|
Background Story
A backstory, background story, back-story, or background is a set of events invented for a plot, presented as preceding and leading up to that plot. It is a literary device of a narrative history all chronologically earlier than the narrative of primary interest. In acting, it is the history of the character before the drama begins, and is created during the actor's preparation. It is the history of characters and other elements that underlie the situation existing at the main narrative's start. Even a purely historical work selectively reveals backstory to the audience. Usage As a literary device, backstory is often employed to lend depth or believability to the main story. The usefulness of having a dramatic revelation was recognized by Aristotle, in ''Poetics''. Backstories are usually revealed, partially or in full, chronologically or otherwise, as the main narrative unfolds. However, a story creator may also create portions of a backstory or even an entire backstory t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
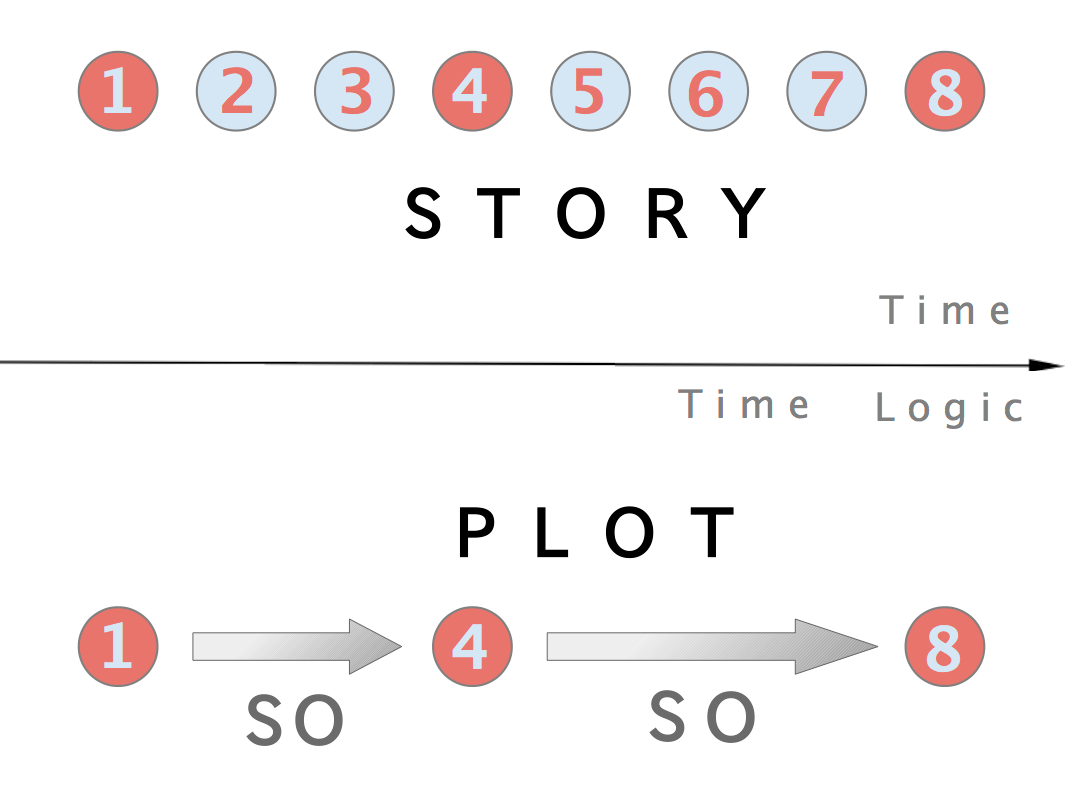
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the sequence of events in which each event affects the next one through the principle of cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a series of events linked by the connector "and so". Plots can vary from the simple—such as in a traditional ballad—to forming complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot or ''imbroglio''. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The term ''plot'' can also serve as a verb, referring to either the writer's crafting of a plot (devising and ordering story events), or else to a character's planning of future actions in the story. The term ''plot'', however, in common usage (for example, a "movie plot") can mean a narrative summary or story synopsis, rather th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Wars (film)
''Star Wars'' (retroactively titled ''Star Wars: Episode IV – A New Hope'') is a 1977 American epic space opera film written and directed by George Lucas, produced by Lucasfilm and distributed by 20th Century Fox. It is the first film in the '' Star Wars'' film series and fourth chronological chapter of the "Skywalker Saga". Set "a long time ago" in a fictional universe where the galaxy is ruled by the tyrannical Galactic Empire, the story focuses on a group of freedom fighters known as the Rebel Alliance, who aim to destroy the Empire's newest weapon, the Death Star. Luke Skywalker becomes caught in the conflict while learning the ways of a metaphysical power known as "the Force" from Jedi Master Obi-Wan Kenobi. The cast includes Mark Hamill, Harrison Ford, Carrie Fisher, Peter Cushing, Alec Guinness, David Prowse, James Earl Jones, Anthony Daniels, Kenny Baker, and Peter Mayhew. Lucas had the idea for a science-fiction film in the vein of '' Flash Gordon'' aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuity (fiction)
In fiction, continuity is a consistency of the characteristics of people, plot, objects, and places seen by the reader or viewer over some period of time. It is relevant to several media. Continuity is particularly a concern in the production of film and television due to the difficulty of rectifying an error in continuity after shooting has wrapped. It also applies to other art forms, including novels, comics, and video games, though usually on a smaller scale. It also applies to fiction used by persons, corporations, and governments in the public eye. Most productions have a script supervisor on hand whose job is to pay attention to and attempt to maintain continuity across the chaotic and typically non-linear production shoot. This takes the form of a large amount of paperwork, photographs, and attention to and memory of large quantities of detail, some of which is sometimes assembled into the story bible for the production. It usually regards factors both within the scene and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prequel
A prequel is a literary, dramatic or cinematic work whose story precedes that of a previous work, by focusing on events that occur before the original narrative. A prequel is a work that forms part of a backstory to the preceding work. The term "prequel" is a 20th-century neologism from the prefix "pre-" (from Latin ''prae'', "before") and "sequel". Like sequels, prequels may or may not concern the same plot as the work from which they are derived. More often they explain the background that led to the events in the original, but sometimes the connections are not completely explicit. Sometimes prequels play on the audience's knowledge of what will happen next, using deliberate references to create dramatic irony. History Though the word "prequel" is of recent origin, works fitting this concept existed long before. The ''Cypria'', presupposing hearers' acquaintance with the events of the Homeric epic, confined itself to what preceded the ''Iliad'', and thus formed a kind of introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Story
In entertainment, an origin story is an account or backstory revealing how a character or group of people become a protagonist or antagonist, and it adds to the overall interest and complexity of a narrative, often giving reasons for their intentions. In American comic books, it also refers to how characters gained their superpowers and/or the circumstances under which they became superheroes or supervillains. In order to keep their characters current, comic book companies, as well as cartoon companies, game companies, children's show companies, and toy companies, frequently rewrite the origins of their oldest characters. This goes from adding details that do not contradict earlier facts to a totally new origin which makes it seem that it is an altogether different character. A pourquoi story, also dubbed an "origin story", is also used in mythology, referring to narratives of how a world began, how creatures and plants came into existence, and why certain things in the cosmos ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characterization
Characterization or characterisation is the representation of persons (or other beings or creatures) in narrative and dramatic works. The term character development is sometimes used as a synonym. This representation may include direct methods like the attribution of qualities in description or commentary, and indirect (or "dramatic") methods inviting readers to infer qualities from characters' actions, dialogue, or appearance. Such a personage is called a character. Character is a literary element. History The term ''characterization'' was introduced in the 19th century.Harrison (1998, pp. 51-2) Aristotle promoted the primacy of plot over characters, that is, a plot-driven narrative, arguing in his ''Poetics'' that tragedy "is a representation, not of men, but of action and life." This view was reversed in the 19th century, when the primacy of the character, that is, a character-driven narrative, was affirmed first with the realist novel, and increasingly later with the inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retcon
Retroactive continuity, or retcon for short, is a literary device in which established diegetic facts in the plot of a fictional work (those established through the narrative itself) are adjusted, ignored, supplemented, or contradicted by a subsequently published work which recontextualizes or breaks continuity with the former. There are various motivations for applying retroactive continuity, including: * To accommodate desired aspects of sequels or derivative works which would otherwise be ruled out. * To respond to negative fan reception of previous stories. * To correct and overcome errors or problems identified in the prior work since its publication. * To change or clarify how the prior work should be interpreted. * To match reality, when assumptions or projections of the future are later proven wrong. Retcons are used by authors to increase their creative freedom, on the assumption that the changes are unimportant to the audience compared to the new story which can be tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroactive Continuity
Retroactive continuity, or retcon for short, is a literary device in which established diegetic facts in the plot of a fictional work (those established through the narrative itself) are adjusted, ignored, supplemented, or contradicted by a subsequently published work which recontextualizes or breaks continuity with the former. There are various motivations for applying retroactive continuity, including: * To accommodate desired aspects of sequels or derivative works which would otherwise be ruled out. * To respond to negative fan reception of previous stories. * To correct and overcome errors or problems identified in the prior work since its publication. * To change or clarify how the prior work should be interpreted. * To match reality, when assumptions or projections of the future are later proven wrong. Retcons are used by authors to increase their creative freedom, on the assumption that the changes are unimportant to the audience compared to the new story which can be tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shared Universe
A shared universe or shared world is a fictional universe from a set of creative works where more than one writer (or other artist) independently contributes a work that can stand alone but fits into the joint development of the storyline, characters, or world of the overall project. It is common in genres like science fiction. It differs from collaborative writing in which multiple artists are working together on the same work and from crossovers where the works and characters are independent except for a single meeting. The term ''shared universe'' is also used within comics to reflect the overall milieu created by the comic book publisher in which characters, events, and premises from one product line appear in other product lines in a media franchise. A specific kind of shared universe that is published across a variety of media (such as novels and films), each of them contributing to the growth, history, and status of the setting is called an "imaginary entertainment enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orson Scott Card
Orson Scott Card (born August 24, 1951) is an American writer known best for his science fiction works. He is the first and (as of 2022) only person to win both a Hugo Award and a Nebula Award in consecutive years, winning both awards for both his novel ''Ender's Game'' (1985) and its sequel ''Speaker for the Dead'' (1986). A feature film adaptation of ''Ender's Game'', which Card co-produced, was released in 2013. Card also wrote the Locus Fantasy Award-winning series ''The Tales of Alvin Maker'' (1987–2003). Card's works were influenced by classic literature, popular fantasy, and science fiction; he often uses tropes from genre fiction. His background as a screenwriter has helped Card make his works accessible. Card's early fiction is original but contains graphic violence. His fiction often features characters with exceptional gifts who make difficult choices with high stakes. Card has also written political, religious, and social commentary in his columns and other writi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiction-writing Modes
A fiction-writing mode is a manner of writing with its own set of conventions regarding how, when, and where it should be used. Fiction is a form of narrative, one of the four rhetorical modes of discourse. Fiction-writing also has distinct forms of expression, or modes, each with its own purposes and conventions. Currently, there is no consensus within the writing community regarding the number and composition of fiction-writing modes and their uses. Some writing modes suggested include action, dialogue, thoughts, summary, scene, description, background, exposition and transition. Overview The concept goes back at least as far as Aristotle who, in ''Poetics'', referred to narration and action as different modes or manner of representing something. For many years, fiction writing was described as having two types: narration and dialogue. Evan Marshall, in ''The Marshall Plan for Novel Writing'' (1998) noted that writers should know what they are doing at all times. He described w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recollection
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieval of information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humansrecall. (2010). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 04, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/493353/recal/ref> and animals. Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of Encoding specificity principle, encoding specificity. Theories Two-stage theory The ''two-stage theory'' states that the process of recall begins with a search and retrieval process, and then a decision or recognition process where the correct information is chosen from what has been retrieved. In this theory, recognition only involves the latter of these two stages, or processes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |