|
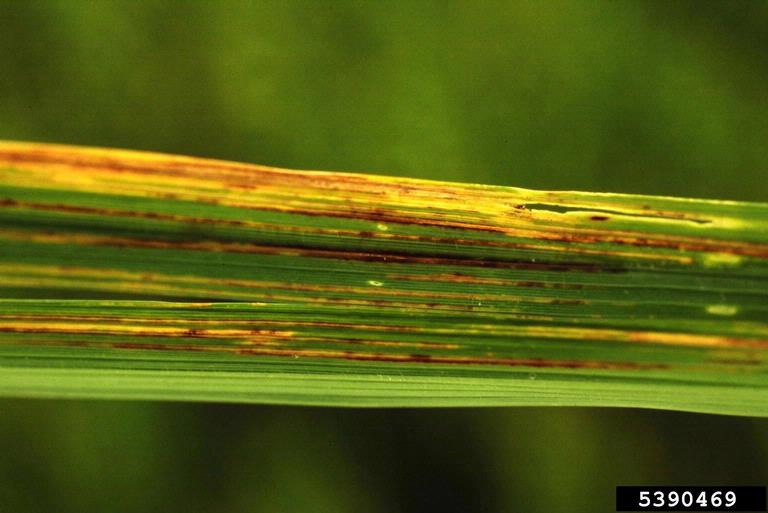
Bacterial Leaf Streak
Bacterial leaf streak (BLS), also known as black chaff, is a common bacterial disease of wheat. The disease is caused by the bacterial species '' Xanthomonas translucens'' pv. ''undulosa''. The pathogen is found globally, but is a primary problem in the US in the lower mid-south and can reduce yields by up to 40 percent. /sup> BLS is primarily seed-borne (the disease is transmitted by seed) and survives in and on the seed, but may also survive in crop residue in the soil in the off-season. During the growing season, the bacteria may transfer from plant to plant by contact, but it is primarily spread by rain, wind and insect contact. The bacteria thrives in moist environments, and produces a cream to yellow bacterial ooze, which, when dry, appears light colored and scale-like, resulting in a streak on the leaves. The invasion of the head of wheat causes bands of necrotic tissue on the awns, which is called Black Chaff. 4/sup> The disease is not easily managed, as there are no pesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
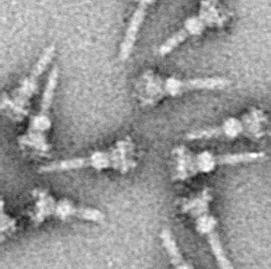
Xanthomonas Translucens
''Xanthomonas translucens'' is a species of phytopathogenic bacteria. It is the causal agent of bacterial leaf streak in of wheat and cereal crop. The bacterium is transmitted as a seed-borne pathogen. The transmission rate is very low but ensures serious outbreaks in the field under suitable conditions. The pathogen is a non-sporing, aerobic, motile, gram-negative, rod bacterium with a single polar flagellum. Subspecies (syn. '' X. campestris'' pv. ''translucens'') causes a bacterial leaf streak of wheat. is developed and presented in Schaad & Forster 1985. Xts medium is semi-selective for ''Xtt''. Although some problems with this agar Agar ( or ), or agar-agar, is a jelly-like substance consisting of polysaccharides obtained from the cell walls of some species of red algae, primarily from ogonori (''Gracilaria'') and "tengusa" (''Gelidiaceae''). As found in nature, agar is ... are known, nothing better is available. References External links Type strain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glume
In botany, a glume is a bract (leaf-like structure) below a spikelet in the inflorescence (flower cluster) of grasses (Poaceae) or the flowers of sedges (Cyperaceae). There are two other types of bracts in the spikelets of grasses: the lemma and palea. In grasses, two bracts known as "glumes" form the lowermost organs of a spikelet (there are usually two but one is sometimes reduced; or rarely, both are absent). Glumes may be similar in form to the lemmas, the bracts at the base of each floret This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary o .... In sedges, by contrast, a glume is a scale at the base of each flower in a spikelet. References {{reflist Plant morphology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perennial Plant
A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the years") is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also widely used to distinguish plants with little or no woody growth (secondary growth in girth) from trees and shrubs, which are also technically perennials. Perennialsespecially small flowering plantsthat grow and bloom over the spring and summer, die back every autumn and winter, and then return in the spring from their rootstock or other overwintering structure, are known as herbaceous perennials. However, depending on the rigours of local climate (temperature, moisture, organic content in the soil, microorganisms), a plant that is a perennial in its native habitat, or in a milder garden, may be treated by a gardener as an annual and planted out every year, from seed, from cuttings, or from divisions. Tomato vines, for example, live several y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAL Effectors
TAL (transcription activator-like) effectors (often referred to as TALEs, but not to be confused with the three amino acid loop extension homeobox class of proteins) are proteins secreted by some β- and γ-proteobacteria. Most of these are Xanthomonads. Plant pathogenic ''Xanthomonas'' bacteria are especially known for TALEs, produced via their type III secretion system. These proteins can bind promoter sequences in the host plant and activate the expression of plant genes that aid bacterial infection. The TALE domain responsible for binding to DNA is known to have 1.5 to 33.5 short sequences that are repeated multiple times (tandem repeats). Each of these repeats was found to be specific for a certain base pair of the DNA. These repeats also have repeat variable residues (RVD) that can detect specific DNA base pairs. They recognize plant DNA sequences through a central repeat domain consisting of a variable number of ~34 amino acid repeats. There appears to be a one-to-one c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 3 Secretion System
The type III secretion system (T3SS or TTSS), also called the injectisome, is one of the bacterial secretion systems used by bacteria to secrete their effector proteins into the host's cells to promote virulence and colonisation. The T3SS is a needle-like protein complex found in several species of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria. Overview The term Type III secretion system was coined in 1993. This secretion system is distinguished from at least five other secretion systems found in gram-negative bacteria. Many animal and plant associated bacteria possess similar T3SSs. These T3SSs are similar as a result of divergent evolution and phylogenetic analysis supports a model in which gram-negative bacteria can transfer the T3SS gene cassette horizontally to other species. The most researched T3SSs are from species of ''Shigella'' (causes bacillary dysentery), '' Salmonella'' (typhoid fever), ''Escherichia coli'' ( Gut flora, some strains cause food poisoning), ''Vibrio'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parenchyma (botany)
The ground tissue of plants includes all tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular. It can be divided into three types based on the nature of the cell walls. # Parenchyma cells have thin primary walls and usually remain alive after they become mature. Parenchyma forms the "filler" tissue in the soft parts of plants, and is usually present in cortex, pericycle, pith, and medullary rays in primary stem and root. # Collenchyma cells have thin primary walls with some areas of secondary thickening. Collenchyma provides extra mechanical and structural support, particularly in regions of new growth. # Sclerenchyma cells have thick lignified secondary walls and often die when mature. Sclerenchyma provides the main structural support to a plant. Parenchyma Parenchyma is a versatile ground tissue that generally constitutes the "filler" tissue in soft parts of plants. It forms, among other things, the cortex (outer region) and pith (central region) of stems, the cortex of roots, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomata
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for regulating the size of the stomatal opening. The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture. Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere in a process called transpiration. Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of all land plant groups except liverworts. In vascular plants the number, size and distribution of stomata varies widely. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time. Epidemics of infectious diseases are generally caused by several factors including a significant change in the ecology of the areal population (e.g., increased stress maybe additional reason or increase in the density of a vector species), the introduction of an emerging pathogen to an areal population (by movement of pathogen or host) or an unexpected genetic change that is in the pathogen reservoir. Generally, epidemics concerns with the patterns of infectious disease spread. An epidemic may occur when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Chaff Symptoms
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and government officials in much of Europe. It became the color worn by English romantic poets, businessmen an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |