|
Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule
Basal cell adhesion molecule, also known as Lutheran antigen, is a plasma membrane glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCAM'' gene. BCAM has also recently been designated CD239 (cluster of differentiation 239). Function Lutheran blood group glycoprotein is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and a receptor for the extracellular matrix protein, laminin. The protein contains five, N-terminus, extracellular immunoglobulin domains, a single transmembrane domain, and a short, C-terminal cytoplasmic tail. This protein may play a role in epithelial cell cancer and in vaso-occlusion of red blood cells in sickle cell disease. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Interactions BCAM has been shown to interact with Laminin, alpha 5 Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran Antigen System
The Lutheran antigen systems is a classification of human blood based on the presence of substances called Lutheran antigens on the surfaces of red blood cells. There are 19 known Lutheran antigens. All of these antigens arise from variations in a gene called BCAM (basal cell adhesion molecule). The system is based on the expression of two codominant alleles, designated Lua and Lub. The antigens Aua and Aub, known as the Auberger antigens, were once thought to make up a separate blood group but were later shown to be Lutheran antigens arising from variations in the BCAM gene. The phenotypes Lu(a+b−) and Lu(a+b+) are found at various frequencies within populations. The Lu(a−b+) phenotype is the most common in all populations, whereas the Lu(a−b−) phenotype is uncommon. Though present in the fetus, it is seldom the cause of erythroblastosis fetalis Hemolytic disease of the newborn, also known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, HDN, HDFN, or erythroblastosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Of Differentiation
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells. In terms of physiology, CD molecules can act in numerous ways, often acting as receptors or ligands important to the cell. A signal cascade is usually initiated, altering the behavior of the cell (see cell signaling). Some CD proteins do not play a role in cell signaling, but have other functions, such as cell adhesion. CD for humans is numbered up to 371 (). Nomenclature The CD nomenclature was proposed and established in the 1st International Workshop and Conference on Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens (HLDA), which was held in Paris in 1982. This system was intended for the classification of the many monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated by different laboratories around the world against epitopes on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) is a large protein superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. Molecules are categorized as members of this superfamily based on shared structural features with immunoglobulins (also known as antibodies); they all possess a domain known as an immunoglobulin domain or fold. Members of the IgSF include cell surface antigen receptors, co-receptors and co-stimulatory molecules of the immune system, molecules involved in antigen presentation to lymphocytes, cell adhesion molecules, certain cytokine receptors and intracellular muscle proteins. They are commonly associated with roles in the immune system. Otherwise, the sperm-specific protein IZUMO1, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has also been identified as the only sperm membrane protein essential for sperm-egg fusion. Immunoglobulin domains Proteins of the IgSF possess a structural domain known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
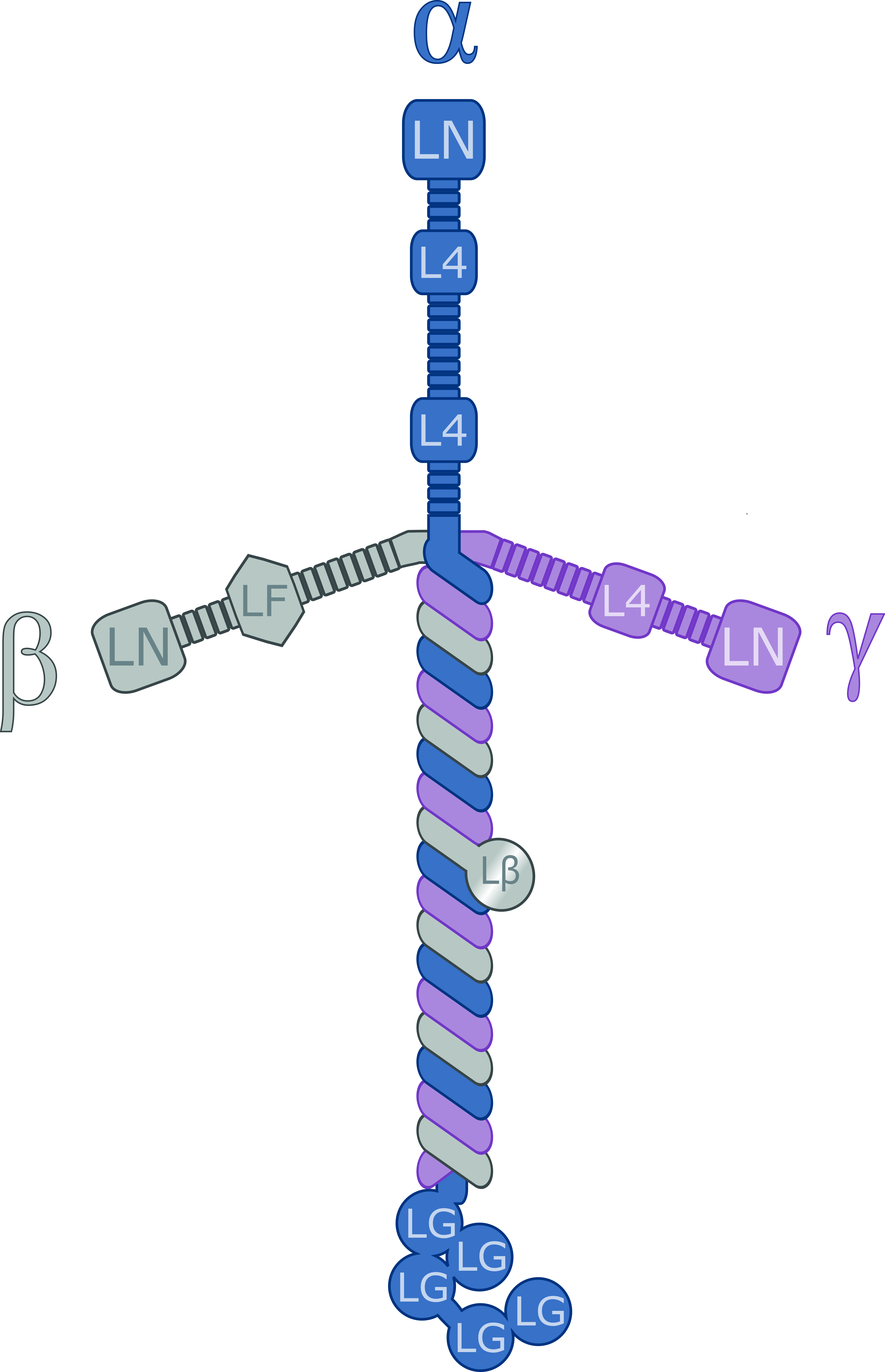
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Domain
The immunoglobulin domain, also known as the immunoglobulin fold, is a type of protein domain that consists of a 2-layer sandwich of 7-9 antiparallel β-strands arranged in two β-sheets with a Greek key topology, consisting of about 125 amino acids. The backbone switches repeatedly between the two β-sheets. Typically, the pattern is (N-terminal β-hairpin in sheet 1)-(β-hairpin in sheet 2)-(β-strand in sheet 1)-(C-terminal β-hairpin in sheet 2). The cross-overs between sheets form an "X", so that the N- and C-terminal hairpins are facing each other. Members of the immunoglobulin superfamily are found in hundreds of proteins of different functions. Examples include antibodies, the giant muscle kinase titin, and receptor tyrosine kinases. Immunoglobulin-like domains may be involved in protein–protein and protein–ligand interactions. Examples Human genes encoding proteins containing the immunoglobulin domain include: * A1BG * ACAM * ADAMTSL1 * ADAMTSL3 * AGER * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminin, Alpha 5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene. Function Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric extracellular glycoproteins, affect tissue development and integrity in such diverse organs as the kidney, lung, skin, and nervous system. It is thought that laminins mediate the attachment, migration, and organization of cells into tissues during embryonic development by interacting with other extracellular matrix components. Laminins function as heterotrimeric complexes of alpha, beta, and gamma chains, with each chain type representing a different subfamily of proteins. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the alpha subfamily of laminin chains and is a major component of basement membranes. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of one of them has not been dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |