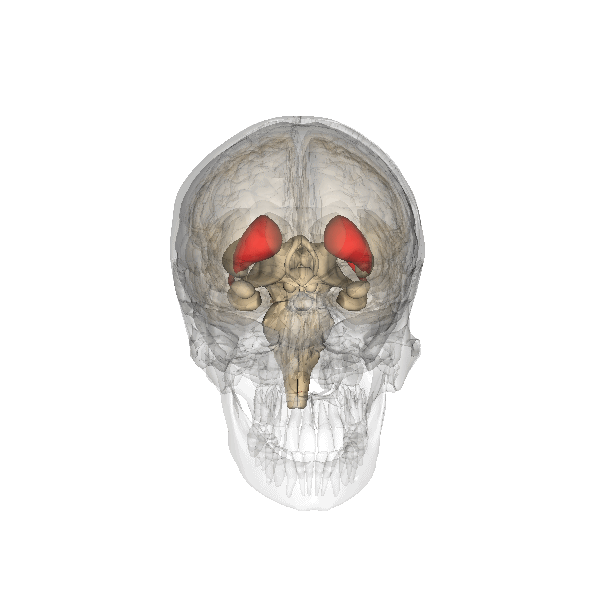
Basal Ganglia System
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an external and internal region, and in the division of the striatum. The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum ( caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum ( nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum prenatal development, develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the Dorsum (biology), dorsal telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or Pallium (neuroanatomy), subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric Lateralization of brain function, left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Learning
Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent stimulus (e.g. food) is paired with a previously neutral stimulus (e.g. a triangle). It also refers to the learning process that results from this pairing, through which the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a response (e.g. salivation) that is usually similar to the one elicited by the potent stimulus. Classical conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (also called instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment. However, classical conditioning can affect operant conditioning in various ways; notably, classically conditioned stimuli may serve to reinforce operant responses. Classical conditioning was first studied in detail by Ivan Pavlov, who conducted experiments with dogs and published his findings in 1897. During the Russian physiologist's study of digestion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subthalamic Nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the subthalamic nucleus is located ventral to the thalamus. It is also dorsal to the substantia nigra and medial to the internal capsule. It was first described by Jules Bernard Luys in 1865, and the term ''corpus Luysi'' or ''Luys' body'' is still sometimes used. Anatomy Structure The principal type of neuron found in the subthalamic nucleus has rather long, sparsely spiny dendrites. In the more centrally located neurons, the dendritic arbors have a more ellipsoidal shape. The dimensions of these arbors (1200 μm, 600 μm, and 300 μm) are similar across many species—including rat, cat, monkey and human—which is unusual. However, the number of neurons increases with brain size as well as the external dimensions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substantia Nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Although the substantia nigra appears as a continuous band in brain sections, anatomical studies have found that it actually consists of two parts with very different connections and functions: the pars compacta (SNpc) and the pars reticulata (SNpr). The pars compacta serves mainly as a projection to the basal ganglia circuit, supplying the striatum with dopamine. The pars reticulata conveys signals from the basal ganglia to numerous other brain structures. Structure The substantia nigra, along with four other nuclei, is part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Pallidum
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus. The VP is a core component of the reward system which forms part of the limbic loop of the basal ganglia, a pathway involved in the regulation of motivational salience, behavior, and emotions. It is involved in addiction. The VP contains one of the brain's pleasure centers, which mediates the subjective perception of pleasure that results from "consuming" certain rewarding stimuli (e.g., palatable food). Anatomy The ventral pallidum lies within the basal ganglia, a group of subcortical nuclei. Along with the external globus pallidus, it is separated from other basal ganglia nuclei by the anterior commissure. Limbic loop The limbic loop is a functional pathway of the basal ganglia, in which the ventral pallidum is involved. It (and the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to play a role in locomotor and attentional behaviors, particularly in relation to social and sensory responsiveness, and it may be necessary for behavioral flexibility. The OT is interconnected with numerous brain regions, especially the sensory, arousal, and reward centers, thus making it a potentially critical interface between processing of sensory information and the subsequent behavioral responses. The OT is a composite structure that receives direct input from the olfactory bulb and contains the morphological and histochemical characteristics of the ventral pallidum and the striatum of the forebrain. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region (D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia. Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition, including both motor and action planning, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures. In primates, the striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and a dorsal striatum, subdivisions that are base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putamen
The putamen (; from Latin, meaning "nutshell") is a round structure located at the base of the forebrain (telencephalon). The putamen and caudate nucleus together form the dorsal striatum. It is also one of the structures that compose the basal nuclei. Through various pathways, the putamen is connected to the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, the claustrum, and the thalamus, in addition to many regions of the cerebral cortex. A primary function of the putamen is to regulate movements at various stages (e.g. preparation and execution) and influence various types of learning. It employs GABA, acetylcholine, and enkephalin to perform its functions. The putamen also plays a role in degenerative neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease. History The word "putamen" is from Latin, referring to that which "falls off in pruning", from "putare", meaning "to prune, to think, or to consider". Until recently, most MRI research focused broadly on the basal ganglia as a who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's disease, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico–basal ganglia– thalamic loop. Structure Together with the putamen, the caudate forms the dorsal striatum, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule, so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |