|
Bandwidth Throttling
Bandwidth throttling consists in the intentional limitation of the communication speed (bytes or kilobytes per second) of the ingoing (received) data and/or in the limitation of the speed of outgoing (sent) data in a network node or in a network device. The data speed and rendering may be limited depending on various parameters and conditions. Overview Limiting the speed of data sent by a data originator (a client computer or a server computer) is much more efficient than limiting the speed in an intermediate network device between client and server because while in the first case usually no network packets are lost, in the second case network packets can be lost / discarded whenever ingoing data speed overcomes the bandwidth limit or the capacity of device and data packets cannot be temporarily stored in a buffer queue (because it is full or it does not exist); the usage of such a buffer queue is to absorb the peaks of incoming data for very short time lapse. In the second ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data is usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and which may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data is commonly used in scientific research, economics, and in virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represents the raw facts and figures which can be used in such a manner in order to capture the useful information out of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Streaming
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of over-the-air programming was the most common form of media distribution. As Internet and IPTV technologies continued to develop in the 1990s, consumers began to gravitate towards non-traditional modes of content consumption, which culminated in the arrival of VOD on televisions and personal computers. Unlike broadcast television, VOD systems initially required each user to have an Internet connection with considerable bandwidth to access each system's content. In 2000, the Fraunhofer Institute IIS developed the JPEG2000 codec, which enabled the distribution of movies via Digital Cinema Packages. This technology has since expanded its services from feature-film productions to include broadcast television programmes and has led to lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comcast
Comcast Corporation (formerly known as American Cable Systems and Comcast Holdings),Before the AT&T merger in 2001, the parent company was Comcast Holdings Corporation. Comcast Holdings Corporation now refers to a subsidiary of Comcast Corporation, not the parent company (seeBloomberg profile on Comcast Holdings Corporation. Technically, the current parent company was founded December 7, 2001 as CAB Holdings Corporation, which changed its name to AT&T Comcast Corporation before finally taking on the Comcast Corporation name (seeNov 2002 8K/A Form anNov 2002 S-4) headquartered in Philadelphia, is the largest American multinational telecommunications conglomerate. It is the second-largest broadcasting and cable television company in the world by revenue (behind AT&T), the largest pay-TV company, the largest cable TV company and largest home Internet service provider in the United States, and the nation's third-largest home telephone service provider. It provides services to U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Shaping
Traffic shaping is a bandwidth management technique used on computer networks which delays some or all datagrams to bring them into compliance with a desired ''traffic profile''. Traffic shaping is used to optimize or guarantee performance, improve latency, or increase usable bandwidth for some kinds of packets by delaying other kinds. It is often confused with traffic policing, the distinct but related practice of packet dropping and packet marking. The most common type of traffic shaping is application-based traffic shaping. In application-based traffic shaping, fingerprinting tools are first used to identify applications of interest, which are then subject to shaping policies. Some controversial cases of application-based traffic shaping include bandwidth throttling of peer-to-peer file sharing traffic. Many application protocols use encryption to circumvent application-based traffic shaping. Another type of traffic shaping is route-based traffic shaping. Route-based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Packet Inspection
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a type of data processing that inspects in detail the data being sent over a computer network, and may take actions such as alerting, blocking, re-routing, or logging it accordingly. Deep packet inspection is often used to baseline application behavior, analyze network usage, troubleshoot network performance, ensure that data is in the correct format, check for malicious code, eavesdropping, and internet censorship, among other purposes. There are multiple headers for IP packets; network equipment only needs to use the first of these (the IP header) for normal operation, but use of the second header (such as TCP or UDP) is normally considered to be shallow packet inspection (usually called stateful packet inspection) despite this definition. There are multiple ways to acquire packets for deep packet inspection. Using port mirroring (sometimes called Span Port) is a very common way, as well physically inserting a network tap which duplicates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of octets (bytes) between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications such as the World Wide Web, email, remote administration, and file transfer rely on TCP, which is part of the Transport Layer of the TCP/IP suite. SSL/TLS often runs on top of TCP. TCP is connection-oriented, and a connection between client and server is established before data can be sent. The server must be listening (passive open) for connection requests from clients before a connection is established. Three-way handshake (active open), retransmission, and error detection adds to reliability but lengthens latency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The International System of Units (SI) defines the prefix '' kilo'' as 1000 (103); per this definition, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information science and technology, International Electrotechnical Commission (2008). The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. In some areas of information technology, particularly in reference to solid-state memory capacity, ''kilobyte'' instead typically refers to 1024 (210) bytes. This arises from the prevalence of sizes that are powers of two in modern digital memory architectures, coupled with the accident that 210 differs from 103 by less than 2.5%. A kibibyte is defined by Clause 4 of IEC 80000-13 as 1024 bytes. Definitions and usage Base 10 (1000 bytes) In the International System of Units (SI) the prefix '' kilo'' means 1000 (103); therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabit
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information. The prefix mega (symbol M) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 106 (1 million), and therefore :1 megabit = = = 1000 kilobits. The megabit has the unit symbol Mbit or Mb. The lowercase 'b' in Mb distinguishes it from MB (for megabyte). The megabit is closely related to the mebibit, a unit multiple derived from the binary prefix mebi (symbol Mi) of the same order of magnitude, which is equal to = , or approximately 5% larger than the megabit. Despite the definitions of these new prefixes for binary-based quantities of storage by international standards organizations, memory semiconductor chips are still marketed using the metric prefix names to designate binary multiples. Using the common byte size of eight bits and the standard decimal definition of megabit and kilobyte, 1 megabit is equal to 125 kilobytes (kB) or approximately 122 kibibytes (KiB). The meg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Its recommended unit symbol is MB. The unit prefix ''mega'' is a multiplier of (106) in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes of information. This definition has been incorporated into the International System of Quantities. In the computer and information technology fields, other definitions have been used that arose for historical reasons of convenience. A common usage has been to designate one megabyte as (220 B), a quantity that conveniently expresses the binary architecture of digital computer memory. The standards bodies have deprecated this usage of the megabyte in favor of a new set of binary prefixes, in which this quantity is designated by the unit mebibyte (MiB). Definitions The unit megabyte is commonly used for 10002 (one million) bytes or 10242 bytes. The interpretation of using base 1024 originated as technical jargon for the byte multiples that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
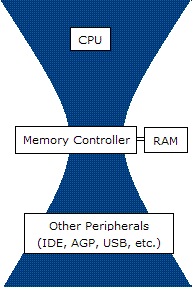
Bottleneck (engineering)
In engineering, a bottleneck is a phenomenon by which the performance or capacity of an entire system is severely limited by a single component. The component is sometimes called a bottleneck point. The term is metaphorically derived from the neck of a bottle, where the flow speed of the liquid is limited by its neck. Formally, a bottleneck lies on a system's critical path and provides the lowest throughput. Bottlenecks are usually avoided by system designers, also a great amount of effort is directed at locating and tuning them. Bottleneck may be for example a processor, a communication link, a data processing software, etc. Bottlenecks in software In computer programming, tracking down bottlenecks (sometimes known as "hot spots" - sections of the code that execute most frequently - i.e. have the highest execution count) is called performance analysis. Reduction is usually achieved with the help of specialized tools, known as performance analyzers or profilers. The objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
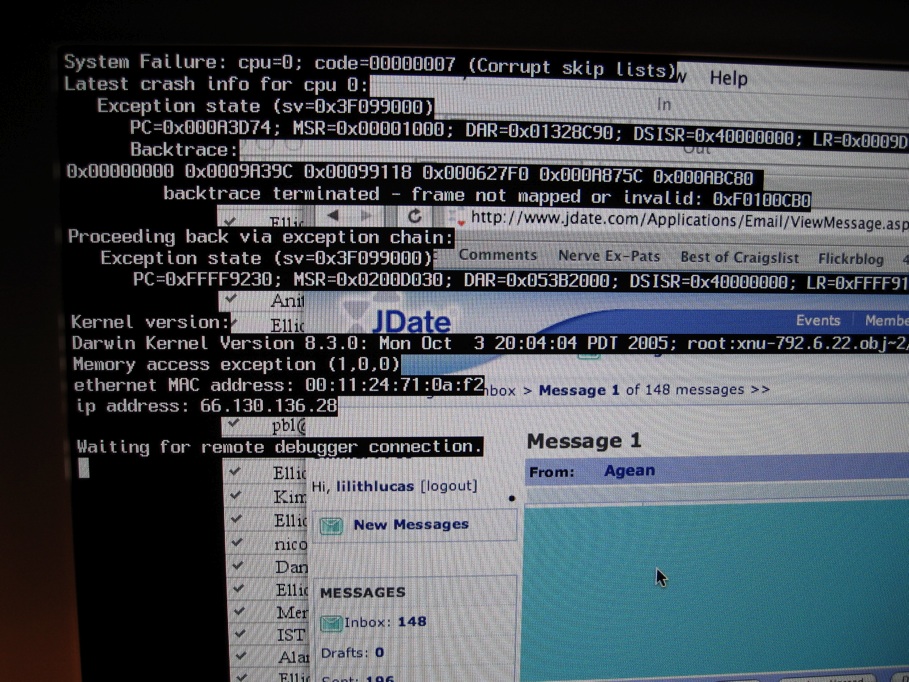
Crash (computing)
In computing, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application or an operating system stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic or fatal system error. Most crashes are the result of a software bug. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considered to be the cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |