|
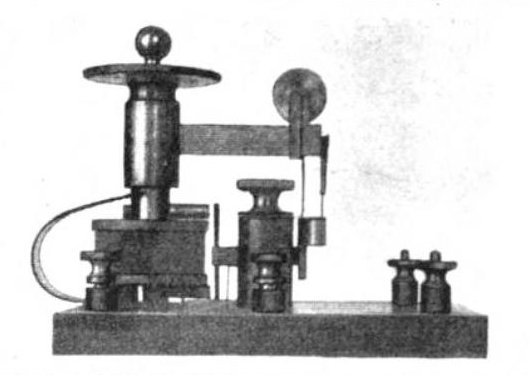
Barretter Detector
The hot-wire barretter was a demodulating detector, invented in 1902 by Reginald Fessenden, that found limited use in early radio receivers. In effect, it was a highly sensitive thermoresistor, which could demodulate amplitude-modulated signals, something that the coherer (the standard detector of the time) could not do. Tapan K. Sarkar, Robert Mailloux, Arthur A. Oliner, Magdalena Salazar-Palma, Dipak L. Sengupta, "History of Wireless", , January 2006, Wiley-IEEE Press, page 369. The first device used to demodulate amplitude modulated signals, it was later superseded by the electrolytic detector, also generally attributed to Fessenden. The barretter principle is still used as a detector for microwave radiation, similar to a bolometer. Description and construction Fessenden's 1902 patent describes the construction of the device. A fine platinum wire, about in diameter, is embedded in the middle of a silver tube having a diameter of about . This compound wire is then drawn until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fessenden Barretter
Fessenden may refer to: People * Fessenden (surname) * Larry Fessenden (born March 23, 1963), an American actor, producer, writer, director, film editor, and cinematographer * Fessenden Nott Otis (1825-c. 1900), American pioneer in the medical field of urology * Reginald Fessenden (1866-1932) Canadian/American inventor * Stirling Fessenden (1875-1944), lawyer and Chairman/Secretary General of the Shanghai Municipal Council * Susan Fessenden (1840–1932), American activist, reformer * William P. Fessenden (1806-1869) Senator and Secretary of the Treasury under Lincoln Places * Fessenden, North Dakota, a city * 15939 Fessenden, an asteroid named after Reginald Fessenden * Fessenden, a fictional princedom in Melanie Rawn's Dragon Prince fantasy novel series Other uses * USS ''Fessenden'' (DE-142), a destroyer escort which served in World War II, named in honor of Reginald Fessenden * Fessenden School, a private day and boarding school for boys in West Newton, Massachusetts * F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Electronics
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves, and received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver. Radio is very widely used in modern technology, in radio communication, radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like aircraft, ships, spacecraft a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Radio
The early history of radio is the history of technology that produces and uses radio equipment, radio instruments that use radio waves. Within the timeline of radio, many people contributed theory and inventions in what became radio. Radio development began as "wireless telegraphy". Later radio history increasingly involves matters of broadcasting. Discovery In an 1864 presentation, published in 1865, James Clerk Maxwell proposed theories of electromagnetism, with mathematical proofs, that showed that light and predicted that radio and x-rays were all types of electromagnetic waves propagating through free space. Between 1886 and 1888 Heinrich Rudolf Hertz published the results of experiments wherein he was able to transmit electromagnetic waves (radio waves) through the air, proving Maxwell's electromagnetic theory. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Electrical Experimenter
''The Electrical Experimenter'' was an American technical science magazine that was published monthly. It was established in May 1913, as the successor to ''Modern Electrics'', a combination of a magazine and mail-order catalog that had been published by Hugo Gernsback starting in 1908. ''The Electrical Experimenter'' continued from May 1913 to July 1920 under that name, focusing on scientific articles about radio, and continued with a broader focus as ''Science and Invention'' until August 1931. The magazine was edited by Hugo Gernsback until March 1929, when the Experimenter Publishing empire of Sidney and Hugo Gernsback was forced into bankruptcy; after that date it was edited by Arthur H. Lynch. Under the editorship of Gernsback, it also published some early science fiction; he published several of his own stories in the magazine starting in 1915, and encouraged others through a 1916 editorial arguing that a "real electrical experimenter, worthy of the name" must have imagin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolytic Detector
The electrolytic detector, or liquid barretter, was a type of detector (demodulator) used in early radio receivers. First used by Canadian radio researcher Reginald Fessenden in 1903, it was used until about 1913, after which it was superseded by crystal detectors and vacuum tube detectors such as the Fleming valve and Audion (triode). It was considered very sensitive and reliable compared to other detectors available at the time such as the magnetic detector and the coherer. It was one of the first rectifying detectors, able to receive AM (sound) transmissions. On December 24, 1906, US Naval ships with radio receivers equipped with Fessenden's electrolytic detectors received the first AM radio broadcast from Fessenden's Brant Rock, Massachusetts transmitter, consisting of a program of Christmas music. History Fessenden, more than any other person, is responsible for developing amplitude modulation (AM) radio transmission around 1900. While working to develop AM transmitters, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Mass
In building design, thermal mass is a property of the mass of a building that enables it to store heat and provide inertia against temperature fluctuations. It is sometimes known as the thermal flywheel effect. The thermal mass of heavy structural elements can be designed to work alongside a construction's lighter thermal resistance components to create energy efficient buildings. For example, when outside temperatures are fluctuating throughout the day, a large thermal mass within the insulated portion of a house can serve to "flatten out" the daily temperature fluctuations, since the thermal mass will absorb thermal energy when the surroundings are higher in temperature than the mass, and give thermal energy back when the surroundings are cooler, without reaching thermal equilibrium. This is distinct from a material's insulative value, which reduces a building's thermal conductivity, allowing it to be heated or cooled relatively separately from the outside, or even just retain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wollaston Wire
Wollaston wire is a very fine (less than 0.01 mm thick) platinum wire clad in silver and used in electrical instruments. For most uses, the silver cladding is etched away by acid to expose the platinum core. History The wire is named after its inventor, William Hyde Wollaston, who first produced it in England in the early 19th century. Platinum wire is drawn through successively smaller dies until it is about in diameter. It is then embedded in the middle of a silver wire having a diameter of about . This composite wire is then drawn until the silver wire has a diameter of about , causing the embedded platinum wire to be reduced by the same 50:1 ratio to a final diameter of . Removal of the silver coating with an acid bath leaves the fine platinum wire as a product of the process. Uses Wollaston wire was used in early radio detectors known as electrolytic detector The electrolytic detector, or liquid barretter, was a type of detector (demodulator) used in early rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Drawing
Wire drawing is a metalworking process used to reduce the cross-section of a wire by pulling the wire through a single, or series of, drawing die(s). There are many applications for wire drawing, including electrical wiring, cables, tension-loaded structural components, springs, paper clips, spokes for wheels, and stringed musical instruments. Although similar in process, drawing is different from extrusion, because in drawing the wire is pulled, rather than pushed, through the die. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process, but it may be performed at elevated temperatures for large wires to reduce forces. Process The wire drawing process is quite simple in concept. The wire is prepared by shrinking the beginning of it, by hammering, filing, rolling or swaging, so that it will fit through the die; the wire is then pulled through the die. As the wire is pulled through the die, its volume remains the same, so as the diameter de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver". Platinum is a member of the platinum group of elements and group 10 of the periodic table of elements. It has six naturally occurring isotopes. It is one of the rarer elements in Earth's crust, with an average abundance of approximately 5 μg/kg. It occurs in some nickel and copper ores along with some native deposits, mostly in South Africa, which accounts for ~80% of the world production. Because of its scarcity in Earth's crust, only a few hundred tonnes are produced annually, and given its important uses, it is highly valuable and is a major precious metal commodity. Platinum is one of the least reactive metals. It has remarkable resistance to corrosion, even at high temperatures, and is therefore considered a noble metal. Consequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |