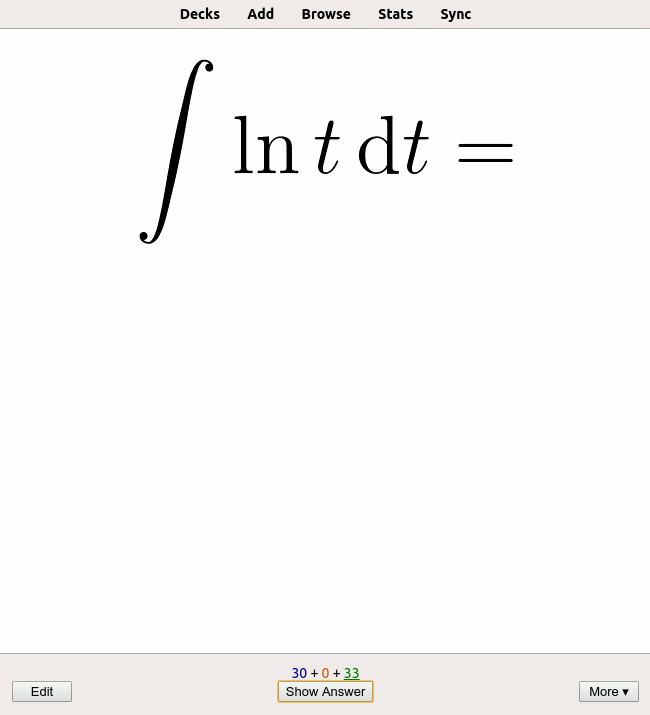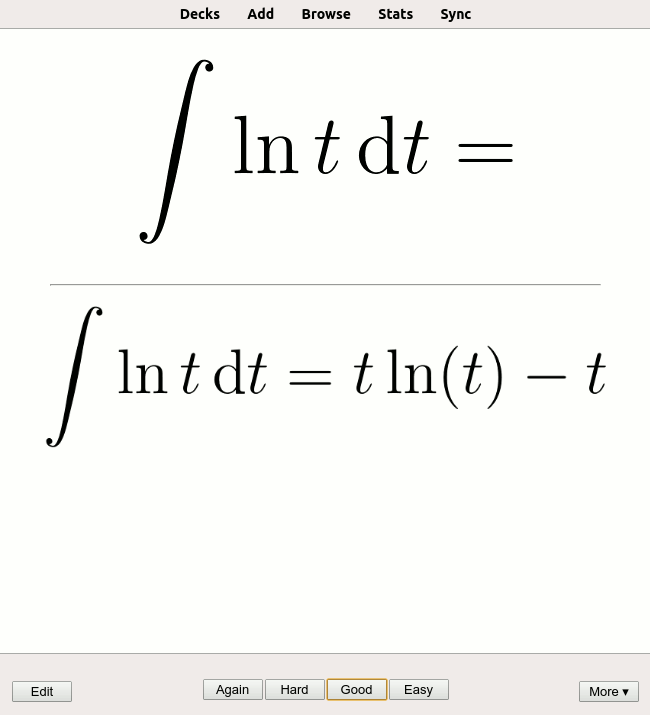|
Recollection
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieving information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humansrecall. (2010). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 04, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/493353/recal/ref> and animals. Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of Encoding specificity principle, encoding specificity. Theories Two-stage theory The ''two-stage theory'' states that the process of recall begins with a search and retrieval process, and then a decision or recognition process where the correct information is chosen from what has been retrieved. In this theory, recognition only involves the latter of these two stages, or processes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recognition Memory
Recognition memory, a subcategory of explicit memory, is the ability to recognize previously encountered events, objects, or people.Medina, J. J. (2008)The biology of recognition memory. ''Psychiatric Times''. When the previously experienced event is reexperienced, this environmental content is matched to stored memory representations, eliciting matching signals. As first established by psychology experiments in the 1970s, recognition memory for pictures is quite remarkable: humans can remember thousands of images at high accuracy after seeing each only once and only for a few seconds.Standing, L. (1973). "Learning 10,000 pictures". ''The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology'', 25(2), 207–222. Retrieved Jan 20 2020, from . Recognition memory can be subdivided into two component processes: recollection and familiarity, sometimes referred to as "remembering" and "knowing", respectively. Recollection is the retrieval of details associated with the previously experienced event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encoding Specificity Principle
The encoding specificity principle is the general principle that matching the encoding contexts of information at recall assists in the retrieval of episodic memories. It provides a framework for understanding how the conditions present while encoding information relate to memory and recall of that information. It was introduced by Thomson and Tulving who suggested that contextual information is encoded with memories which affect the retrieval process. When a person uses information stored in their memory it is necessary that the information is accessible. The accessibility is governed by retrieval cues, these cues are dependent on the encoding pattern; the specific encoding pattern may vary from instance to instance, even if nominally the item is the same, as encoding depends on the context. This conclusion was drawn from a recognition-memory task. A series of psychological experiments were undertaken in the 1970s which continued this work and further showed that context affects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at particular times and places; for example, the party on one's 7th birthday. Along with semantic memory, it comprises the category of explicit memory, one of the two major divisions of long-term memory (the other being implicit memory). The term "episodic memory" was coined by Endel Tulving in 1972, referring to the distinction between knowing and remembering: ''knowing'' is factual recollection (semantic) whereas ''remembering'' is a feeling that is located in the past (episodic). One of the main components of episodic memory is the process of recollection, which elicits the retrieval of contextual information pertaining to a specific event or experience that has occurred. Tulving seminally defined three key properties of episodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atkinson–Shiffrin Memory Model
The Atkinson–Shiffrin model (also known as the multi-store model or modal model) is a model of memory proposed in 1968 by Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin. The model asserts that human memory has three separate components: # a '' sensory register'', where sensory information enters memory, # a '' short-term store'', also called ''working memory'' or ''short-term memory'', which receives and holds input from both the sensory register and the long-term store, and # a '' long-term store'', where information which has been rehearsed (explained below) in the short-term store is held indefinitely. Since its first publication this model has come under much scrutiny and has been criticized for various reasons (described below). But it is notable for the significant influence it had in stimulating memory research. Summary The model of memories is an explanation of how memory processes work. The three-part, multi-store model was first described by Atkinson and Shiffrin in 1968, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Baddeley
Alan David Baddeley CBE Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (born 23 March 1934) is a British psychologist. He is known for his research on memory and for developing the three-component model of working memory. He is a professor of psychology at the University of York. Biography Baddeley was born in Leeds, Yorkshire on 23 March 1934. He lived there with his parents, Donald and Nellie Baddeley, until leaving for university. He decided to study psychology and was originally interested in psychoanalysis. Later he changed his focus to evidence-based psychology. In 1956, Baddeley went to the United States of America to continue his studies. After spending a year in America, he returned home. He then went to Cambridge, where he met and married Hilary Ann White. Baddeley and his wife have three sons. Baddeley has taught and conducted research at University of Sussex, University of Stirling, MRC Applied Psychology Unit, Churchill College, Cambridge, Churchill College, University of Cambr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonemes
A phoneme () is any set of similar speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word from another. All languages contain phonemes (or the spatial-gestural equivalent in sign languages), and all spoken languages include both consonant and vowel phonemes; phonemes are primarily studied under the branch of linguistics known as phonology. Examples and notation The English words ''cell'' and ''set'' have the exact same sequence of sounds, except for being different in their final consonant sounds: thus, versus in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), a writing system that can be used to represent phonemes. Since and alone distinguish certain words from others, they are each examples of phonemes of the English language. Specifically they are consonant phonemes, along with , while is a vowel phoneme. The spelling of English does not strictly conform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testing Effect
The testing effect (also known as retrieval practice, active recall, practice testing, or test-enhanced learning) suggests long-term memory is increased when part of the learning period is devoted to retrieving information from memory. It is different from the more general '' practice effect'', defined in the APA Dictionary of Psychology as "any change or improvement that results from practice or repetition of task items or activities." Cognitive psychologists are working with educators to look at how to take advantage of tests—not as an assessment tool, but as a teaching tool since testing prior knowledge is more beneficial for learning when compared to only reading or passively studying material (even more so when the test is more challenging for memory). History Before much experimental evidence had been collected, the utility of testing was already evident to some perceptive observers including Francis Bacon who discussed it as a learning strategy as early as 1620. ''"He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irvin Rock
Irvin Rock (1922–1995) was an American experimental psychologist who studied visual perception at the University of California at Berkeley. He wrote a book, titled ''The Logic of Perception'', and was regarded as an excellent perception psychologist. Rock is notable in the field of psychology for his 1957 experiment where he tilted a square to make it look like a diamond and then tilted his test subjects and asked them what shape they saw. The experiment tested Rock's hypothesis that perceptual phenomena could be explained by higher-level mental processes instead of merely by automatic processes. When his test subjects continued to perceive the shape as a diamond after being tilted to view the shape as a square, Rock concluded that perception is an intelligent, higher-level mental process. This differed from previous conclusions by Gestalt psychologists that perception was not a higher-level process. Rock later wrote another important book on the field of inattentional blindnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Position Effect
Serial-position effect is the tendency of a person to recall the first and last items in a series best, and the middle items worst. The term was coined by Hermann Ebbinghaus through studies he performed on himself, and refers to the finding that recall accuracy varies as a function of an item's position within a study list. When asked to recall a list of items in any order ( free recall), people tend to begin recall with the end of the list, recalling those items best (the recency effect). Among earlier list items, the first few items are recalled more frequently than the middle items (the primacy effect). One suggested reason for the primacy effect is that the initial items presented are most effectively stored in long-term memory because of the greater amount of processing devoted to them. (The first list item can be rehearsed by itself; the second must be rehearsed along with the first, the third along with the first and second, and so on.) The primacy effect is reduced when i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |