|
Backspread
The backspread is the converse strategy to the ratio spread and is also known as reverse ratio spread. Using calls, a bullish strategy known as the call backspread can be constructed and with puts, a strategy known as the put backspread can be constructed. Call backspread The call backspread (reverse call ratio spread) is a bullish strategy in options trading whereby the options trader writes a number of call options and buys more call options of the same underlying stock and expiration date but at a higher strike price. It is an unlimited profit, limited risk strategy that is used when the trader thinks that the price of the underlying stock will rise sharply in the near future. A 2:1 call backspread can be created by selling a number of calls at a lower strike price and buying twice the number of calls at a higher strike. Put backspread The put backspread is a strategy in options trading whereby the options trader writes a number of put options at a higher strike price (often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Put Backspread
The backspread is the converse strategy to the ratio spread and is also known as reverse ratio spread. Using calls, a bullish strategy known as the call backspread can be constructed and with puts, a strategy known as the put backspread can be constructed. Call backspread The call backspread (reverse call ratio spread) is a bullish strategy in options trading whereby the options trader writes a number of call options and buys more call options of the same underlying stock and expiration date but at a higher strike price. It is an unlimited profit, limited risk strategy that is used when the trader thinks that the price of the underlying stock will rise sharply in the near future. A 2:1 call backspread can be created by selling a number of calls at a lower strike price and buying twice the number of calls at a higher strike. Put backspread The put backspread is a strategy in options trading whereby the options trader writes a number of put options at a higher strike price (often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratio Spread
A Ratio spread is a, multi-leg options position. Like a vertical, the ratio spread involves buying and selling options on the same underlying security with different strike prices and the same expiration date. In this spread, the number of option contracts sold is not equal to a number of contracts bought. An unequal number of options contracts gives this spread certain unique properties compared to a regular vertical spread. A typical ''ratio spread'' would be where twice as many option contracts are sold, thus forming a 1:2 ratio. Purpose Ideally, this strategy should be used when either A) the implied volatility of the options expiring in a particular month has recently moved sharply higher and is now beginning to decline, or B) the trader believes for whatever reason that the underlying market of the option(s) will move steadily in his favor during the life of the option. The trader will use call options in this strategy if they believe the underlying market will move steadil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike Price
In finance, the strike price (or exercise price) of an option is a fixed price at which the owner of the option can buy (in the case of a call), or sell (in the case of a put), the underlying security or commodity. The strike price may be set by reference to the spot price, which is the market price of the underlying security or commodity on the day an option is taken out. Alternatively, the strike price may be fixed at a discount or premium. The strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the market price of the underlying instrument at that time. Moneyness Moneyness is the value of a financial contract if the contract settlement is financial. More specifically, it is the difference between the strike price of the option and the current trading price of its underlying security. In options trading, terms such as ''in-the-mone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
At-the-money
In finance, moneyness is the relative position of the current price (or future price) of an underlying asset (e.g., a stock) with respect to the strike price of a derivative, most commonly a call option or a put option. Moneyness is firstly a three-fold classification: * If the derivative would have positive intrinsic value if it were to expire today, it is said to be in the money; * If the derivative would be worthless if expiring with the underlying at its current price, it is said to be out of the money; * And if the current underlying price and strike price are equal, the derivative is said to be at the money. There are two slightly different definitions, according to whether one uses the current price (spot) or future price (forward), specified as "at the money spot" or "at the money forward", etc. This rough classification can be quantified by various definitions to express the moneyness as a number, measuring how far the asset is in the money or out of the money with res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out-of-the-money
In finance, moneyness is the relative position of the current price (or future price) of an underlying asset (e.g., a stock) with respect to the strike price of a derivative, most commonly a call option or a put option. Moneyness is firstly a three-fold classification: * If the derivative would have positive intrinsic value if it were to expire today, it is said to be in the money; * If the derivative would be worthless if expiring with the underlying at its current price, it is said to be out of the money; * And if the current underlying price and strike price are equal, the derivative is said to be at the money. There are two slightly different definitions, according to whether one uses the current price (spot) or future price (forward), specified as "at the money spot" or "at the money forward", etc. This rough classification can be quantified by various definitions to express the moneyness as a number, measuring how far the asset is in the money or out of the money with res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Put Backspread Increasing Volatility
Put or PUT may refer to: Finance * Put option, a financial contract between a buyer and a seller * CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite Index (ticker symbol) Science and technology * Programmable unijunction transistor Computing * Parameterized unit testing, in computer programming * Put, a Hypertext Transfer Protocol request method * Put, a File Transfer Protocol option to copy a file to a remote system; see List of FTP commands * Put, an output procedure in Pascal, Turing, and other programming languages ** In C, simple functions, puts and puts(), that put text on the screen Education * Petroleum University of Technology, Abadan, Ahvaz, Mahmud Abad and Tehran, Iran * Poznań University of Technology, Poland (Polish name: ''Politechnika Poznańska'') Transportation * Pui To stop (MTR station code), Hong Kong * Putney railway station (National Rail station code), London * Sri Sathya Sai Airport (IATA code), Puttaparthi, Andhra Pradesh, India Other uses * Phut or Put, Biblical grandson of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
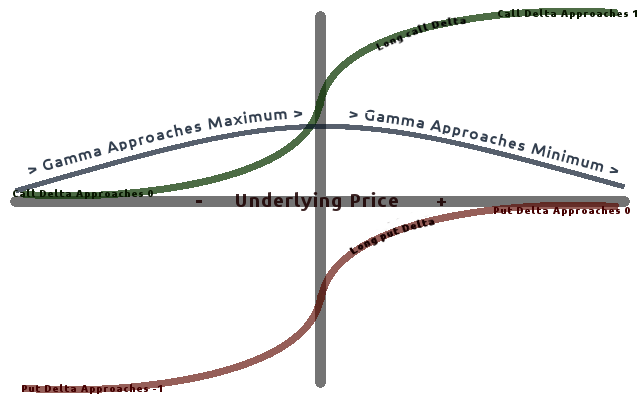
Greeks (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities representing the sensitivity of the price of derivatives such as options to a change in underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model are relatively easy to calculate, a desirable property of financial models, and are very useful for derivatives traders, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity Index
In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures a stock market, or a subset of the stock market, that helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance. Two of the primary criteria of an index are that it is ''investable'' and ''transparent'': The methods of its construction are specified. Investors can invest in a stock market index by buying an index fund, which are structured as either a mutual fund or an exchange-traded fund, and "track" an index. The difference between an index fund's performance and the index, if any, is called ''tracking error''. For a list of major stock market indices, see List of stock market indices. Types of indices by weighting method Stock market indices could be segmented by their index weight methodology, or the rules on how stocks are allocated in the index, independent of its stock coverage. For example, the S&P 500 and the S&P 500 Equal Weight both covers the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
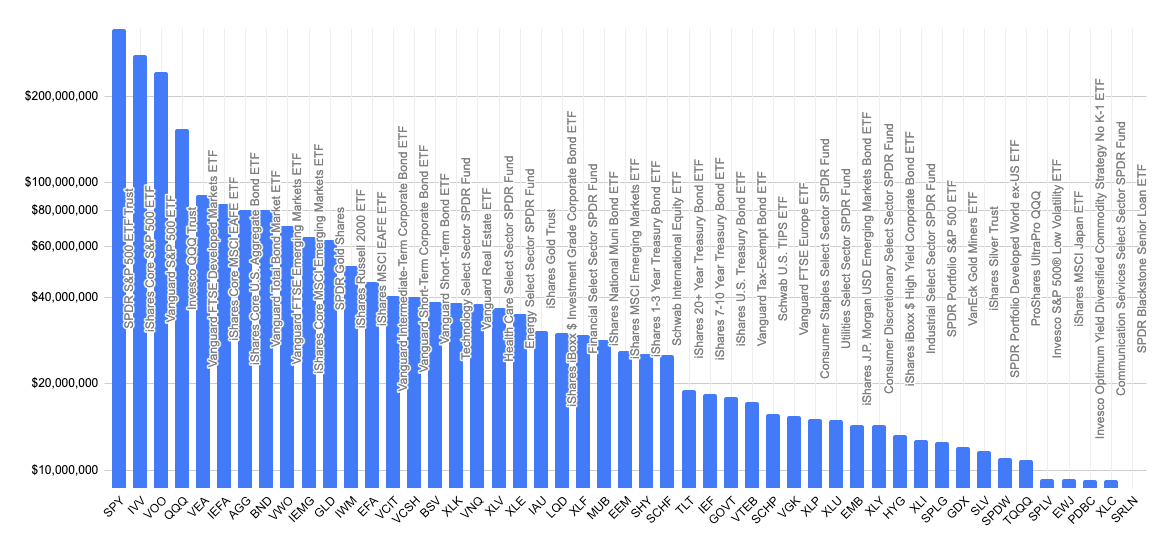
Exchange-traded Fund
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, i.e. they are traded on stock exchanges. ETFs are similar in many ways to mutual funds, except that ETFs are bought and sold from other owners throughout the day on stock exchanges whereas mutual funds are bought and sold from the issuer based on their price at day's end. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars, and generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occasionally occur. Most ETFs are index funds: that is, they hold the same securities in the same proportions as a certain stock market index or bond market index. The most popular ETFs in the U.S. replicate the S&P 500, the total market index, the NASDAQ-100 index, the price of gold, the "growth" stocks in the Russell 1000 Index, or the index of the largest technology companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Exchange-traded Fund
An inverse exchange-traded fund is an exchange-traded fund (ETF), traded on a public stock market, which is designed to perform as the ''inverse'' of whatever index or benchmark it is designed to track. These funds work by using short selling, trading derivatives such as futures contracts, and other leveraged investment techniques. By providing over short investing horizons and excluding the impact of fees and other costs, performance opposite to their benchmark, inverse ETFs give a result similar to short selling the stocks in the index. An inverse S&P 500 ETF, for example, seeks a daily percentage movement opposite that of the S&P. If the S&P 500 rises by 1%, the inverse ETF is designed to fall by 1%; and if the S&P falls by 1%, the inverse ETF should rise by 1%. Because their value rises in a declining market environment, they are popular investments in bear markets. Short sales have the potential to expose an investor to unlimited losses, whether or not the sale involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |