|
Broken Vowel
In historical linguistics, vowel breaking, vowel fracture, or diphthongization is the sound change of a monophthong into a diphthong or triphthong. Types Vowel breaking may be unconditioned or conditioned. It may be triggered by the presence of another sound, by stress, or in no particular way. Assimilation Vowel breaking is sometimes defined as a subtype of diphthongization, when it refers to harmonic ( assimilatory) process that involves diphthongization triggered by a following vowel or consonant. The original pure vowel typically breaks into two segments. The first segment matches the original vowel, and the second segment is harmonic with the nature of the triggering vowel or consonant. For example, the second segment may be (a back vowel) if the following vowel or consonant is back (such as velar or pharyngeal), and the second segment may be (a front vowel) if the following vowel or consonant is front (such as palatal). Thus, vowel breaking, in the restricted sense, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also termed diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time. Principal concerns of historical linguistics include: # to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages # to reconstruct the pre-history of languages and to determine their relatedness, grouping them into language families (comparative linguistics) # to develop general theories about how and why language changes # to describe the history of speech communities # to study the history of words, i.e. etymology Historical linguistics is founded on the Uniformitarian Principle, which is defined by linguist Donald Ringe as: History and development Western modern historical linguistics dates from the late-18th century. It grew out of the earlier discipline of philology, the study of ancient texts and documents dating back to antiquity. At first, historical linguistics served as the cornerstone of comparative linguistics, primarily as a tool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Germanic Language
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages. Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branches during the fifth century BC to fifth century AD: West Germanic, East Germanic and North Germanic, which however remained in contact over a considerable time, especially the Ingvaeonic languages (including English), which arose from West Germanic dialects and remained in continued contact with North Germanic. A defining feature of Proto-Germanic is the completion of the process described by Grimm's law, a set of sound changes that occurred between its status as a dialect of Proto-Indo-European and its gradual divergence into a separate language. As it is probable that the development of this sound shift spanned a considerable time (several centuries), Proto-Germanic cannot adequately be reconstructed as a simple node in a tree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
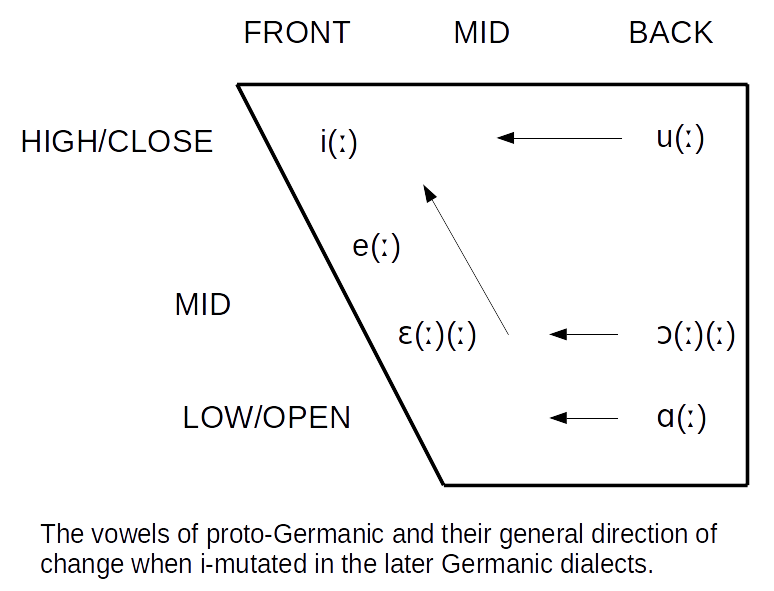
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel (fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to ( raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around AD 450 or 500 and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Paul
Hermann Otto Theodor Paul (August 7, 1846, Salbke – December 29, 1921, Munich) was a German philologist, linguist and lexicographer. Biography He studied at Berlin and Leipzig, and in 1874 became professor of German language and literature in the University of Freiburg. In 1893 he was appointed professor of German philology at the University of Munich. He was a prominent Neogrammarian. Works His main work, ''Prinzipien der Sprachgeschichte'' (Halle: Max Niemeyer, 1st ed. 1880; 3d ed. 1898), has been translated into English: Paul, Hermann 1970. ''Principles of the History of Language'', translated from 2nd edition by H. A. Strong (1888; retranslated with changes by Strong, Logeman, and Wheeler in 1891). College Park: McGroth Publishing Company, . According to Paul, sentences are the sum of their parts. They arise sequentially from individual associations, linked together in a linear form (1886. See also, Blumenthal, 1970). Wilhelm Wundt opposed this theory of sentences, arguing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epenthesis
In phonology, epenthesis (; Greek ) means the addition of one or more sounds to a word, especially in the beginning syllable ('' prothesis'') or in the ending syllable ('' paragoge'') or in-between two syllabic sounds in a word. The word ''epenthesis'' comes from "in addition to" and ''en-'' "in" and ''thesis'' "putting". Epenthesis may be divided into two types: excrescence for the addition of a consonant, and for the addition of a vowel, svarabhakti (in Hindi, Bengali and other North Indian languages, stemming from Sanskrit) or alternatively anaptyxis (). The opposite process, where one or more sounds are removed, is referred to as elision In linguistics, an elision or deletion is the omission of one or more sounds (such as a vowel, a consonant, or a whole syllable) in a word or phrase. However, these terms are also used to refer more narrowly to cases where two words are run toget .... Uses Epenthesis arises for a variety of reasons. The phonotactics of a given langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( no, norsk, links=no ) is a North Germanic language spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' Norwegian, (lite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suðuroy
Suðuroy (literally South Island, da, Suderø) is the southernmost of the Faroe Islands. The island covers 163.7 square kilometres (63.2 sq mi). In 2018 the population was 4,601. Suðuroy region (sýsla) comprises this island and Lítla Dímun, the next isle northward in the Faroes, which is uninhabited. History One ancient settlement, Víkarbyrgi was abandoned late in the 1990s. Another settlement, Akraberg was abandoned around 1350 because of the Black Death; the people who lived there at that time came from Friesland, and legend has it that people in Hørg (in Sumba) can trace their ancestry back to this settlement, which was situated on the southernmost point of the island. In the 17th century, Suðuroy was subjected to repeated attacks by North African pirates, who in the Faroe Islands were referred to as Turks when North Africa belonged to the Ottoman Empire. One well known such incident was the Slave raid of Suðuroy .They abducted several women and child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroese Language
Faroese ( ; ''føroyskt mál'' ) is a North Germanic language spoken as a first language by about 72,000 Faroe Islanders, around 53,000 of whom reside on the Faroe Islands and 23,000 in other areas, mainly Denmark. It is one of five languages descended from Old West Norse spoken in the Middle Ages, the others being Norwegian, Icelandic, and the extinct Norn and Greenlandic Norse. Faroese and Icelandic, its closest extant relative, are not mutually intelligible in speech, but the written languages resemble each other quite closely, largely owing to Faroese's etymological orthography. History Around 900 AD, the language spoken in the Faroes was Old Norse, which Norse settlers had brought with them during the time of the settlement of Faroe Islands () that began in 825. However, many of the settlers were not from Scandinavia, but descendants of Norse settlers in the Irish Sea region. In addition, women from Norse Ireland, Orkney, or Shetland often married native Scandinavian men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nynorsk
Nynorsk () () is one of the two written standards of the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. From 12 May 1885, it became the state-sanctioned version of Ivar Aasen's standard Norwegian language ( no, Landsmål) parallel to the Dano-Norwegian written language ('' Riksmål''). Nynorsk became the name in 1929, and it is after a series of reforms still a variation which is closer to , whereas Bokmål is closer to ''Riksmål'' and Danish. Between 10 and 15 percent of Norwegians (Primarily in the west around the city of Bergen,) have Nynorsk as their official language form, estimated by the number of students attending ''videregående skole'' (secondary education). Nynorsk is also taught as a mandatory subject in both high school and elementary school for all Norwegians who do not have it as their own language form. History Danish was the written language of Norway until 1814, and Danish with Norwegian intonation and pronunciation was on occasion spoken in the cities ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutlandic
Jutlandic, or Jutish (Danish: ''jysk''; ), is the western variety of Danish, spoken on the peninsula of Jutland in Denmark. Generally, Jutlandic can be divided into two different dialects: general or Northern Jutlandic ( ; further divided into western and eastern) and Southern Jutlandic ( ). However, the linguistic variation is considerably more complicated and well over 20 separate isoglosses exist throughout Jutland. There are major phonological differences between the dialects, but also very noteworthy morphological, syntactic, and semantic variations. Subdialects The different subdialects of Jutlandic differ somewhat from each other, and are generally grouped in three main dialects, where two of them are sometimes considered together. ''Sønderjysk'' *''Sønderjysk'' (South Jutlandic) is often seen as very difficult for other speakers of Danish, even other Jutlandic dialects to understand. Instead of the normal Danish ''stød'', it has tonal accents like Swedish. Many of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Language
Icelandic (; is, íslenska, link=no ) is a North Germanic language spoken by about 314,000 people, the vast majority of whom live in Iceland, where it is the national language. Due to being a West Scandinavian language, it is most closely related to Faroese, western Norwegian dialects, and the extinct language, Norn. The language is more conservative than most other Germanic languages. While most of them have greatly reduced levels of inflection (particularly noun declension), Icelandic retains a four-case synthetic grammar (comparable to German, though considerably more conservative and synthetic) and is distinguished by a wide assortment of irregular declensions. Icelandic vocabulary is also deeply conservative, with the country's language regulator maintaining an active policy of coining terms based on older Icelandic words rather than directly taking in loanwords from other languages. Since the written language has not changed much, Icelandic speakers can read cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bokmål
Bokmål () (, ; ) is an official written standard for the Norwegian language, alongside Nynorsk. Bokmål is the preferred written standard of Norwegian for 85% to 90% of the population in Norway. Unlike, for instance, the Italian language, there is no nationwide standard or agreement on the pronunciation of Bokmål. Bokmål is regulated by the governmental Language Council of Norway. A more conservative orthographic standard, commonly known as '' Riksmål'', is regulated by the non-governmental Norwegian Academy for Language and Literature. The written standard is a Norwegianised variety of the Danish language. The first Bokmål orthography was officially adopted in 1907 under the name ''Riksmål'' after being under development since 1879. The architects behind the reform were Marius Nygaard and Jacob Jonathan Aars. It was an adaptation of written Danish, which was commonly used since the past union with Denmark, to the Dano-Norwegian koiné spoken by the Norwegian urban elite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |