|
Barium Chloride
Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Ba Cl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is white, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting first to the dihydrate BaCl2(H2O)2. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry. Structure and properties BaCl2 crystallizes in two forms ( polymorphs). One form has the cubic fluorite ( CaF2) structure and the other the orthorhombic cotunnite ( PbCl2) structure. Both polymorphs accommodate the preference of the large Ba2+ ion for coordination numbers greater than six. The coordination of Ba2+ is 8 in the fluorite structure and 9 in the cotunnite structure. When cotunnite-structure BaCl2 is subjected to pressures of 7–10 GPa, it transforms to a third structure, a monoclinic post-cotunnite phase. The coordination number of Ba2+ increases from 9 to 10. In aqueous solution BaCl2 behaves as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals. Occurrence Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, healthy hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Applied Crystallography
The ''Journal of Applied Crystallography'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International Union of Crystallography. It was established in 1968 and covers the application of crystallography and crystallographic techniques. William Parrish (1914–1991) chaired the committee that started the journal. The ''Journal of Applied Crystallography'' publishes articles on the crystallographic methods that are used to study crystalline and non-crystalline matter with neutrons, X-rays and electrons, their application in condensed matter research, materials science and the life sciences, and their use in identifying phase transformations and structural changes of defects, structure-property relationships, interfaces and surfaces etc. The journal also covers developments in crystallographic instrumentation and apparatus, theory and interpretation and numerical analysis Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic Crystal System
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Physical Chemistry
''The Journal of Physical Chemistry A'' is a scientific journal which reports research on the chemistry of molecules - including their dynamics, spectroscopy, kinetics, structure, bonding, and quantum chemistry. It is published weekly by the American Chemical Society. Before 1997 the title was simply ''Journal of Physical Chemistry''. Owing to the ever-growing amount of research in the area, in 1997 the journal was split into ''Journal of Physical Chemistry A'' (molecular theoretical and experimental physical chemistry) and '' The Journal of Physical Chemistry B'' (solid state, soft matter, liquids, etc.). Beginning in 2007, the latter underwent a further split, with ''The Journal of Physical Chemistry C'' now being dedicated to nanotechnology, molecular electronics, and related subjects. Editors-in-chief *1896–1932 Wilder Dwight Bancroft, Joseph E. Trevor *1933–1951 S. C. Lind *1952–1964 William A. Noyes *1965–1969 F. T. Wall *1970–1980 Bryce Crawford *1980–2004 Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitschrift Für Anorganische Und Allgemeine Chemie
The ''Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie'' (''Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry'') is a semimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering inorganic chemistry, published by Wiley-VCH. The editors-in-chief are Thomas F. Fässler, Christian Limberg, Guodong Qian, and David Scheschkewitz. Originally the journal was published in German, but nowadays it is completely in English. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 1.414, ranking it 40th out of 46 journals in the category "Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear". References External links * Chemistry journals Wiley-VCH aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Number
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion/molecule/atom is called a ligand. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules than for crystals. For molecules and polyatomic ions the coordination number of an atom is determined by simply counting the other atoms to which it is bonded (by either single or multiple bonds). For example, r(NH3)2Cl2Br2sup>− has Cr3+ as its central cation, which has a coordination number of 6 and is described as ''hexacoordinate''. The common coordination numbers are 4, 6 and 8. Molecules, polyatomic ions and coordination complexes In chemistry, coordination number, defined originally in 1893 by Alfred Werner, is the total number of neighbors of a central atom in a molecule or ion. The concept is most commonly applied to coordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotunnite
Cotunnite is the natural mineral form of lead(II) chloride with formula PbCl2. It was first described in 1825 from an occurrence on Mount Vesuvius, Naples Province, Campania, Italy. It was named for Domenico Cotugno (Cotunnius) (1736–1822), Italian physician and Professor of Anatomy. It was first recognized in volcanic fumarole deposits. It occurs as a secondary alteration product in lead ore deposits. It has also been reported as an alteration of archaeological objects that contain lead. It occurs in association with galena, cerussite, anglesite and matlockite in the Caracoles, Chile. At the Tolbachik volcano on the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia it occurs with the rare to uncommon minerals tenorite, ponomarevite, sofiite, burnsite, ilinskite, georgbokite, chloromenite, halite, sylvite and native gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
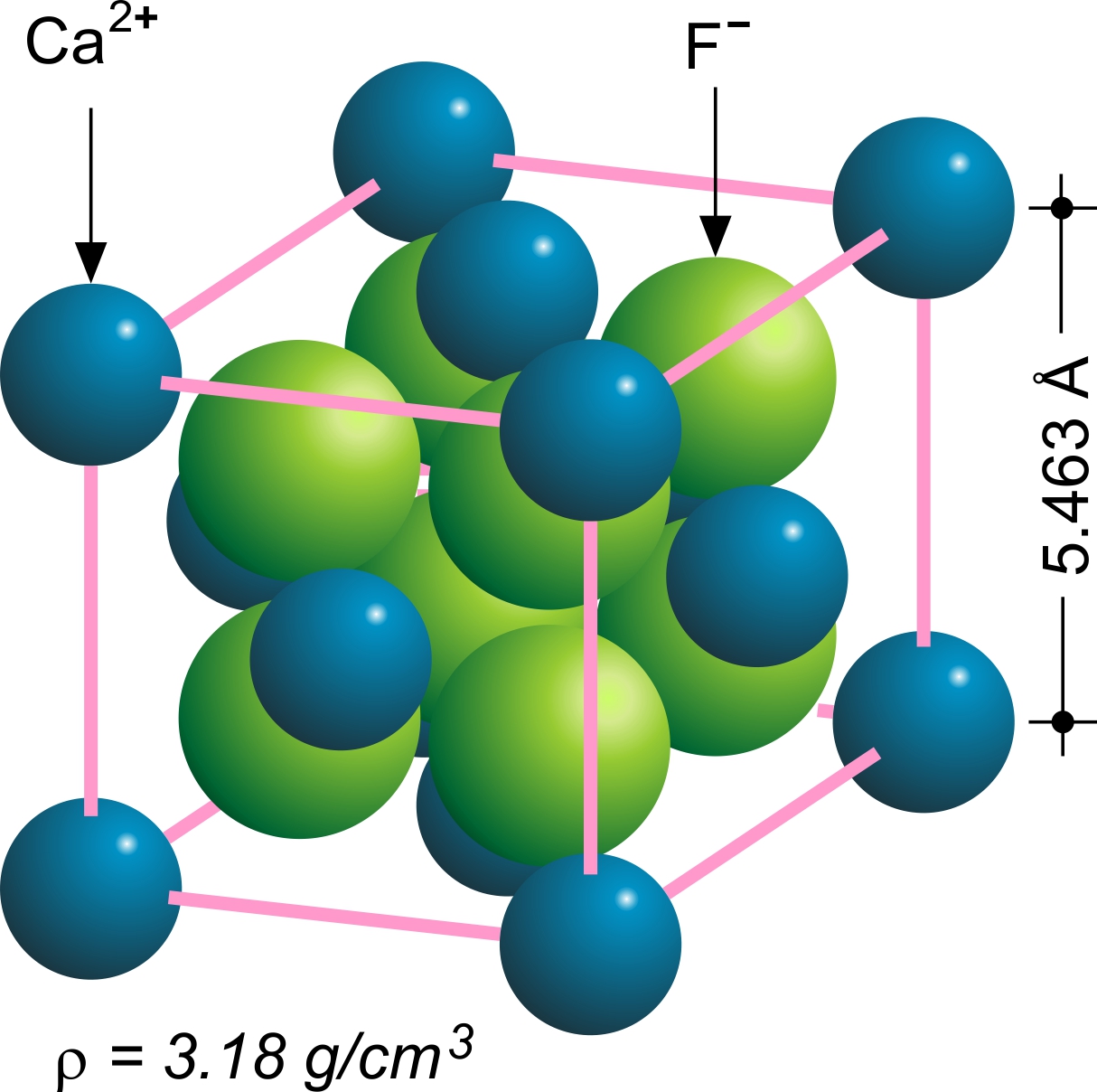
Calcium Fluoride
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white insoluble solid. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities. Chemical structure The compound crystallizes in a cubic motif called the fluorite structure. Ca2+ centres are eight-coordinate, being centered in a cube of eight F− centres. Each F− centre is coordinated to four Ca2+ centres in the shape of a tetrahedron. Although perfectly packed crystalline samples are colorless, the mineral is often deeply colored due to the presence of F-centers. The same crystal structure is found in numerous ionic compounds with formula AB2, such as CeO2, cubic ZrO2, UO2, ThO2, and PuO2. In the corresponding anti-structure, called the antifluorite structure, anions and cations are swapped, such as Be2C. Gas phase The gas phase is noteworthy for failing the predictions of VSEPR theory; the molecule is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal_structure#Unit_cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called Close-packing_of_equal_spheres, ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive_cell, primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one Lattice_(group), lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |